Graphics operators specialize in creating and managing on-screen visuals, such as lower thirds, animations, and real-time graphics, ensuring seamless integration during live broadcasts. Video editors focus on assembling, trimming, and enhancing pre-recorded footage to produce polished, cohesive video segments for playback. Both roles are essential in broadcasting pet content, with graphics operators elevating live presentations and video editors refining recorded material.
Table of Comparison
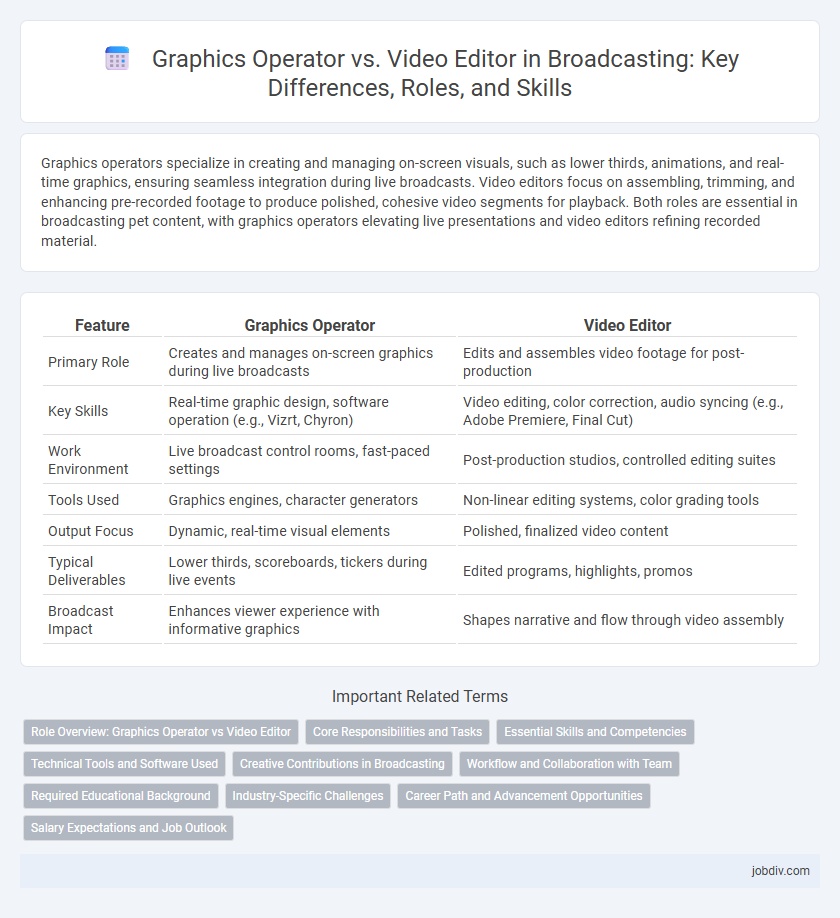
| Feature | Graphics Operator | Video Editor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Creates and manages on-screen graphics during live broadcasts | Edits and assembles video footage for post-production |
| Key Skills | Real-time graphic design, software operation (e.g., Vizrt, Chyron) | Video editing, color correction, audio syncing (e.g., Adobe Premiere, Final Cut) |
| Work Environment | Live broadcast control rooms, fast-paced settings | Post-production studios, controlled editing suites |
| Tools Used | Graphics engines, character generators | Non-linear editing systems, color grading tools |
| Output Focus | Dynamic, real-time visual elements | Polished, finalized video content |
| Typical Deliverables | Lower thirds, scoreboards, tickers during live events | Edited programs, highlights, promos |
| Broadcast Impact | Enhances viewer experience with informative graphics | Shapes narrative and flow through video assembly |
Role Overview: Graphics Operator vs Video Editor
Graphics Operators specialize in creating and managing on-screen visuals, including animations, titles, and lower thirds, ensuring seamless integration with live broadcasts. Video Editors focus on assembling, trimming, and enhancing raw footage into polished video content, managing elements such as color correction, transitions, and pacing to craft a cohesive narrative. Both roles require technical proficiency with industry-standard software but serve distinct functions in the broadcasting production pipeline.
