Internal Communications Managers specialize in enhancing communication within an organization, focusing on employee engagement, information flow, and culture building. External Communications Managers handle the organization's public image, managing media relations, brand messaging, and stakeholder communications. Both roles require strategic messaging skills but differ in target audiences and communication channels.
Table of Comparison
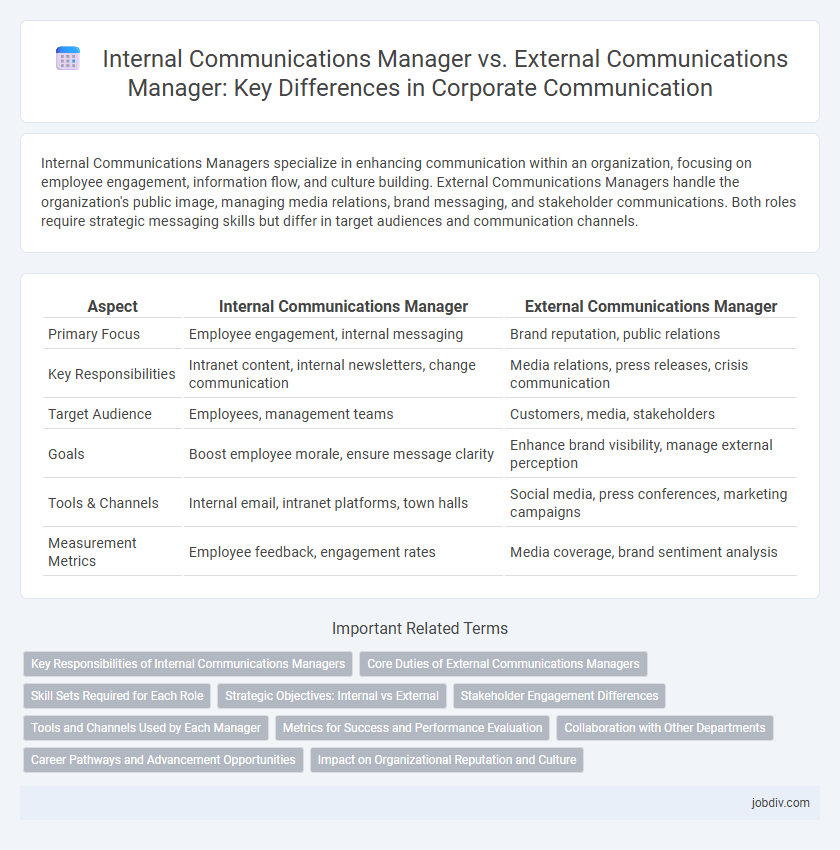
| Aspect | Internal Communications Manager | External Communications Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Employee engagement, internal messaging | Brand reputation, public relations |
| Key Responsibilities | Intranet content, internal newsletters, change communication | Media relations, press releases, crisis communication |
| Target Audience | Employees, management teams | Customers, media, stakeholders |
| Goals | Boost employee morale, ensure message clarity | Enhance brand visibility, manage external perception |
| Tools & Channels | Internal email, intranet platforms, town halls | Social media, press conferences, marketing campaigns |
| Measurement Metrics | Employee feedback, engagement rates | Media coverage, brand sentiment analysis |
Key Responsibilities of Internal Communications Managers
Internal Communications Managers focus on enhancing employee engagement by crafting clear, consistent messages that align with company goals and culture. They manage internal channels such as intranets, newsletters, and town hall meetings to facilitate effective information flow and foster collaboration. Their key responsibilities include developing communication strategies that support organizational change, improving employee understanding, and ensuring timely dissemination of critical updates.
Core Duties of External Communications Managers
External Communications Managers oversee public relations, media interactions, and corporate messaging to shape a company's external image. They coordinate press releases, manage social media strategies, and handle crisis communications to maintain brand reputation. Their core duties involve building relationships with stakeholders, including customers, investors, and the media, ensuring consistent and positive communication across all external channels.
Skill Sets Required for Each Role
An Internal Communications Manager requires strong skills in organizational behavior, employee engagement strategies, and proficiency in collaboration tools to foster transparent and effective communication within the company. In contrast, an External Communications Manager must excel in media relations, brand management, crisis communication, and digital marketing techniques to build and maintain a positive public image. Both roles demand exceptional writing and presentation abilities, but the internal role emphasizes interpersonal communication, while the external position prioritizes stakeholder outreach and public influence.
Strategic Objectives: Internal vs External
Internal Communications Managers prioritize strategic objectives that enhance employee engagement, align organizational culture, and facilitate transparent information flow within the company. External Communications Managers focus on building brand reputation, managing public relations, and driving customer engagement through targeted messaging to external stakeholders. Both roles require tailored strategies to address distinct audiences while supporting overarching corporate goals.
Stakeholder Engagement Differences
Internal Communications Managers concentrate on engaging employees, fostering alignment with company goals, and promoting organizational culture through targeted messages and feedback channels. External Communications Managers focus on building relationships with external stakeholders such as customers, investors, and media, managing brand reputation, and conveying strategic narratives to influence public perception. The primary difference lies in the audience scope, where internal roles prioritize employee engagement, while external roles emphasize broader stakeholder influence and public relations.
Tools and Channels Used by Each Manager
Internal Communications Managers often utilize intranet platforms, email newsletters, and collaboration tools like Microsoft Teams or Slack to ensure seamless information flow within the organization. External Communications Managers typically leverage media relations, social media platforms such as LinkedIn and Twitter, and press release distribution services to engage with external audiences and stakeholders. Both roles rely on content management systems and analytics tools to optimize message delivery and measure communication effectiveness.
Metrics for Success and Performance Evaluation
Internal Communications Managers measure success by employee engagement scores, information retention rates, and feedback loop effectiveness, ensuring clear and consistent messaging within the organization. External Communications Managers focus on media impressions, social media engagement, brand sentiment analysis, and lead generation metrics to evaluate public perception and campaign impact. Both roles rely on tailored analytics tools and key performance indicators (KPIs) aligned with their target audiences and communication objectives.
Collaboration with Other Departments
Internal Communications Managers coordinate closely with HR, IT, and Operations to ensure consistent messaging and employee engagement across the organization. External Communications Managers collaborate with Marketing, Sales, and Public Relations teams to align brand messaging and manage public perception effectively. Both roles require strategic teamwork to integrate communication efforts and support overall business objectives.
Career Pathways and Advancement Opportunities
Internal Communications Managers typically advance through roles such as Employee Engagement Specialist or Corporate Communications Director, leveraging expertise in organizational culture and internal messaging strategies. External Communications Managers often progress toward positions like Public Relations Director or Brand Communications Lead, emphasizing media relations and stakeholder engagement skills. Both career pathways offer leadership roles but differ in focus, with internal roles centering on employee connectivity and external roles prioritizing public perception and reputation management.
Impact on Organizational Reputation and Culture
An Internal Communications Manager shapes organizational culture by fostering employee engagement, enhancing transparency, and aligning staff with company values, directly impacting morale and productivity. An External Communications Manager safeguards and builds organizational reputation through media relations, public messaging, and crisis management, influencing stakeholder trust and brand perception. Together, these roles coordinate to ensure consistent messaging that strengthens both internal culture and external reputation.
Internal Communications Manager vs External Communications Manager Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com