Broadcast producers oversee live or recorded content for television or radio stations, managing technical aspects and coordinating teams to deliver seamless programming. Podcast producers focus on creating on-demand audio shows, emphasizing editing, storytelling, and audience engagement to cater to niche listeners. Both roles require strong project management skills but differ in format, distribution methods, and production workflows.
Table of Comparison
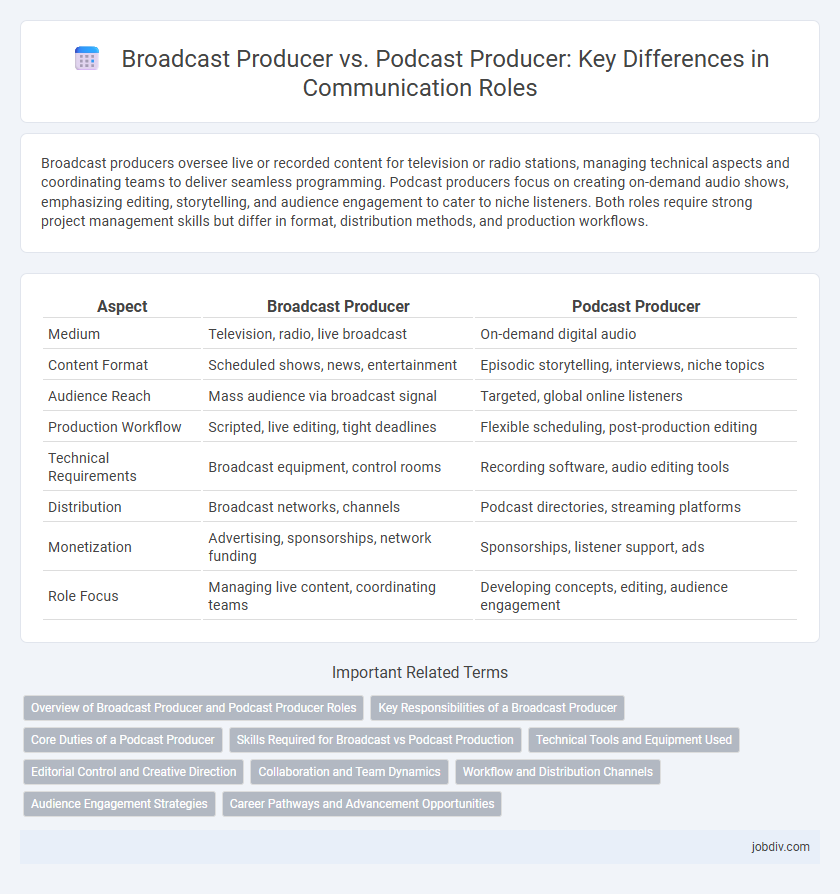
| Aspect | Broadcast Producer | Podcast Producer |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Television, radio, live broadcast | On-demand digital audio |
| Content Format | Scheduled shows, news, entertainment | Episodic storytelling, interviews, niche topics |
| Audience Reach | Mass audience via broadcast signal | Targeted, global online listeners |
| Production Workflow | Scripted, live editing, tight deadlines | Flexible scheduling, post-production editing |
| Technical Requirements | Broadcast equipment, control rooms | Recording software, audio editing tools |
| Distribution | Broadcast networks, channels | Podcast directories, streaming platforms |
| Monetization | Advertising, sponsorships, network funding | Sponsorships, listener support, ads |
| Role Focus | Managing live content, coordinating teams | Developing concepts, editing, audience engagement |
Overview of Broadcast Producer and Podcast Producer Roles
Broadcast producers oversee live or recorded television and radio programs, managing logistics, coordinating with talent, and ensuring smooth production flow to meet strict deadlines. Podcast producers focus on content planning, audio editing, and distribution strategies tailored for on-demand digital audiences, often working with smaller teams and flexible schedules. Both roles require strong project management skills, but broadcast producers prioritize real-time broadcasting constraints while podcast producers emphasize post-production quality and audience engagement.
