An Administrative Coordinator typically manages office operations, streamlines workflows, and supports team communication to ensure efficiency. An Administrative Officer holds a more strategic role, overseeing administrative policies, budgeting, and compliance within an organization. Both positions require strong organizational skills, but the Administrative Officer's responsibilities tend to encompass higher-level decision-making and leadership.
Table of Comparison
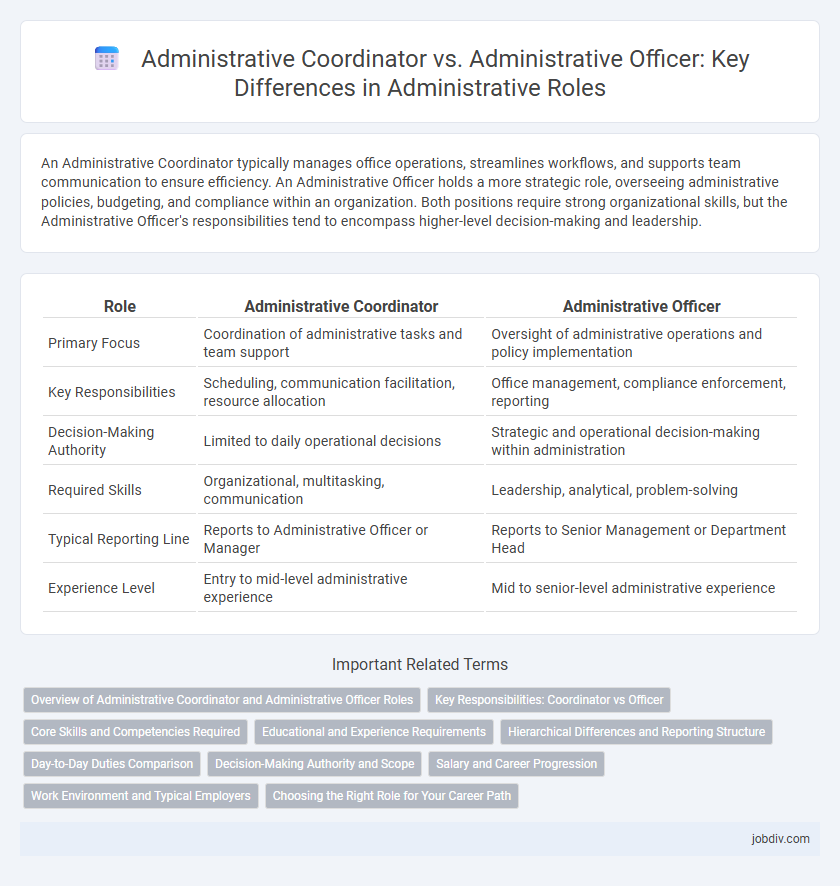
| Role | Administrative Coordinator | Administrative Officer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Coordination of administrative tasks and team support | Oversight of administrative operations and policy implementation |
| Key Responsibilities | Scheduling, communication facilitation, resource allocation | Office management, compliance enforcement, reporting |
| Decision-Making Authority | Limited to daily operational decisions | Strategic and operational decision-making within administration |
| Required Skills | Organizational, multitasking, communication | Leadership, analytical, problem-solving |
| Typical Reporting Line | Reports to Administrative Officer or Manager | Reports to Senior Management or Department Head |
| Experience Level | Entry to mid-level administrative experience | Mid to senior-level administrative experience |
Overview of Administrative Coordinator and Administrative Officer Roles
Administrative Coordinators manage office operations by coordinating schedules, communication, and supporting team activities to ensure efficiency. Administrative Officers oversee broader administrative functions including policy implementation, budget management, and supervising staff to maintain organizational compliance. Both roles require strong organizational skills but differ in scope, with Coordinators focusing on tactical support and Officers handling strategic administrative responsibilities.
