Arms Control Inspectors specialize in verifying adherence to international arms control agreements by conducting inspections and assessments to prevent the proliferation of weapons. Arms Export Compliance Officers focus on ensuring that all arms exports comply with national laws and regulations, mitigating the risk of unauthorized or illegal transfers. Both roles are critical in maintaining global security, but the Inspector works on-site monitoring compliance, whereas the Compliance Officer manages export transactions and documentation.
Table of Comparison
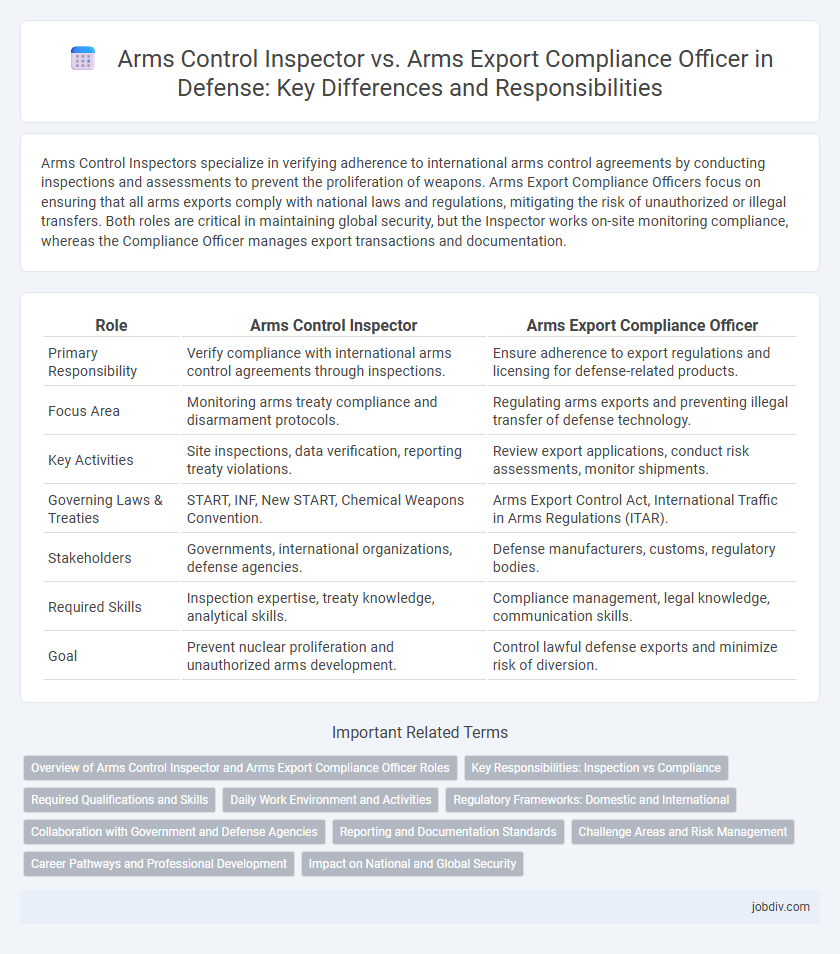
| Role | Arms Control Inspector | Arms Export Compliance Officer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Responsibility | Verify compliance with international arms control agreements through inspections. | Ensure adherence to export regulations and licensing for defense-related products. |
| Focus Area | Monitoring arms treaty compliance and disarmament protocols. | Regulating arms exports and preventing illegal transfer of defense technology. |
| Key Activities | Site inspections, data verification, reporting treaty violations. | Review export applications, conduct risk assessments, monitor shipments. |
| Governing Laws & Treaties | START, INF, New START, Chemical Weapons Convention. | Arms Export Control Act, International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR). |
| Stakeholders | Governments, international organizations, defense agencies. | Defense manufacturers, customs, regulatory bodies. |
| Required Skills | Inspection expertise, treaty knowledge, analytical skills. | Compliance management, legal knowledge, communication skills. |
| Goal | Prevent nuclear proliferation and unauthorized arms development. | Control lawful defense exports and minimize risk of diversion. |
Overview of Arms Control Inspector and Arms Export Compliance Officer Roles
Arms Control Inspectors conduct on-site inspections to verify compliance with international arms control agreements, ensuring the reduction and non-proliferation of weapons of mass destruction and conventional arms. Arms Export Compliance Officers oversee and enforce regulations related to the export of defense articles and technology, ensuring that all transactions comply with national and international laws such as the International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR). Both roles are critical in maintaining global security by preventing illicit arms trading and promoting transparency in defense-related activities.
