Legal Administrators oversee the management and operation of legal departments, ensuring compliance, budgeting, and staffing align with organizational goals. Legal Secretaries provide essential support by preparing legal documents, managing correspondence, and scheduling appointments for attorneys. While both roles are crucial, Legal Administrators focus on strategic and operational tasks, whereas Legal Secretaries concentrate on administrative and clerical duties within legal settings.
Table of Comparison
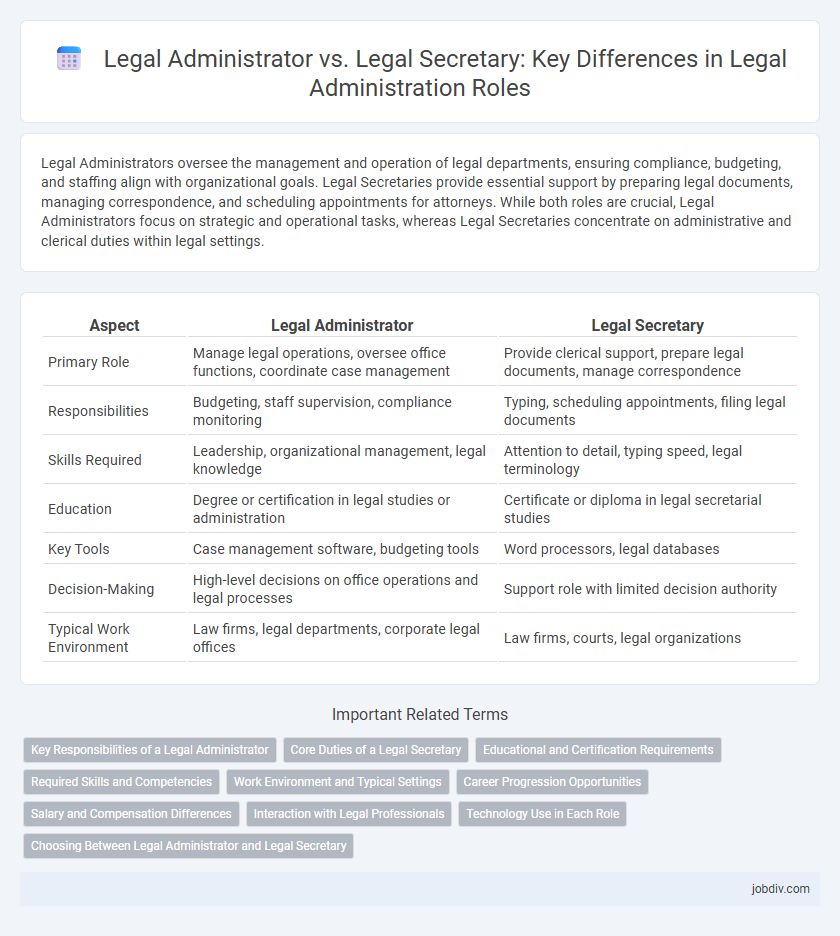
| Aspect | Legal Administrator | Legal Secretary |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Manage legal operations, oversee office functions, coordinate case management | Provide clerical support, prepare legal documents, manage correspondence |
| Responsibilities | Budgeting, staff supervision, compliance monitoring | Typing, scheduling appointments, filing legal documents |
| Skills Required | Leadership, organizational management, legal knowledge | Attention to detail, typing speed, legal terminology |
| Education | Degree or certification in legal studies or administration | Certificate or diploma in legal secretarial studies |
| Key Tools | Case management software, budgeting tools | Word processors, legal databases |
| Decision-Making | High-level decisions on office operations and legal processes | Support role with limited decision authority |
| Typical Work Environment | Law firms, legal departments, corporate legal offices | Law firms, courts, legal organizations |
Key Responsibilities of a Legal Administrator
Legal Administrators oversee the management of legal office operations, including budgeting, compliance, and staff coordination, ensuring efficient workflow and adherence to legal regulations. They handle case management systems, manage contracts, and coordinate with attorneys and clients to support legal proceedings. Unlike Legal Secretaries who primarily focus on document preparation and transcription, Legal Administrators play a strategic role in office administration and policy implementation.
