Cyber Defense Analysts focus on identifying and mitigating cyber threats by analyzing security systems and incident data to protect digital assets. Information Assurance Analysts ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information by implementing policies and controls that safeguard data throughout its lifecycle. Both roles are critical in maintaining organizational cybersecurity, with Cyber Defense Analysts specializing in threat detection and response, while Information Assurance Analysts emphasize compliance and risk management.
Table of Comparison
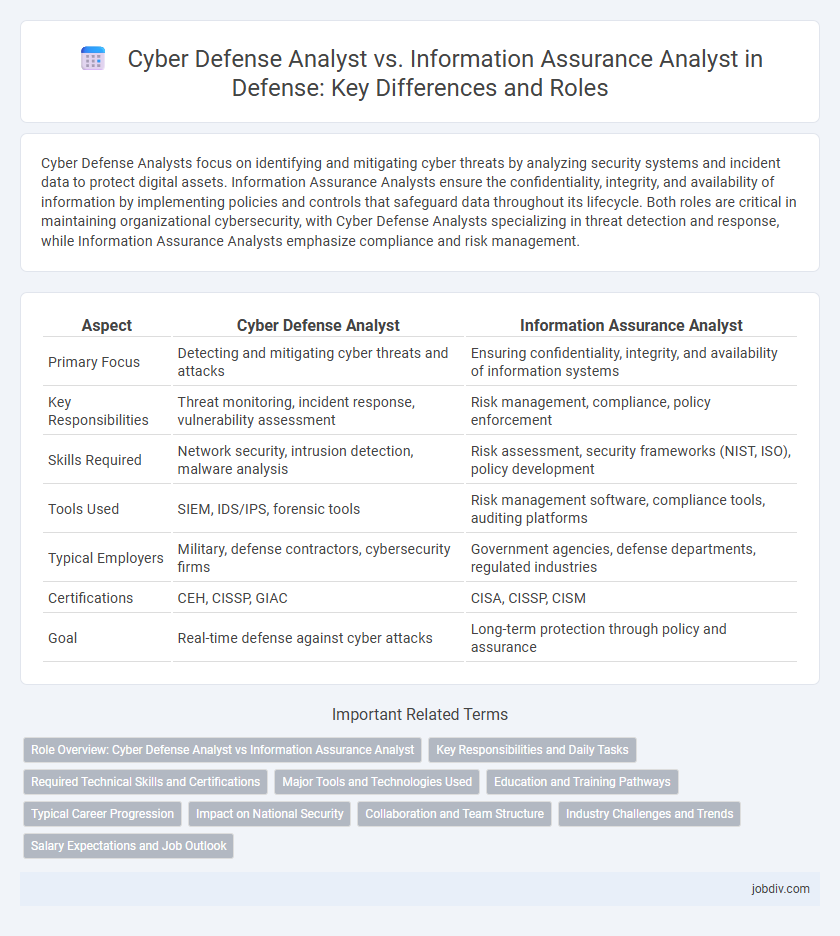
| Aspect | Cyber Defense Analyst | Information Assurance Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Detecting and mitigating cyber threats and attacks | Ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information systems |
| Key Responsibilities | Threat monitoring, incident response, vulnerability assessment | Risk management, compliance, policy enforcement |
| Skills Required | Network security, intrusion detection, malware analysis | Risk assessment, security frameworks (NIST, ISO), policy development |
| Tools Used | SIEM, IDS/IPS, forensic tools | Risk management software, compliance tools, auditing platforms |
| Typical Employers | Military, defense contractors, cybersecurity firms | Government agencies, defense departments, regulated industries |
| Certifications | CEH, CISSP, GIAC | CISA, CISSP, CISM |
| Goal | Real-time defense against cyber attacks | Long-term protection through policy and assurance |
Role Overview: Cyber Defense Analyst vs Information Assurance Analyst
A Cyber Defense Analyst monitors and responds to cyber threats by analyzing network traffic, identifying vulnerabilities, and implementing real-time security measures to prevent attacks. An Information Assurance Analyst focuses on ensuring data integrity, confidentiality, and availability by developing and enforcing security policies, conducting compliance audits, and managing risk assessments. Both roles are critical in protecting organizational information systems but differ in their approach--active threat mitigation versus strategic policy enforcement.
Key Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
Cyber Defense Analysts actively monitor network traffic and system logs to detect and respond to cyber threats, conduct vulnerability assessments, and implement security protocols to protect digital assets. Information Assurance Analysts focus on developing and enforcing policies related to data integrity, confidentiality, and compliance with regulatory standards, while regularly auditing systems to ensure adherence to security frameworks. Both roles collaborate to fortify organizational cybersecurity posture but emphasize proactive threat mitigation versus policy-driven risk management respectively.
