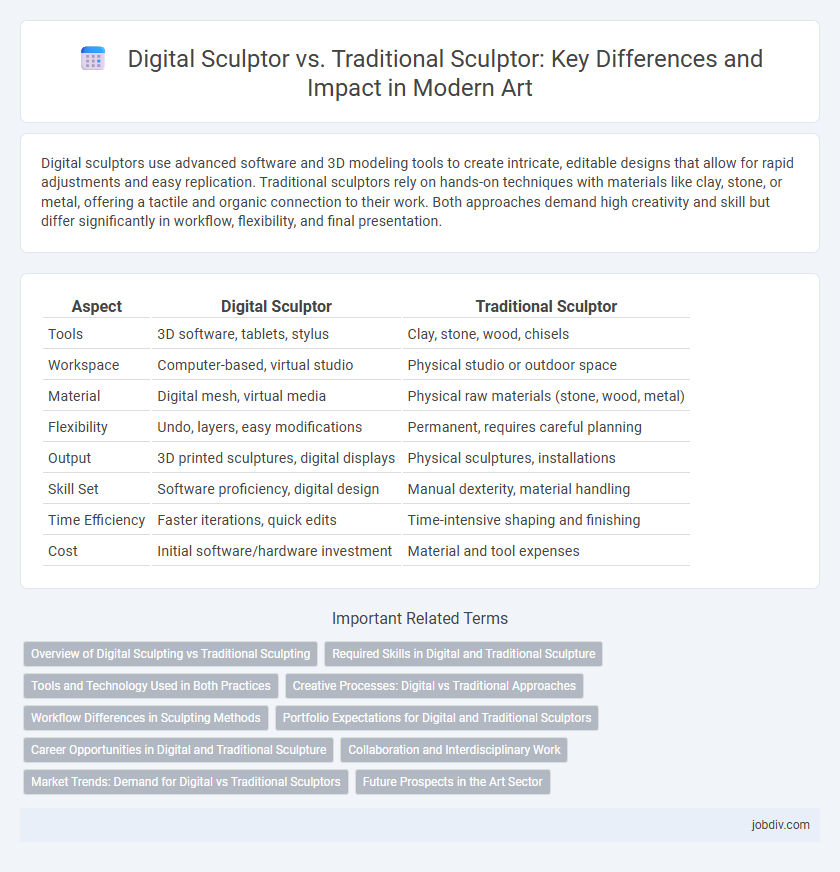
Digital sculptors use advanced software and 3D modeling tools to create intricate, editable designs that allow for rapid adjustments and easy replication. Traditional sculptors rely on hands-on techniques with materials like clay, stone, or metal, offering a tactile and organic connection to their work. Both approaches demand high creativity and skill but differ significantly in workflow, flexibility, and final presentation.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Digital Sculptor | Traditional Sculptor |
|---|---|---|
| Tools | 3D software, tablets, stylus | Clay, stone, wood, chisels |
| Workspace | Computer-based, virtual studio | Physical studio or outdoor space |
| Material | Digital mesh, virtual media | Physical raw materials (stone, wood, metal) |
| Flexibility | Undo, layers, easy modifications | Permanent, requires careful planning |
| Output | 3D printed sculptures, digital displays | Physical sculptures, installations |
| Skill Set | Software proficiency, digital design | Manual dexterity, material handling |
| Time Efficiency | Faster iterations, quick edits | Time-intensive shaping and finishing |
| Cost | Initial software/hardware investment | Material and tool expenses |
Overview of Digital Sculpting vs Traditional Sculpting
Digital sculpting leverages advanced software like ZBrush and Blender to create intricate 3D models with high precision and flexibility, enabling easy modifications and rapid prototyping. In contrast, traditional sculpting relies on hands-on techniques using materials such as clay, stone, or wood, emphasizing tactile skill and physical interaction with the medium. Digital sculpting offers advantages in scalability and integration with animation and virtual reality, while traditional sculpting provides a unique, tangible connection to the artwork through direct manipulation of physical materials.