Core Duties of a Legal Secretary
A Legal Secretary primarily manages document preparation, such as drafting legal correspondence, typing contracts, and organizing case files to support attorneys efficiently. They handle scheduling appointments, maintaining calendars, and coordinating communication between clients and legal professionals. Their core duties also include filing legal documents with courts, proofreading materials for accuracy, and ensuring compliance with legal protocols.
Educational and Certification Requirements
Legal Administrators typically require a bachelor's degree in business administration, paralegal studies, or a related field, often supplemented by certifications such as Certified Legal Manager (CLM) for advanced professional recognition. Legal Secretaries usually need a high school diploma or equivalent, with additional specialized training in legal terminology, office procedures, and certification programs like the Professional Legal Secretary (PLS) designation improving job prospects. Both roles benefit from knowledge of legal software, but Legal Administrators emphasize management and leadership skills aligned with their broader administrative responsibilities.
Required Skills and Competencies
Legal Administrators require strong leadership, organizational, and project management skills to oversee legal department operations and ensure compliance with regulations. Legal Secretaries must possess excellent typing, transcription, and document management abilities, along with proficiency in legal terminology and software for accurate correspondence and record-keeping. Both roles demand attention to detail, effective communication, and confidentiality, but Legal Administrators emphasize strategic planning and resource allocation while Legal Secretaries focus on administrative support and clerical precision.
Work Environment and Typical Settings
Legal Administrators typically operate in law firms, corporate legal departments, and government agencies where they manage office operations and coordinate legal support services. Legal Secretaries commonly work closely with attorneys in similar environments, handling document preparation, scheduling, and communication tasks. Both roles require familiarity with legal procedures, but Legal Administrators usually engage in broader management responsibilities within professional legal settings.
Career Progression Opportunities
Legal Administrators typically have broader career progression opportunities than Legal Secretaries, often advancing to roles such as office managers, compliance officers, or practice managers within law firms or corporate legal departments. Legal Secretaries usually progress by specializing in complex legal documentation, gaining expertise that may lead to roles like senior legal secretary or paralegal; however, their advancement tends to be more limited to support functions. Legal Administrators benefit from a wider skill set in management and administration, enabling movement into strategic roles with greater responsibilities and higher salaries.
Salary and Compensation Differences
Legal administrators typically earn higher salaries than legal secretaries due to their broader scope of responsibilities, including managing law firm operations, budgets, and compliance. According to industry data, the median salary for a legal administrator ranges from $70,000 to $90,000 annually, while legal secretaries generally earn between $40,000 and $60,000. Compensation packages for legal administrators often include bonuses and benefits tied to firm performance, reflecting their managerial role compared to the more clerical focus of legal secretaries.
Interaction with Legal Professionals
Legal Administrators coordinate case management and liaise directly with attorneys to ensure deadlines and documentation comply with legal standards, playing an integral role in office operations. Legal Secretaries primarily support lawyers by preparing correspondence, managing schedules, and organizing files, facilitating efficient communication within legal teams. Interaction with legal professionals for legal administrators involves strategic oversight and process management, while legal secretaries focus on administrative support and detailed task execution.
Technology Use in Each Role
Legal Administrators utilize advanced practice management software and enterprise resource planning tools to streamline case workflows, billing, and compliance tracking, enhancing overall office efficiency. Legal Secretaries primarily rely on specialized document management systems, legal research databases, and electronic scheduling tools to support attorneys with precise and timely information handling. Both roles increasingly incorporate secure cloud-based platforms and digital communication technologies to facilitate collaboration and ensure data confidentiality within legal operations.
Choosing Between Legal Administrator and Legal Secretary
Choosing between a Legal Administrator and a Legal Secretary depends on the scope of responsibilities and organizational needs within legal administration. A Legal Administrator typically manages office operations, budgeting, and staff coordination, ensuring efficient legal department performance, while a Legal Secretary focuses on document preparation, scheduling, and direct support to lawyers. Understanding the specific demands of your legal practice will guide the decision toward either strategic administrative oversight or specialized clerical support.
Legal Administrator vs Legal Secretary Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com