Key Responsibilities: Coordinator vs Officer
Administrative Coordinators primarily focus on organizing schedules, managing communication channels, and supporting project logistics to ensure smooth daily operations. Administrative Officers take on broader responsibilities including policy implementation, compliance monitoring, and overseeing administrative staff performance. Both roles require strong organizational skills, but Officers typically engage in higher-level strategic tasks and decision-making within administrative frameworks.
Core Skills and Competencies Required
Administrative Coordinators require strong organizational skills, proficiency in project management, and effective communication abilities to coordinate schedules and support team operations efficiently. Administrative Officers must demonstrate leadership competencies, policy compliance knowledge, and strategic planning expertise to oversee administrative functions and ensure regulatory adherence. Both roles demand attention to detail, problem-solving aptitude, and proficiency in office software, but the Administrative Officer typically handles higher-level decision making and broader operational responsibilities.
Educational and Experience Requirements
Administrative Coordinators typically require a bachelor's degree in business administration or a related field, along with 2-4 years of experience in office management or coordination roles. Administrative Officers often demand a higher level of education, such as a bachelor's or master's degree in public administration, management, or a similar discipline, combined with 4-6 years of progressively responsible administrative experience. Both roles emphasize strong organizational, communication, and problem-solving skills, but Administrative Officers usually handle more strategic responsibilities requiring advanced knowledge and extensive practical expertise.
Hierarchical Differences and Reporting Structure
Administrative Coordinators typically manage daily operational tasks and support multiple departments, reporting directly to Administrative Officers or mid-level managers. Administrative Officers hold higher hierarchical positions with broader responsibilities in policy implementation and decision-making, often reporting to senior management or department heads. The reporting structure places Administrative Coordinators as operational support roles under Administrative Officers who oversee administrative functions at a strategic level.
Day-to-Day Duties Comparison
Administrative Coordinators manage scheduling, organize meetings, and coordinate communication between departments to ensure smooth daily operations. Administrative Officers handle broader responsibilities such as overseeing office protocols, managing budgets, and supervising support staff to maintain organizational efficiency. Both roles require strong organizational skills, but Coordinators focus on task execution while Officers emphasize policy implementation and resource management.
Decision-Making Authority and Scope
An Administrative Coordinator typically manages day-to-day office operations with limited decision-making authority, focusing on coordinating schedules, communication, and supporting administrative tasks within a department. In contrast, an Administrative Officer holds broader decision-making responsibilities, often overseeing multiple teams or departments, implementing policies, and handling higher-level administrative functions. The scope of an Administrative Officer is more strategic, involving budget management and compliance oversight, while the Coordinator's role remains operational and task-oriented.
Salary and Career Progression
Administrative Coordinators typically earn an average salary ranging from $45,000 to $60,000 annually, while Administrative Officers command higher salaries, often between $55,000 and $75,000 due to broader responsibilities and strategic roles. Career progression for Administrative Coordinators usually involves advancement to Administrative Officer or Office Manager positions, whereas Administrative Officers can progress to senior management or specialized administrative roles such as Operations Manager or Executive Administrator. Salary growth and career trajectory are influenced by industry, experience, and organizational size, with Administrative Officers generally experiencing faster advancement and higher compensation ceilings.
Work Environment and Typical Employers
Administrative Coordinators typically work in dynamic office settings, supporting various departments within sectors such as education, healthcare, and corporate businesses. Administrative Officers are often employed in government agencies, non-profits, and large corporations, thriving in structured environments that demand policy adherence and regulatory compliance. Both roles require strong organizational skills but differ in work environment focus, with Coordinators emphasizing coordination and communication, while Officers concentrate on administration and operational oversight.
Choosing the Right Role for Your Career Path
Selecting between an Administrative Coordinator and an Administrative Officer depends on your career goals and skills; Administrative Coordinators typically manage daily office operations and coordinate between departments, emphasizing multitasking and communication. Administrative Officers often engage in higher-level responsibilities such as policy implementation, budgeting, and staff supervision, offering a pathway toward managerial roles. Understanding these distinctions helps align your career trajectory with desired responsibilities and growth opportunities in administrative fields.
Administrative Coordinator vs Administrative Officer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com