Key Responsibilities of a Broadcast Producer
A Broadcast Producer oversees the entire production process of television or radio programs, managing script development, scheduling, and live broadcast execution to ensure timely and seamless content delivery. They coordinate with directors, technical crews, and on-air talent to maintain high-quality production standards and adhere to regulatory guidelines. Their role also includes budget management, audience analysis, and troubleshooting technical issues during live broadcasts.
Core Duties of a Podcast Producer
A podcast producer manages the entire production process, including scripting, recording, editing, and sound design to ensure high-quality audio content. They coordinate with hosts, guests, and technical teams while overseeing distribution on multiple platforms to maximize audience reach. Unlike a broadcast producer, their focus centers on digital content tailored for podcasts, emphasizing storytelling, audience engagement, and episode pacing.
Skills Required for Broadcast vs Podcast Production
Broadcast producers require skills in live event coordination, real-time troubleshooting, and managing large production teams to ensure seamless transmission. Podcast producers need expertise in audio editing, storytelling, and content planning to create engaging, on-demand episodes. Both roles demand strong communication, project management, and audience analysis abilities tailored to their respective media formats.
Technical Tools and Equipment Used
Broadcast producers utilize advanced studio equipment such as mixers, satellite feeds, and multi-camera setups to manage live television or radio content, ensuring seamless transmission and high-quality audio-visual output. Podcast producers rely heavily on digital audio workstations (DAWs) like Adobe Audition or Audacity, portable microphones, and editing software tailored for non-linear editing and remote collaboration. Both roles require expertise in audio processing tools and sound engineering techniques, but broadcast producers often engage with real-time broadcasting technology, whereas podcast producers focus more on post-production refinement and distribution platforms.
Editorial Control and Creative Direction
Broadcast producers hold significant editorial control, managing content compliance with network standards and overseeing live show execution to maintain consistent quality. Podcast producers exercise greater creative direction, often collaborating closely with hosts to shape episode themes and storytelling styles, allowing for more personalized and flexible content creation. Both roles require strategic decision-making, but podcast producers typically enjoy enhanced autonomy in content innovation and audience engagement strategies.
Collaboration and Team Dynamics
Broadcast producers coordinate complex teams including directors, technical staff, and on-air talent to ensure seamless live or recorded content, emphasizing real-time communication and swift decision-making. Podcast producers work closely with hosts, editors, and marketing specialists, fostering a collaborative environment centered on storytelling and audience engagement across digital platforms. Both roles require strong interpersonal skills and adaptability, but broadcast production demands rapid coordination, while podcast production prioritizes creative collaboration and iterative feedback.
Workflow and Distribution Channels
Broadcast producers coordinate live television or radio programming workflows, managing real-time content scheduling and multi-camera operations to ensure seamless audience engagement. Podcast producers focus on asynchronous content creation, emphasizing episode scripting, audio editing, and hosting platform distribution such as Spotify, Apple Podcasts, and Google Podcasts. Distribution for broadcast relies on terrestrial and satellite networks with strict time slots, while podcasts utilize on-demand streaming and RSS feeds, allowing flexible global accessibility.
Audience Engagement Strategies
Broadcast producers employ real-time audience interaction methods such as live calls, social media integration, and instant feedback loops to boost listener participation and retention. Podcast producers focus on tailored content delivery, leveraging listener data analytics and personalized storytelling to deepen audience connection and encourage subscription growth. Both roles prioritize engagement but utilize platform-specific strategies to optimize listener experience and brand loyalty.
Career Pathways and Advancement Opportunities
Broadcast producers typically advance through roles in television or radio, gaining experience in live programming and large-scale productions, leading to senior positions like executive producer or production manager. Podcast producers often start with content creation, audio editing, and marketing skills, progressing to roles such as showrunner, network content strategist, or independent production company owner. Career pathways in both fields emphasize storytelling expertise, technical proficiency, and leadership, with podcast production offering more entrepreneurial opportunities due to the industry's digital and on-demand nature.
Broadcast Producer vs Podcast Producer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com