Art therapists use creative processes to support mental health and emotional well-being, tailoring sessions to address psychological challenges and promote healing. Art teachers focus on developing technical skills, artistic techniques, and fostering creativity in students through structured lessons and skill-building activities. While both professions involve art, therapists prioritize therapeutic outcomes, whereas teachers emphasize educational growth and artistic proficiency.
Table of Comparison
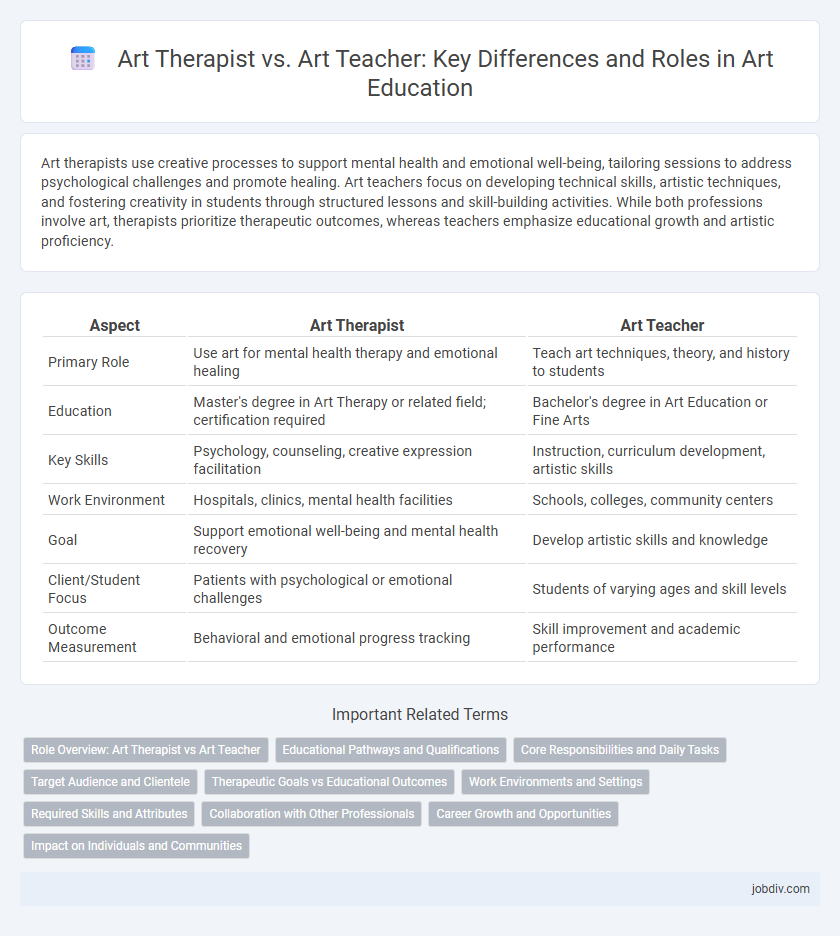
| Aspect | Art Therapist | Art Teacher |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Use art for mental health therapy and emotional healing | Teach art techniques, theory, and history to students |
| Education | Master's degree in Art Therapy or related field; certification required | Bachelor's degree in Art Education or Fine Arts |
| Key Skills | Psychology, counseling, creative expression facilitation | Instruction, curriculum development, artistic skills |
| Work Environment | Hospitals, clinics, mental health facilities | Schools, colleges, community centers |
| Goal | Support emotional well-being and mental health recovery | Develop artistic skills and knowledge |
| Client/Student Focus | Patients with psychological or emotional challenges | Students of varying ages and skill levels |
| Outcome Measurement | Behavioral and emotional progress tracking | Skill improvement and academic performance |
Role Overview: Art Therapist vs Art Teacher
An Art Therapist uses creative processes to support mental health, focusing on emotional healing and psychological well-being through therapeutic techniques. An Art Teacher emphasizes developing artistic skills, techniques, and art history knowledge to nurture student creativity and educational growth. While both roles engage with art, therapists apply clinical methods for therapy, whereas teachers concentrate on instruction and artistic development.
