Internal communications facilitate collaboration and information sharing within an organization, promoting employee engagement and alignment with company goals. External communications manage interactions with customers, partners, and the public, shaping brand reputation and driving business growth. Effective strategies balance both to ensure consistency, clarity, and trust across all audiences.
Table of Comparison
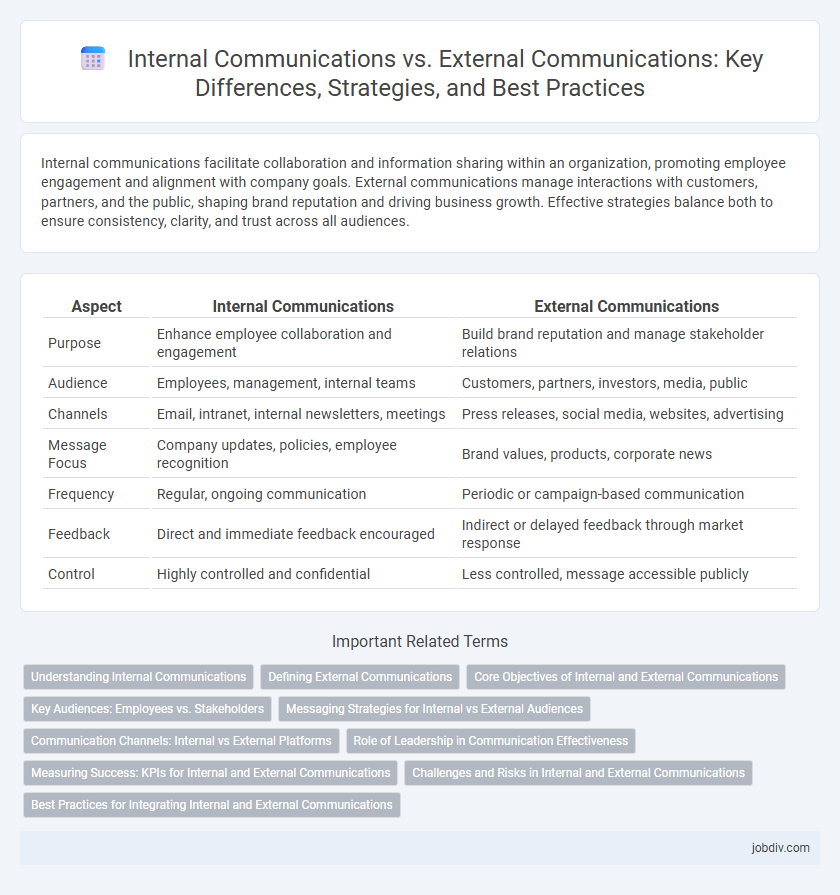
| Aspect | Internal Communications | External Communications |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Enhance employee collaboration and engagement | Build brand reputation and manage stakeholder relations |
| Audience | Employees, management, internal teams | Customers, partners, investors, media, public |
| Channels | Email, intranet, internal newsletters, meetings | Press releases, social media, websites, advertising |
| Message Focus | Company updates, policies, employee recognition | Brand values, products, corporate news |
| Frequency | Regular, ongoing communication | Periodic or campaign-based communication |
| Feedback | Direct and immediate feedback encouraged | Indirect or delayed feedback through market response |
| Control | Highly controlled and confidential | Less controlled, message accessible publicly |
Understanding Internal Communications
Internal communications involve the exchange of information within an organization, fostering employee engagement, collaboration, and alignment with company goals. Effective internal communication strategies utilize channels such as intranets, emails, and team meetings to ensure clarity and transparency among staff. Understanding internal communications is crucial for enhancing workplace productivity, employee satisfaction, and organizational culture.
Defining External Communications
External communications refer to the exchanges of information between an organization and outside parties, including customers, investors, suppliers, and the public. This type of communication encompasses marketing messages, press releases, social media interactions, and stakeholder reports designed to shape public perception and build relationships. Effective external communications ensure transparency, consistency, and alignment with the organization's brand identity to enhance reputation and drive engagement.
Core Objectives of Internal and External Communications
Internal communications aim to foster employee engagement, streamline collaboration, and ensure alignment with organizational goals by delivering clear, consistent messages within the company. External communications focus on building brand reputation, managing public perception, and cultivating relationships with customers, stakeholders, and the media through strategic messaging and outreach. Both channels prioritize clarity and consistency but differ in audience targeting and ultimate impact on business success.
Key Audiences: Employees vs. Stakeholders
Internal communications target employees to enhance engagement, alignment, and productivity through clear messaging and feedback channels. External communications focus on stakeholders such as customers, investors, and partners to build brand reputation, trust, and market positioning. Tailoring content to these distinct audiences ensures effective information flow and relationship management.
Messaging Strategies for Internal vs External Audiences
Messaging strategies for internal communications prioritize clarity, consistency, and alignment with company values to foster employee engagement and organizational culture. External communications focus on brand image, customer trust, and market positioning through targeted messaging tailored to diverse audience segments. Effective messaging differentiates tone, language, and content complexity to resonate appropriately with internal staff versus external stakeholders.
Communication Channels: Internal vs External Platforms
Internal communications utilize platforms such as intranets, email, instant messaging, and collaboration tools like Microsoft Teams and Slack to facilitate information flow within an organization. External communications rely on channels including press releases, social media, official websites, and email marketing to engage customers, stakeholders, and the public. Choosing the appropriate internal or external communication platform enhances message clarity, audience targeting, and overall organizational effectiveness.
Role of Leadership in Communication Effectiveness
Leadership plays a critical role in communication effectiveness by setting the tone and modeling transparency in both internal and external communications. Effective leaders tailor messages to align with organizational goals, ensuring internal communications foster employee engagement and external communications enhance brand reputation. Strong leadership drives consistency, clarity, and trust, which are essential for successful communication strategies across all channels.
Measuring Success: KPIs for Internal and External Communications
Key performance indicators (KPIs) for internal communications focus on employee engagement metrics such as message reach, open rates, employee feedback scores, and participation in internal campaigns. External communications KPIs emphasize brand awareness, media share of voice, social media engagement, website traffic, and customer sentiment analysis. Tracking these metrics enables organizations to assess the effectiveness and alignment of communication strategies with business objectives.
Challenges and Risks in Internal and External Communications
Internal communications face challenges such as maintaining message consistency, ensuring confidentiality, and overcoming employee disengagement, which can lead to misunderstandings and reduced productivity. External communications carry risks related to brand reputation, public perception, and compliance with legal regulations, requiring careful message crafting to avoid misinformation and negative publicity. Both communication types demand strategic planning to manage information flow and protect organizational integrity effectively.
Best Practices for Integrating Internal and External Communications
Effective integration of internal and external communications requires consistent messaging aligned with the company's mission, values, and brand voice to ensure coherence across all channels. Utilizing collaborative platforms and feedback loops enhances transparency, fosters employee engagement, and improves information flow between internal teams and external audiences. Leveraging data analytics to monitor communication performance helps tailor strategies, optimize outreach, and maintain a unified narrative that strengthens organizational reputation.
Internal Communications vs External Communications Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com