Required Technical Skills and Certifications
Cyber Defense Analysts require expertise in network security, intrusion detection, malware analysis, and incident response, often holding certifications like CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker) and CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional). Information Assurance Analysts focus on risk management, compliance frameworks, and data protection, frequently obtaining certifications such as CISA (Certified Information Systems Auditor) and Security+. Both roles demand proficiency in cybersecurity tools and knowledge of standards like NIST and ISO 27001 to safeguard organizational assets.
Major Tools and Technologies Used
Cyber Defense Analysts primarily utilize intrusion detection systems (IDS) such as Snort and Suricata, Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) platforms like Splunk and IBM QRadar, alongside endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools including CrowdStrike and Carbon Black. Information Assurance Analysts frequently work with risk management frameworks (RMF), data loss prevention (DLP) technologies, encryption software like VeraCrypt, and compliance tools that facilitate adherence to standards such as NIST and ISO 27001. Both roles employ vulnerability assessment tools such as Nessus and Qualys but differ as Cyber Defense focuses on threat detection and response, while Information Assurance emphasizes policy enforcement and data integrity.
Education and Training Pathways
Cyber Defense Analysts typically require a bachelor's degree in cybersecurity, computer science, or information technology, with specialized certifications such as CISSP, CEH, or CompTIA Security+ enhancing their expertise in threat detection and incident response. Information Assurance Analysts often pursue degrees in information systems, cybersecurity, or risk management, complemented by certifications like CISA, CRISC, or CompTIA Security+ to focus on compliance, risk assessment, and policy enforcement. Both roles benefit from continuous training through cybersecurity bootcamps, government-sponsored programs, and hands-on experience with security frameworks and tools critical for protecting organizational assets.
Typical Career Progression
Cyber Defense Analysts typically advance from entry-level security monitoring roles to positions involving threat detection, incident response, and eventually senior analyst or cybersecurity manager roles, emphasizing hands-on defense strategies against cyber threats. Information Assurance Analysts often begin in compliance or risk assessment positions, progressing to roles centered on policy development, risk management, and certification and accreditation processes, eventually moving into senior information assurance or governance roles. Both career paths may converge at senior cybersecurity leadership positions, but Cyber Defense Analysts focus more on technical defense operations while Information Assurance Analysts concentrate on strategic risk and compliance frameworks.
Impact on National Security
Cyber Defense Analysts play a crucial role in national security by actively monitoring and mitigating cyber threats to protect critical infrastructure and defense systems from adversarial attacks. Information Assurance Analysts ensure the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of sensitive government data through rigorous risk management and compliance with security policies. Both roles are vital for safeguarding national defense capabilities, but Cyber Defense Analysts focus more on real-time threat response while Information Assurance Analysts concentrate on long-term data protection and policy enforcement.
Collaboration and Team Structure
Cyber Defense Analysts and Information Assurance Analysts collaborate closely within defense teams to identify threats, assess vulnerabilities, and implement robust security measures. Cyber Defense Analysts focus on real-time threat detection and incident response, while Information Assurance Analysts emphasize risk management, policy development, and compliance with security standards. Effective collaboration between these roles ensures a comprehensive cybersecurity posture by integrating operational defense tactics with strategic risk mitigation and governance frameworks.
Industry Challenges and Trends
Cyber Defense Analysts face challenges in real-time threat detection and response amid evolving cyberattack tactics, emphasizing advanced intrusion detection systems and machine learning integration. Information Assurance Analysts prioritize maintaining data integrity, compliance with regulatory frameworks like NIST and ISO 27001, and implementing comprehensive risk management strategies to safeguard sensitive defense information. Both roles must adapt to industry trends such as zero-trust architectures, AI-driven threat intelligence, and increasing emphasis on supply chain cybersecurity resilience.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Cyber Defense Analysts typically earn an average salary range between $75,000 and $110,000 annually, reflecting their role in protecting networks from cyber threats, while Information Assurance Analysts command salaries from $70,000 to $105,000, focusing on risk management and compliance. The job outlook for Cyber Defense Analysts is projected to grow faster than average, with a demand increase of approximately 32% over the next decade due to rising cyberattack threats. Information Assurance Analysts also experience strong growth, around 15%, driven by increasing regulatory requirements across industries seeking to safeguard sensitive information.
Cyber Defense Analyst vs Information Assurance Analyst Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com