Educational Pathways and Qualifications
Art Therapists require a master's degree in art therapy or a related mental health field, along with clinical training and certification such as the ATR-BC credential. Art Teachers typically earn a bachelor's degree in art education and must obtain state licensure to teach in public schools, focusing on pedagogy and curriculum development. Both roles demand specialized knowledge, but Art Therapists emphasize psychological principles, whereas Art Teachers concentrate on educational methods and artistic skill-building.
Core Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
Art therapists utilize creative processes to support mental health, helping clients express emotions and resolve psychological challenges through art. Art teachers focus on developing students' technical skills, art history knowledge, and creative expression within an educational curriculum. Daily tasks for art therapists include client assessments, guided art activities, and therapeutic progress evaluations, while art teachers prepare lesson plans, conduct classes, and evaluate artistic projects.
Target Audience and Clientele
Art therapists primarily work with individuals facing mental health challenges, trauma, or emotional difficulties, tailoring sessions to therapeutic goals for clients across various ages and backgrounds. Art teachers focus on students ranging from children to adults in educational settings, emphasizing skill development, creative expression, and art appreciation. While art therapists address psychological needs through structured interventions, art teachers aim to cultivate artistic techniques and knowledge in classroom or workshop environments.
Therapeutic Goals vs Educational Outcomes
Art therapists prioritize therapeutic goals by using creative processes to promote mental health, emotional expression, and psychological healing, targeting issues such as trauma and anxiety. Art teachers focus on educational outcomes, teaching technical skills, art history, and fostering creativity to develop students' artistic abilities and appreciation. The core difference lies in art therapists addressing emotional well-being, while art teachers emphasize skill acquisition and academic growth in art.
Work Environments and Settings
Art therapists typically work in clinical settings such as hospitals, mental health clinics, rehabilitation centers, and private practice, where they use art to support emotional and psychological healing. Art teachers are primarily employed in educational institutions, including schools, colleges, and community centers, focusing on developing students' artistic skills and creativity. The distinct work environments reflect each role's goals: therapy prioritizes mental health treatment, while teaching emphasizes art education and skill-building.
Required Skills and Attributes
Art therapists require strong psychological insight, empathy, and knowledge of therapeutic techniques to effectively support clients' mental health through creative expression. Art teachers must possess excellent instructional skills, creativity, and the ability to inspire and engage students in developing their artistic talents. Both roles demand a deep understanding of art fundamentals, but art therapists focus more on emotional intelligence and counseling skills, while art teachers emphasize educational strategies and curriculum development.
Collaboration with Other Professionals
Art therapists collaborate closely with psychologists, social workers, and healthcare providers to address patients' emotional and mental health needs through creative expression. Art teachers work alongside educators, curriculum developers, and school counselors to enhance students' artistic skills and integrate art education into broader learning objectives. Both professionals benefit from interdisciplinary teamwork, yet their collaborative focus diverges between therapeutic outcomes and educational development.
Career Growth and Opportunities
Art therapists leverage psychological principles and creative techniques to support mental health, with career growth often tied to clinical settings, healthcare facilities, and specialized counseling roles. Art teachers focus on developing students' artistic skills and creativity in educational institutions, where opportunities expand through curriculum development, administrative positions, and art education leadership. Both professions benefit from continued education and certification, but art therapists generally experience faster growth due to increasing recognition of mental health services.
Impact on Individuals and Communities
Art therapists use creative processes to support mental health and emotional healing, helping individuals overcome trauma and improve well-being. Art teachers focus on skill development and artistic expression, fostering creativity and cultural appreciation in students. Both professionals significantly impact communities by promoting self-awareness and strengthening social connections through art.
Art Therapist vs Art Teacher Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com