Key Responsibilities: Inspection vs Compliance
Arms Control Inspectors conduct thorough onsite evaluations to verify adherence to international treaties and regulations, ensuring that weapons systems and related materials are accurately reported and secured. Arms Export Compliance Officers focus on enforcing domestic and international export laws by reviewing transactions, auditing documentation, and preventing unauthorized transfer of controlled defense articles. The inspector's role centers on physical verification and treaty compliance, while the compliance officer prioritizes regulatory oversight and legal conformity in arms export activities.
Required Qualifications and Skills
Arms Control Inspectors require expertise in international arms control treaties, proficiency in technical weapons systems analysis, and strong investigative skills to ensure compliance with regulations. Arms Export Compliance Officers must possess in-depth knowledge of export control laws, regulatory frameworks like ITAR and EAR, and adeptness in risk assessment to manage and oversee lawful arms exports. Both roles demand excellent attention to detail, analytical capabilities, and clear communication to enforce defense policies effectively.
Daily Work Environment and Activities
Arms Control Inspectors conduct on-site evaluations to verify compliance with international treaties, examining military installations and scrutinizing weapon inventories. Arms Export Compliance Officers oversee regulatory adherence in the transfer of defense materials, reviewing export documentation and coordinating with government agencies to prevent unauthorized distribution. Both roles demand detailed record-keeping, risk assessments, and collaboration with defense and intelligence personnel to ensure national security and legal compliance.
Regulatory Frameworks: Domestic and International
Arms Control Inspectors enforce regulatory frameworks established by international treaties such as the Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) and the Arms Trade Treaty (ATT), ensuring compliance with global disarmament agreements. Arms Export Compliance Officers focus on domestic export control laws like the International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) and the Export Administration Regulations (EAR), overseeing legal authorization for arms transfers. Both roles require thorough understanding of overlapping regulatory environments to prevent unauthorized proliferation and support national security objectives.
Collaboration with Government and Defense Agencies
Arms Control Inspectors collaborate closely with government and defense agencies to verify treaty compliance, conduct on-site inspections, and ensure disarmament protocols are followed accurately. Arms Export Compliance Officers work alongside these entities by monitoring and regulating the export of defense materials, ensuring adherence to national security laws and international agreements. Their joint efforts safeguard global security by enforcing strict controls on arms distribution and verifying lawful armament practices.
Reporting and Documentation Standards
Arms Control Inspectors adhere to rigorous reporting standards by producing detailed inspection reports that verify compliance with international treaties and arms agreements, ensuring transparency and enforcement accuracy. Arms Export Compliance Officers maintain comprehensive documentation related to export licenses, transaction records, and regulatory adherence to prevent unauthorized arms transfers and support audit trails. Both roles prioritize precise, verifiable records, but Inspectors focus on treaty verification while Compliance Officers emphasize export regulation enforcement.
Challenge Areas and Risk Management
Arms Control Inspectors face challenges in verifying treaty compliance, requiring meticulous documentation review and on-site inspections to mitigate risks of unauthorized weapon development. Arms Export Compliance Officers manage export license approvals and monitor shipment tracking to prevent illicit proliferation and sanctions violations. Both roles demand rigorous risk assessment frameworks to address operational security gaps and ensure adherence to international arms control agreements.
Career Pathways and Professional Development
Arms Control Inspectors specialize in monitoring and verifying treaty compliance, requiring expertise in international law, inspection protocols, and technical assessments, often advancing through roles in government agencies or international organizations. Arms Export Compliance Officers focus on ensuring that arms transactions adhere to national and international regulations, developing skills in export laws, policy interpretation, and risk management, with career growth commonly occurring within defense contractors, regulatory bodies, or corporate compliance departments. Both career pathways offer professional development through specialized training, certifications in arms control or export compliance, and opportunities to engage in policy development and international collaboration.
Impact on National and Global Security
Arms Control Inspectors verify adherence to international treaties, directly preventing the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction and enhancing global security frameworks. Arms Export Compliance Officers ensure that arms exports comply with national laws and international agreements, reducing the risk of unauthorized weapons transfers that could destabilize regions. Both roles are critical in maintaining national defense integrity and promoting global peace through stringent monitoring and enforcement.
Arms Control Inspector vs Arms Export Compliance Officer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com