A camera operator captures live footage by controlling camera angles, framing shots, and following action on set, ensuring dynamic and engaging visuals. A vision mixer selects and transitions between multiple video feeds in real-time, blending live sources to create a seamless broadcast output. Both roles require technical precision and teamwork to deliver high-quality pet broadcasting content.
Table of Comparison
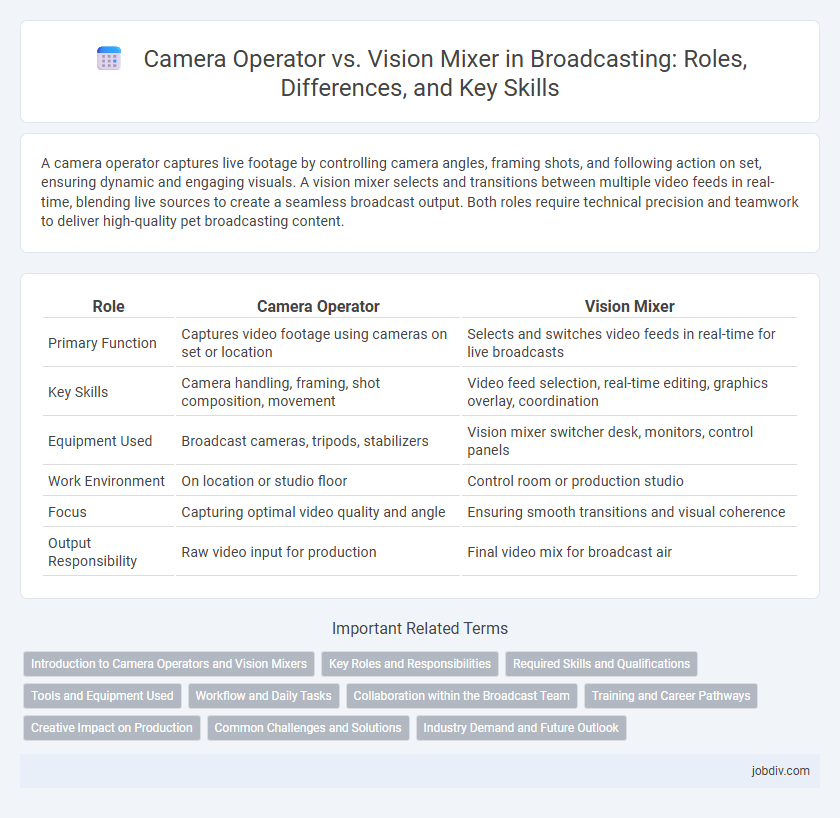
| Role | Camera Operator | Vision Mixer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Captures video footage using cameras on set or location | Selects and switches video feeds in real-time for live broadcasts |
| Key Skills | Camera handling, framing, shot composition, movement | Video feed selection, real-time editing, graphics overlay, coordination |
| Equipment Used | Broadcast cameras, tripods, stabilizers | Vision mixer switcher desk, monitors, control panels |
| Work Environment | On location or studio floor | Control room or production studio |
| Focus | Capturing optimal video quality and angle | Ensuring smooth transitions and visual coherence |
| Output Responsibility | Raw video input for production | Final video mix for broadcast air |
Introduction to Camera Operators and Vision Mixers
Camera operators are responsible for capturing live footage by controlling camera equipment, framing shots, and adjusting focus and exposure during broadcasts or productions. Vision mixers, also known as technical directors, manage the live video feed by switching between multiple camera sources, adding graphics, and ensuring smooth transitions in real-time. Both roles are integral to producing professional and visually engaging broadcast content.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Camera operators are responsible for capturing live or recorded footage by controlling camera equipment, framing shots, and adjusting focus and exposure to ensure high-quality visuals. Vision mixers manage the live video feed during broadcasts, selecting and switching between various camera angles, graphics, and video sources to create a seamless final output. Both roles require strong technical skills and real-time decision-making to maintain broadcast production standards and viewer engagement.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Camera operators must excel in framing, focus control, and camera movement, requiring technical knowledge of camera equipment and strong hand-eye coordination. Vision mixers need expertise in live video switching, understanding broadcast signal flow, and proficiency with vision mixing consoles or software to seamlessly transition between multiple video sources. Both roles demand quick decision-making, attention to detail, and experience in live broadcasting environments.
Tools and Equipment Used
Camera operators rely on advanced professional cameras, tripods, and stabilizers to capture dynamic live footage with precision and fluid motion control. Vision mixers utilize hardware switchers, control panels, and software interfaces to seamlessly blend multiple video sources, adjust visual effects, and manage real-time transitions during broadcasts. Both roles depend on synchronized communication systems and monitoring tools to ensure cohesive production output.
Workflow and Daily Tasks
Camera operators capture live footage by adjusting framing, focus, and camera movement to ensure optimal visual quality during broadcasts. Vision mixers manage the live video feed by selecting and switching between multiple camera angles, adding overlays, and coordinating visual effects to create a seamless final output. Both roles require close communication to synchronize shots and maintain broadcast continuity.
Collaboration within the Broadcast Team
Camera operators and vision mixers collaborate closely to ensure seamless live broadcasts, with camera operators capturing dynamic visuals while vision mixers select and switch between these feeds in real-time. Effective communication between these roles is crucial for synchronizing shots and maintaining the broadcast's visual coherence. Their teamwork enhances production quality by combining technical skill and creative decision-making under fast-paced conditions.
Training and Career Pathways
Camera operators typically undergo specialized training in camera techniques, shot composition, and equipment handling through vocational courses, apprenticeships, or media production degrees, which prepare them for on-site filming and live-event capturing. Vision mixers focus on mastering live video switching, signal processing, and broadcast software, often gaining expertise through technical courses in video production and extensive hands-on experience in control room environments. Career pathways for camera operators usually lead to roles in field production and cinematography, while vision mixers progress toward broadcast directing and technical management positions within television studios.
Creative Impact on Production
Camera operators capture dynamic shots that shape the visual narrative, influencing the mood and energy of a broadcast. Vision mixers blend live video feeds, applying transitions and effects to craft a cohesive and engaging story in real-time. Their combined creative impact ensures seamless production flow and enhances audience engagement through compelling visual storytelling.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Camera operators and vision mixers often face challenges like maintaining seamless communication during live broadcasts and managing rapid technical adjustments under pressure. Solutions include implementing real-time collaboration tools and standardized protocols to ensure synchronized camera angles and smooth transitions. Training programs focusing on cross-functional skills help both roles adapt to dynamic production environments efficiently.
Industry Demand and Future Outlook
Camera operators and vision mixers play distinct roles in broadcasting, with camera operators experiencing steady demand due to the rise in live event coverage and digital content production, while vision mixers are increasingly sought after for their expertise in real-time video editing and multi-camera switching during broadcasts. The future outlook for camera operators shows growth aligned with expanding streaming services and virtual events, whereas vision mixers benefit from advancements in broadcast technology and remote production workflows, driving demand for skilled professionals in immersive and interactive content creation. Both roles require adaptability to evolving equipment and software, with vision mixers gaining an edge in industry demand due to the integration of AI and automation in live broadcasting environments.
Camera Operator vs Vision Mixer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com