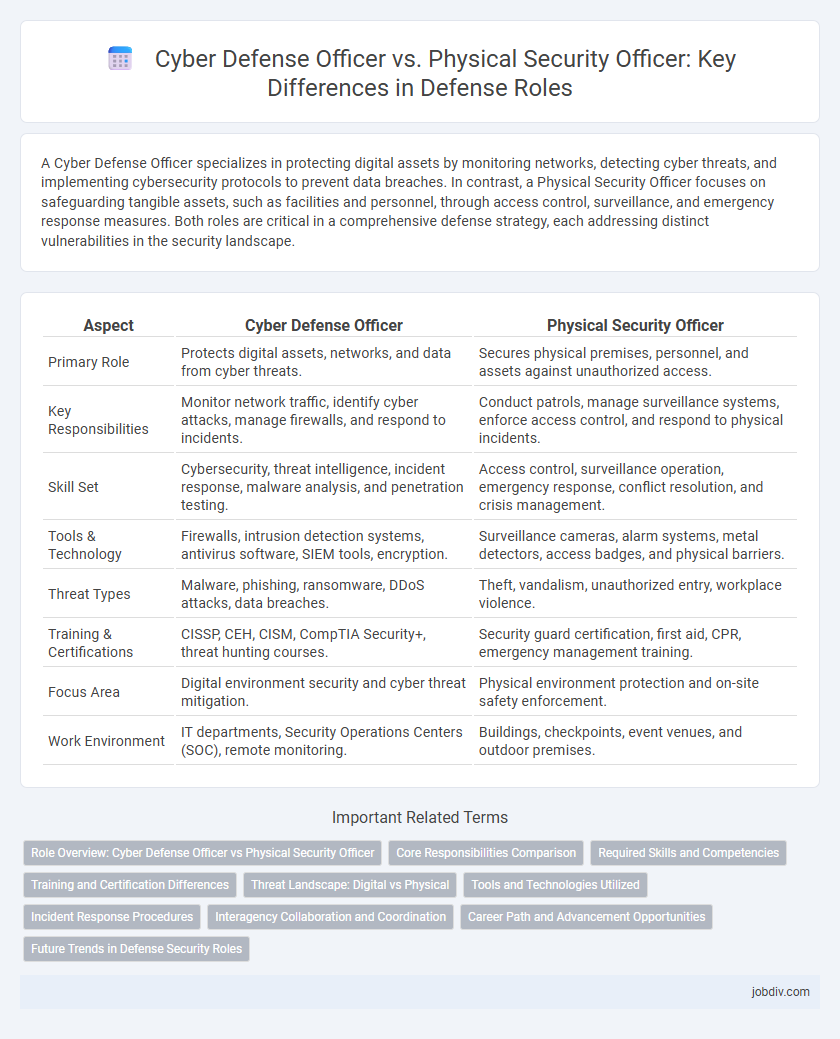
A Cyber Defense Officer specializes in protecting digital assets by monitoring networks, detecting cyber threats, and implementing cybersecurity protocols to prevent data breaches. In contrast, a Physical Security Officer focuses on safeguarding tangible assets, such as facilities and personnel, through access control, surveillance, and emergency response measures. Both roles are critical in a comprehensive defense strategy, each addressing distinct vulnerabilities in the security landscape.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Cyber Defense Officer | Physical Security Officer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Protects digital assets, networks, and data from cyber threats. | Secures physical premises, personnel, and assets against unauthorized access. |
| Key Responsibilities | Monitor network traffic, identify cyber attacks, manage firewalls, and respond to incidents. | Conduct patrols, manage surveillance systems, enforce access control, and respond to physical incidents. |
| Skill Set | Cybersecurity, threat intelligence, incident response, malware analysis, and penetration testing. | Access control, surveillance operation, emergency response, conflict resolution, and crisis management. |
| Tools & Technology | Firewalls, intrusion detection systems, antivirus software, SIEM tools, encryption. | Surveillance cameras, alarm systems, metal detectors, access badges, and physical barriers. |
| Threat Types | Malware, phishing, ransomware, DDoS attacks, data breaches. | Theft, vandalism, unauthorized entry, workplace violence. |
| Training & Certifications | CISSP, CEH, CISM, CompTIA Security+, threat hunting courses. | Security guard certification, first aid, CPR, emergency management training. |
| Focus Area | Digital environment security and cyber threat mitigation. | Physical environment protection and on-site safety enforcement. |
| Work Environment | IT departments, Security Operations Centers (SOC), remote monitoring. | Buildings, checkpoints, event venues, and outdoor premises. |
Role Overview: Cyber Defense Officer vs Physical Security Officer
Cyber Defense Officers specialize in protecting an organization's digital assets by monitoring network traffic, detecting cyber threats, and implementing security protocols against hacking, malware, and data breaches. Physical Security Officers focus on safeguarding personnel, facilities, and physical assets through access control, surveillance, and emergency response measures. Both roles require collaboration to ensure comprehensive security, integrating cyber defense strategies with physical security operations to mitigate risks effectively.
