Organic farming specialists prioritize sustainable practices that enhance soil health and biodiversity by avoiding synthetic chemicals, while conventional farming specialists focus on maximizing crop yields through the use of fertilizers, pesticides, and mechanized techniques. Expertise in organic farming involves knowledge of composting, crop rotation, and natural pest control, whereas conventional specialists leverage advanced technology and chemical inputs to optimize production efficiency. Both approaches require a deep understanding of plant biology and soil science, but their methodologies and environmental impacts differ significantly.
Table of Comparison
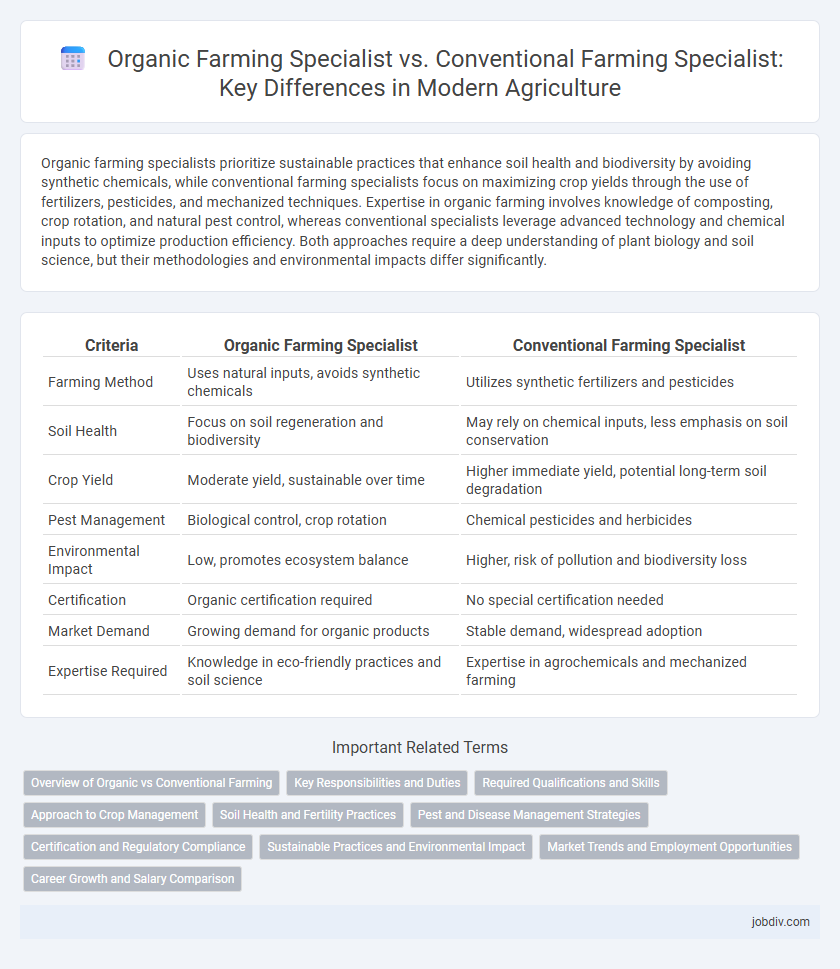
| Criteria | Organic Farming Specialist | Conventional Farming Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Farming Method | Uses natural inputs, avoids synthetic chemicals | Utilizes synthetic fertilizers and pesticides |
| Soil Health | Focus on soil regeneration and biodiversity | May rely on chemical inputs, less emphasis on soil conservation |
| Crop Yield | Moderate yield, sustainable over time | Higher immediate yield, potential long-term soil degradation |
| Pest Management | Biological control, crop rotation | Chemical pesticides and herbicides |
| Environmental Impact | Low, promotes ecosystem balance | Higher, risk of pollution and biodiversity loss |
| Certification | Organic certification required | No special certification needed |
| Market Demand | Growing demand for organic products | Stable demand, widespread adoption |
| Expertise Required | Knowledge in eco-friendly practices and soil science | Expertise in agrochemicals and mechanized farming |
Overview of Organic vs Conventional Farming
Organic farming relies on natural fertilizers and pest control methods, promoting biodiversity and soil health, while conventional farming often uses synthetic chemicals and genetically modified organisms to maximize crop yields. Organic specialists focus on sustainable practices that enhance ecosystem balance and reduce environmental impact, whereas conventional specialists emphasize high-efficiency production through advanced machinery and chemical inputs. Both approaches address food security, but organic farming prioritizes long-term environmental sustainability, and conventional farming targets immediate productivity and scalability.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
An Organic Farming Specialist manages soil health through natural methods, emphasizes crop rotation, composting, and pest control without synthetic chemicals, ensuring sustainable and eco-friendly practices. A Conventional Farming Specialist focuses on maximizing crop yields using chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and mechanized equipment, optimizing production efficiency. Both specialists monitor crop growth, analyze soil conditions, and implement farming strategies but differ fundamentally in their approach to input use and environmental impact.