Core Responsibilities and Tasks
Graphics Operators specialize in creating and managing on-screen visual elements such as titles, lower thirds, and animations during live broadcasts, ensuring seamless integration with the video feed. Video Editors focus on assembling, cutting, and enhancing recorded footage by applying transitions, effects, and color correction to produce polished final content for broadcast or digital distribution. Both roles require technical proficiency with industry-standard software, but Graphics Operators emphasize real-time visual presentation while Video Editors prioritize post-production refinement.
Essential Skills and Competencies
Graphics Operators in broadcasting require strong proficiency in software like Adobe After Effects and real-time graphics insertion tools, alongside keen attention to visual detail and timing accuracy. Video Editors must excel in non-linear editing systems such as Avid Media Composer or Final Cut Pro, demonstrating skills in color grading, storytelling, and seamless transitions to maintain narrative flow. Both roles demand excellent collaboration and communication abilities to work effectively within fast-paced production environments.
Technical Tools and Software Used
Graphics Operators in broadcasting primarily utilize software such as Adobe After Effects, Vizrt, and ChyronHego to create real-time visual elements, lower thirds, and on-screen graphics that integrate seamlessly during live broadcasts. Video Editors focus on post-production tools like Adobe Premiere Pro, Final Cut Pro, and Avid Media Composer to assemble, cut, and enhance video footage for polished final broadcasts. Both roles demand proficiency in industry-standard programs, but Graphics Operators emphasize live visual effects software, while Video Editors rely on advanced nonlinear editing systems for detailed video refinement.
Creative Contributions in Broadcasting
Graphics operators enhance broadcasting content by designing visually engaging elements such as lower thirds, animations, and overlays that support storytelling and brand identity. Video editors contribute creatively by assembling footage, selecting shots, and adding effects to craft a coherent narrative and evoke emotional responses from viewers. Both roles are essential for delivering polished broadcasts, with graphics operators focusing on visual augmentation and video editors shaping the overall story flow.
Workflow and Collaboration with Team
Graphics Operators streamline live broadcast workflows by integrating real-time visual content with on-air video, ensuring synchronized graphics insertion and enhancing viewer engagement. Video Editors focus on post-production workflows, assembling raw footage into polished segments, collaborating closely with producers and directors to align edits with the broadcast narrative. Effective collaboration between Graphics Operators and Video Editors is crucial for seamless content delivery, requiring clear communication and shared project timelines to manage transitions between live and pre-recorded segments.
Required Educational Background
Graphics operators typically require a background in graphic design, animation, or multimedia arts, often supported by a diploma or degree in digital media or visual communication. Video editors usually hold a degree or certification in film production, video editing, or broadcasting, emphasizing video software proficiency and storytelling techniques. Both roles demand technical skills, but graphic operators focus more on design principles, while video editors prioritize narrative construction and footage assembly.
Industry-Specific Challenges
Graphics Operators in broadcasting face challenges such as real-time rendering of dynamic visuals, synchronization with live feeds, and managing graphic overlays under strict time constraints. Video Editors must handle high-resolution footage, ensure seamless continuity, and adapt to last-minute script or content changes while maintaining broadcast standards. Both roles require specialized software proficiency and the ability to work efficiently in fast-paced, deadline-driven environments.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
Graphics Operators specialize in creating and managing visual effects and animations for live broadcasts, with career advancement often leading to roles such as Senior Graphics Designer or Broadcast Technical Director. Video Editors focus on assembling raw footage into polished content for television or online platforms, progressing towards positions like Lead Video Editor or Post-Production Supervisor. Both career paths offer opportunities to develop technical expertise and leadership skills within the broadcasting industry.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Graphics Operators in broadcasting typically earn an average salary ranging from $40,000 to $60,000 annually, reflecting demand for their expertise in live visual content management. Video Editors command salaries between $45,000 and $70,000, driven by the increasing need for polished, post-production editing across various media platforms. Job outlook for Graphics Operators remains steady with growth in live broadcasting, while Video Editors face a higher demand due to expanding digital content creation and streaming services.
Graphics Operator vs Video Editor Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com