Core Responsibilities Comparison
Cyber Defense Officers specialize in protecting digital assets, securing networks, monitoring threats, and responding to cyberattacks through advanced technologies like firewalls and intrusion detection systems. Physical Security Officers focus on safeguarding personnel, facilities, and physical assets by managing access control, surveillance systems, and emergency response protocols. Both roles require risk assessment and incident management, but Cyber Defense Officers emphasize cybersecurity strategies while Physical Security Officers prioritize tangible security measures.
Required Skills and Competencies
Cyber Defense Officers require advanced expertise in network security protocols, intrusion detection systems, and threat intelligence analysis to counteract sophisticated cyber attacks. Physical Security Officers must demonstrate strong situational awareness, emergency response skills, and proficiency in surveillance technologies to protect personnel and facilities. Both roles demand critical thinking, risk assessment capabilities, and effective communication for coordinated defense strategies.
Training and Certification Differences
Cyber Defense Officers typically undergo specialized training in information security, network defense, and cyber threat intelligence, often obtaining certifications such as CISSP, CEH, or CompTIA Security+. Physical Security Officers receive training focused on access control, surveillance systems, emergency response, and physical risk assessment, with certifications like CPP (Certified Protection Professional) or PSP (Physical Security Professional). The divergence in training and certification reflects the distinct operational environments and skill sets required for cyber versus physical security roles.
Threat Landscape: Digital vs Physical
Cyber Defense Officers specialize in identifying and mitigating digital threats such as malware, phishing, and network intrusions, operating within an ever-evolving cyber threat landscape driven by advanced persistent threats and zero-day vulnerabilities. Physical Security Officers focus on protecting assets against tangible risks like unauthorized access, theft, and sabotage, managing threats including insider threats, perimeter breaches, and physical attacks. The digital threat environment demands continuous monitoring of cyber intelligence and rapid incident response, whereas physical security relies on surveillance, access control, and emergency preparedness to counteract physical intrusions.
Tools and Technologies Utilized
Cyber Defense Officers utilize advanced threat detection software, intrusion prevention systems, and encryption technologies to protect digital infrastructure from cyberattacks. Physical Security Officers rely on surveillance cameras, biometric access control systems, and alarm monitoring tools to safeguard physical premises and personnel. Both roles employ specialized technology tailored to their domain, with Cyber Defense focusing on network security platforms and Physical Security emphasizing hardware-based protection systems.
Incident Response Procedures
Cyber Defense Officers implement incident response procedures that prioritize rapid identification, containment, and remediation of cyber threats such as malware, phishing, and network intrusions, utilizing advanced cybersecurity tools and threat intelligence platforms. Physical Security Officers focus on incident response protocols involving unauthorized access, physical breaches, and emergency evacuations by coordinating with law enforcement and employing surveillance systems and access control measures. Both roles require detailed incident documentation and communication to ensure threat mitigation and continuity of defense operations.
Interagency Collaboration and Coordination
Cyber Defense Officers specialize in securing digital infrastructure by collaborating with intelligence agencies and cybersecurity task forces to share threat intelligence and coordinate incident responses. Physical Security Officers work closely with law enforcement, military units, and emergency responders to implement coordinated perimeter security and access control measures. Effective interagency collaboration between these roles enhances overall defense posture by integrating cyber and physical security strategies to protect critical assets.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
Cyber Defense Officers typically progress by gaining expertise in network security, threat analysis, and incident response, advancing into roles such as cybersecurity manager or chief information security officer (CISO). Physical Security Officers often move into supervisory positions overseeing security operations, risk management, or facility protection, with potential advancement to security director or corporate security manager. Both career paths offer growth through specialized certifications, leadership experience, and sector-specific knowledge, but Cyber Defense Officers benefit from the rapid evolution of technology and increasing cyber threats driving demand.
Future Trends in Defense Security Roles
Cyber Defense Officers will increasingly leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning to predict and counter sophisticated cyber threats, while Physical Security Officers will integrate advanced surveillance technologies such as biometric sensors and autonomous drones to safeguard critical infrastructure. The convergence of cyber and physical security domains will create hybrid roles requiring expertise in both digital threat intelligence and on-site tactical response. Emerging defense strategies emphasize continuous real-time monitoring, automated threat detection, and rapid incident response to enhance overall security posture against evolving multi-vector attacks.
Cyber Defense Officer vs Physical Security Officer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com