Required Qualifications and Skills
Organic Farming Specialists require expertise in sustainable agriculture practices, soil health management, and organic pest control methods, often holding certifications in organic farming or agroecology. Conventional Farming Specialists typically possess strong knowledge in chemical fertilizers, genetically modified organisms (GMOs), and mechanized farming techniques, with qualifications in agronomy or agricultural engineering. Both roles demand skills in crop management, data analysis, and regulatory compliance, but focus on different cultivation strategies and environmental impacts.
Approach to Crop Management
Organic Farming Specialists emphasize natural pest control methods, crop rotation, and soil fertility through compost and green manure to maintain ecological balance. Conventional Farming Specialists rely heavily on synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and genetically modified seeds to maximize crop yield and control pests efficiently. The organic approach prioritizes sustainability and biodiversity, whereas conventional methods focus on productivity and cost-effectiveness.
Soil Health and Fertility Practices
Organic farming specialists prioritize soil health through natural amendments like compost, cover crops, and crop rotation, enhancing microbial diversity and long-term fertility. Conventional farming specialists often rely on synthetic fertilizers and chemical inputs to quickly boost nutrient availability but may risk soil degradation over time. Maintaining soil structure and nutrient balance remains a key focus for both, with differing approaches to sustainability and environmental impact.
Pest and Disease Management Strategies
Organic farming specialists prioritize pest and disease management through natural predators, crop rotation, and organic pesticides such as neem oil and pyrethrin to maintain soil health and biodiversity. Conventional farming specialists rely on synthetic chemical pesticides, herbicides, and genetically modified crops for rapid and targeted pest control, often enhancing immediate crop yields. Both strategies aim to reduce crop losses, but organic methods emphasize ecological balance while conventional approaches focus on efficiency and productivity.
Certification and Regulatory Compliance
Organic farming specialists must obtain certifications such as USDA Organic or EU Organic to ensure compliance with strict regulations on pesticide use, soil management, and crop rotation. Conventional farming specialists adhere to broader agricultural standards and often focus on compliance with regulations related to synthetic fertilizers, genetically modified organisms (GMOs), and pesticide application limits. Both roles require thorough knowledge of local and international agricultural laws, but organic farming certification processes are typically more rigorous and ongoing to maintain market access.
Sustainable Practices and Environmental Impact
Organic Farming Specialists prioritize sustainable practices by utilizing natural pest control, crop rotation, and organic fertilizers to enhance soil health and reduce chemical runoff. Conventional Farming Specialists often rely on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, which can lead to soil degradation and water pollution over time. Emphasizing biodiversity and long-term ecosystem balance, organic methods minimize environmental impact compared to conventional approaches focused on maximizing short-term yield.
Market Trends and Employment Opportunities
Organic farming specialists are experiencing increased demand due to rising consumer preference for sustainable and chemical-free produce, driving market growth in health-conscious and eco-friendly sectors. Conventional farming specialists remain crucial for large-scale food production but face challenges from regulatory pressures and environmental concerns, influencing shifts in employment trends. Market data shows a growing investment in organic agriculture, correlating with expanded job opportunities and specialized skill requirements in organic farming practices.
Career Growth and Salary Comparison
Organic Farming Specialists experience increasing demand due to rising consumer awareness of sustainable agriculture, leading to career growth opportunities in niche markets and government programs. Conventional Farming Specialists typically command higher average salaries, benefiting from established agribusiness sectors and larger-scale operations with robust funding. Salary comparisons reveal Organic Farming Specialists earn between $45,000 and $70,000, while Conventional Specialists often range from $55,000 to $85,000, reflecting differences in market scale and technological advancement.
Organic Farming Specialist vs Conventional Farming Specialist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com