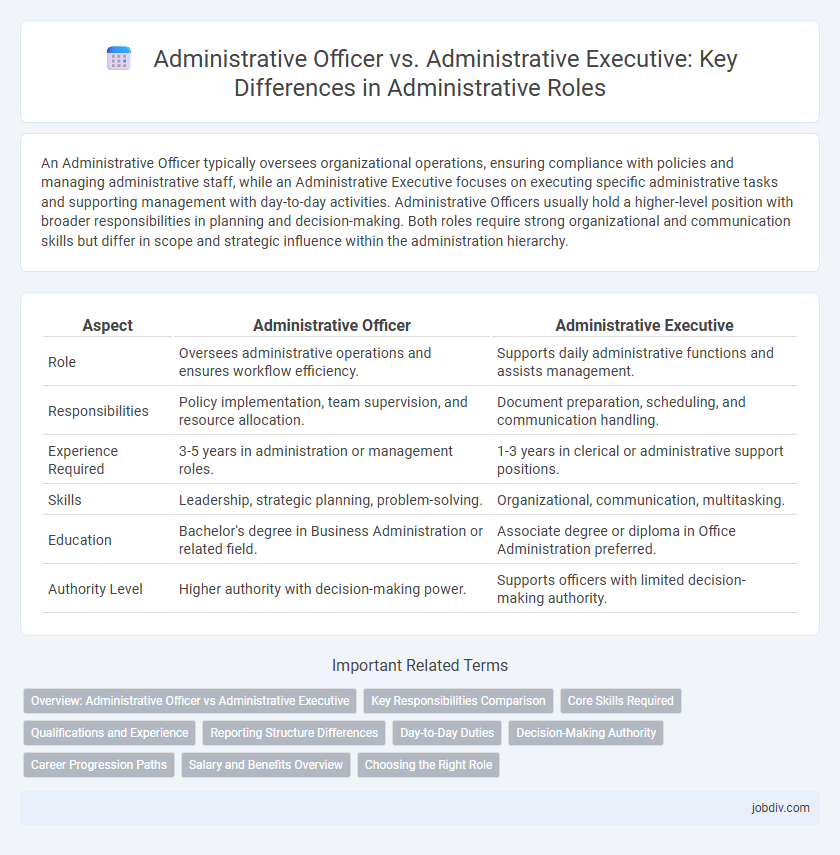
An Administrative Officer typically oversees organizational operations, ensuring compliance with policies and managing administrative staff, while an Administrative Executive focuses on executing specific administrative tasks and supporting management with day-to-day activities. Administrative Officers usually hold a higher-level position with broader responsibilities in planning and decision-making. Both roles require strong organizational and communication skills but differ in scope and strategic influence within the administration hierarchy.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Administrative Officer | Administrative Executive |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Oversees administrative operations and ensures workflow efficiency. | Supports daily administrative functions and assists management. |
| Responsibilities | Policy implementation, team supervision, and resource allocation. | Document preparation, scheduling, and communication handling. |
| Experience Required | 3-5 years in administration or management roles. | 1-3 years in clerical or administrative support positions. |
| Skills | Leadership, strategic planning, problem-solving. | Organizational, communication, multitasking. |
| Education | Bachelor's degree in Business Administration or related field. | Associate degree or diploma in Office Administration preferred. |
| Authority Level | Higher authority with decision-making power. | Supports officers with limited decision-making authority. |
Overview: Administrative Officer vs Administrative Executive
An Administrative Officer typically oversees office operations, manages staff, and ensures compliance with organizational policies, emphasizing strategic planning and resource allocation. An Administrative Executive focuses more on executing administrative tasks, supporting senior management, and coordinating daily activities to maintain efficient workflow. Both roles require strong organizational skills, but the Administrative Officer holds greater responsibility in decision-making and policy implementation within the administration.
Key Responsibilities Comparison
An Administrative Officer primarily oversees office operations, policy implementation, and staff coordination, ensuring compliance with organizational standards. An Administrative Executive focuses on strategic planning, managing higher-level administrative functions, and supporting senior management with decision-making processes. Both roles require strong organizational skills, but the Officer handles routine administration while the Executive manages complex administrative strategies.
Core Skills Required
Administrative Officers require strong organizational skills, proficiency in office software, and effective communication abilities to manage daily operations and coordinate between departments efficiently. Administrative Executives need advanced leadership skills, strategic planning capabilities, and expertise in project management to oversee administrative functions and support executive-level decision-making. Both roles demand attention to detail, problem-solving aptitude, and adaptability to dynamic work environments.
Qualifications and Experience
Administrative Officers typically require a bachelor's degree in business administration, management, or a related field, along with 3 to 5 years of experience in office management or administrative roles. Administrative Executives often need similar academic qualifications but usually possess more extensive experience, often exceeding 5 years, with a focus on strategic planning and executive-level support. Proficiency in organizational software and strong leadership skills are critical for both positions, whereas Administrative Executives are expected to demonstrate advanced decision-making abilities and project management expertise.
Reporting Structure Differences
An Administrative Officer typically reports to senior management or department heads, overseeing administrative operations and ensuring policy compliance. In contrast, an Administrative Executive often reports to the Administrative Officer or middle management, focusing on executing administrative tasks and supporting office functions. The distinction in reporting structure reflects their varying levels of responsibility and decision-making authority within the organization.
Day-to-Day Duties
Administrative Officers primarily manage office operations, coordinate schedules, and oversee administrative staff to ensure efficient workflow. Administrative Executives focus more on strategic planning, implementing policies, and liaising between departments to support organizational objectives. Both roles require strong communication skills, but Administrative Officers handle routine tasks while Executives engage in higher-level decision-making.
Decision-Making Authority
An Administrative Officer typically holds greater decision-making authority, responsible for overseeing departmental operations and implementing policies, while an Administrative Executive generally focuses on executing assigned tasks with limited discretion. The Officer often approves budgets, manages staff, and drives strategic initiatives, whereas the Executive supports these decisions through coordination and communication. Understanding the hierarchy clarifies that the Administrative Officer plays a more pivotal role in organizational governance and resource allocation.
Career Progression Paths
Career progression for an Administrative Officer often leads to roles such as Senior Administrative Officer or Administration Manager, emphasizing operational oversight and team management. In contrast, an Administrative Executive typically advances towards strategic positions like Executive Administrator or Chief Administrative Officer, focusing on policy development and executive support. Both paths require strengthening leadership skills and expanding organizational knowledge to progress effectively within administrative hierarchies.
Salary and Benefits Overview
Administrative Officers typically earn a higher salary than Administrative Executives due to their broader scope of responsibilities and decision-making authority. Benefits for Administrative Officers often include comprehensive health insurance, retirement plans, and performance bonuses, reflecting their seniority level. Administrative Executives may receive standard benefits such as paid time off and basic insurance coverage, with opportunities for advancement tied to experience and organizational needs.
Choosing the Right Role
Choosing between an Administrative Officer and an Administrative Executive depends on the scope of responsibilities and decision-making authority. Administrative Officers typically oversee daily operations, manage staff, and ensure compliance with organizational policies, making them ideal for leadership roles requiring strategic oversight. Administrative Executives focus more on supporting senior management through scheduling, correspondence, and coordination, suitable for candidates skilled in organization and communication.
Administrative Officer vs Administrative Executive Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com