Required Skills in Digital and Traditional Sculpture
Digital sculptors require proficiency in 3D modeling software such as ZBrush, Blender, or Maya, combined with a strong understanding of digital texture mapping and rendering techniques. Traditional sculptors rely heavily on hands-on skills with materials like clay, stone, or metal, mastering tools like chisels, rasps, and welding equipment to shape physical forms. Both disciplines demand a keen sense of spatial awareness, anatomy, and artistic creativity, but digital sculpture emphasizes technical digital literacy while traditional sculpture prioritizes tactile craftsmanship.
Tools and Technology Used in Both Practices
Digital sculptors utilize advanced software such as ZBrush, Blender, and Autodesk Maya, combined with hardware like graphic tablets and 3D printers to create precise, editable models. Traditional sculptors rely on physical tools including chisels, hammers, rasps, and molding materials like clay, wood, stone, or metal to shape their artworks manually. The integration of digital technology enables intricate detail customization and rapid prototyping, contrasting with the tactile, hands-on craftsmanship intrinsic to traditional methods.
Creative Processes: Digital vs Traditional Approaches
Digital sculptors utilize advanced software and 3D modeling tools to manipulate virtual clay, enabling rapid prototyping, undo functions, and intricate detailing that traditional methods struggle to achieve. Traditional sculptors engage directly with physical materials such as marble, clay, or wood, relying on tactile feedback and manual techniques that foster a deep, intuitive connection with the medium. Both approaches require distinct skill sets: digital sculpting demands proficiency in software and digital tools, while traditional sculpting emphasizes craftsmanship, patience, and physical manipulation.
Workflow Differences in Sculpting Methods
Digital sculptors utilize software like ZBrush or Blender, enabling iterative adjustments, seamless scaling, and rapid prototyping, streamlining the creative workflow. Traditional sculptors rely on physical materials such as clay, stone, or wood, requiring manual carving, molding, and surface refinement, which demands meticulous skill and extended time. The digital workflow offers non-destructive editing and easy duplication, while traditional methods emphasize tactile interaction and the tangible evolution of form.
Portfolio Expectations for Digital and Traditional Sculptors
Digital sculptors are expected to showcase high-resolution 3D models, detailed texture maps, and interactive turnarounds in their portfolios, emphasizing proficiency with software like ZBrush, Blender, or Maya. Traditional sculptors must present a range of physical works captured through high-quality photographs that highlight various angles, surface textures, and materials used, demonstrating mastery of carving, modeling, or casting techniques. Both portfolios should include concept sketches or process documentation to illustrate artistic development and technical skills, reflecting the standards of galleries or potential clients in fine art and entertainment industries.
Career Opportunities in Digital and Traditional Sculpture
Careers in digital sculpture offer expansive opportunities in industries such as video games, film, virtual reality, and 3D printing, leveraging software like ZBrush and Blender to create intricate, customizable models. Traditional sculpture careers often focus on fine art galleries, public installations, and restoration projects, emphasizing mastery of materials like clay, stone, and metal with techniques developed over centuries. The digital sculpting field demands proficiency in digital workflows, while traditional sculptors rely on tactile skills, though hybrid approaches are emerging, blending both methods for innovative career pathways.
Collaboration and Interdisciplinary Work
Digital sculptors leverage advanced software and 3D printing technology to collaborate seamlessly with architects, designers, and engineers, fostering interdisciplinary innovation. Traditional sculptors bring tactile expertise and material knowledge that enhance collaborative projects requiring hands-on craftsmanship and historical techniques. Integrating digital precision with traditional skills expands creative possibilities, driving forward mixed-media installations and large-scale public art collaborations.
Market Trends: Demand for Digital vs Traditional Sculptors
The market demand for digital sculptors is rapidly increasing due to the rise of industries such as video games, virtual reality, and film, which require intricate 3D models and animations. Traditional sculptors continue to hold strong appeal in fine art, galleries, and public installations, where tactile, handcrafted work remains highly valued. However, digital sculpting's integration with emerging technologies is driving higher growth rates and expanding job opportunities compared to traditional methods.
Future Prospects in the Art Sector
Digital sculptors leverage advanced software and 3D printing technology, positioning themselves at the forefront of innovation in the art sector. Traditional sculptors maintain relevance through mastery of tactile materials and historical techniques, appealing to collectors who value craftsmanship and authenticity. Future prospects indicate a hybrid approach may dominate, combining digital precision with traditional artistry to expand creative possibilities and market reach.
Digital Sculptor vs Traditional Sculptor Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com