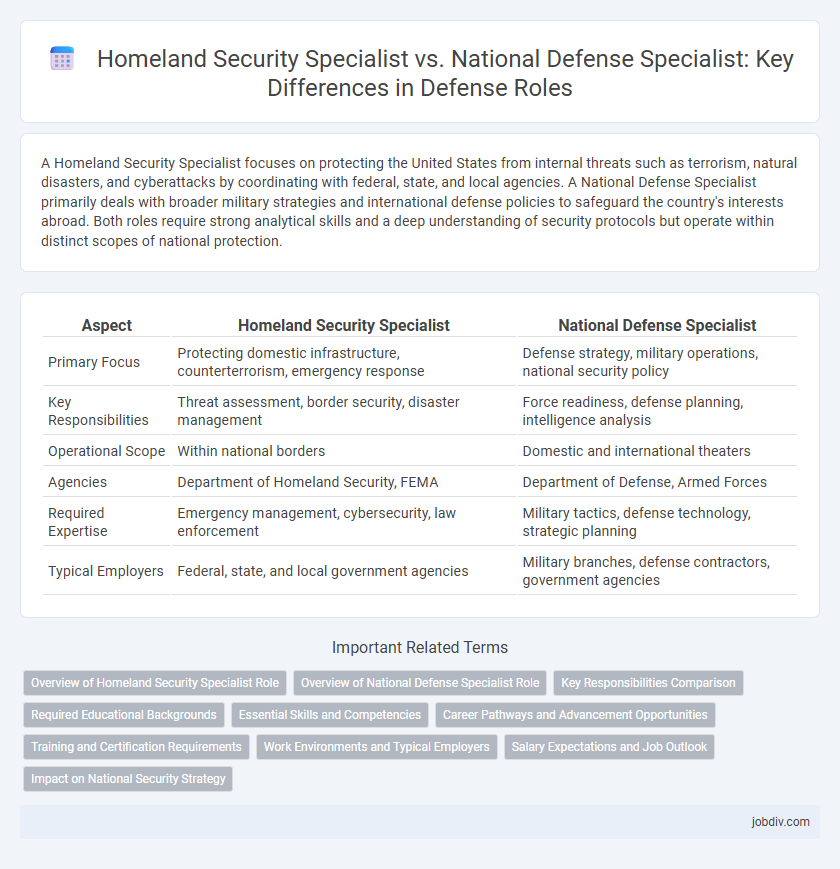
A Homeland Security Specialist focuses on protecting the United States from internal threats such as terrorism, natural disasters, and cyberattacks by coordinating with federal, state, and local agencies. A National Defense Specialist primarily deals with broader military strategies and international defense policies to safeguard the country's interests abroad. Both roles require strong analytical skills and a deep understanding of security protocols but operate within distinct scopes of national protection.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Homeland Security Specialist | National Defense Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Protecting domestic infrastructure, counterterrorism, emergency response | Defense strategy, military operations, national security policy |
| Key Responsibilities | Threat assessment, border security, disaster management | Force readiness, defense planning, intelligence analysis |
| Operational Scope | Within national borders | Domestic and international theaters |
| Agencies | Department of Homeland Security, FEMA | Department of Defense, Armed Forces |
| Required Expertise | Emergency management, cybersecurity, law enforcement | Military tactics, defense technology, strategic planning |
| Typical Employers | Federal, state, and local government agencies | Military branches, defense contractors, government agencies |
Overview of Homeland Security Specialist Role
A Homeland Security Specialist focuses on protecting the nation from domestic threats such as terrorism, natural disasters, and cyber-attacks, ensuring public safety through intelligence analysis and emergency preparedness. This role involves collaboration with federal, state, and local agencies to develop and implement security protocols and response strategies. Expertise in risk assessment, threat detection, and crisis management is critical to maintaining the integrity of homeland security operations.
Overview of National Defense Specialist Role
National Defense Specialists play a critical role in formulating strategies to protect a nation's security through comprehensive threat assessments and defense policy development. They coordinate with military, intelligence, and government agencies to enhance national defense capabilities against conventional and unconventional threats. Their expertise supports decision-making processes that ensure the safeguarding of territorial integrity and critical infrastructure.
Key Responsibilities Comparison
Homeland Security Specialists primarily focus on protecting the United States from domestic threats by analyzing intelligence, coordinating emergency response efforts, and implementing border security measures. National Defense Specialists emphasize strategic military planning, defense policy development, and the management of armed forces to ensure national security against external threats. Both roles require expertise in threat assessment and interagency collaboration, but Homeland Security Specialists concentrate on internal threat mitigation while National Defense Specialists focus on external defense strategies.
Required Educational Backgrounds
Homeland Security Specialists typically require a bachelor's degree in criminal justice, public administration, or homeland security, emphasizing counterterrorism and emergency management. National Defense Specialists often hold degrees in political science, international relations, or military science, focusing on defense policy and strategic military operations. Advanced certifications or security clearances are commonly needed for both roles to handle sensitive national security information.
Essential Skills and Competencies
Homeland Security Specialists excel in risk assessment, emergency preparedness, and interagency coordination, ensuring effective threat detection and response within national borders. National Defense Specialists demonstrate expertise in strategic planning, military operations, and intelligence analysis to safeguard national sovereignty and support defense objectives. Both roles require critical thinking, communication skills, and knowledge of federal regulations, but Homeland Security focuses more on domestic protection, whereas National Defense emphasizes military strategy and international security.
Career Pathways and Advancement Opportunities
Homeland Security Specialists primarily engage in protecting the nation from domestic threats, focusing on emergency preparedness, cybersecurity, and counterterrorism, which opens career pathways in federal agencies such as the Department of Homeland Security, FEMA, and the TSA. National Defense Specialists focus on broader military and strategic defense operations, offering advancement opportunities within the Department of Defense, intelligence agencies, and defense contractors. Both career paths demand specialized training but differ in scope, with Homeland Security emphasizing civil protection and National Defense centering on military readiness and strategic defense initiatives.
Training and Certification Requirements
Homeland Security Specialists typically require certification in emergency management, cybersecurity, and counterterrorism, with extensive training in threat assessment and incident response protocols. National Defense Specialists often undergo rigorous military training, including strategic defense planning, intelligence analysis, and advanced weapons systems certification. Both roles demand continuous professional development to stay updated with evolving security threats and defense technologies.
Work Environments and Typical Employers
Homeland Security Specialists primarily operate within federal agencies such as the Department of Homeland Security, Customs and Border Protection, and FEMA, emphasizing roles in emergency management, border security, and counterterrorism. National Defense Specialists are commonly employed by the Department of Defense, military branches, and defense contractors, focusing on strategic defense planning, intelligence analysis, and military operations. Both specialists often work in high-security government facilities, command centers, and field environments requiring coordination with multiple agencies to safeguard national interests.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Homeland Security Specialists typically earn an average salary ranging from $70,000 to $95,000 annually, with job growth projected at 5% over the next decade due to increasing domestic security needs. National Defense Specialists often command higher salaries, averaging between $80,000 and $110,000, driven by a growing demand for expertise in military strategy and defense technologies. Both career paths offer stable job outlooks, but National Defense Specialists may experience stronger growth in government and private defense contractor sectors.
Impact on National Security Strategy
Homeland Security Specialists concentrate on protecting critical infrastructure, counterterrorism, and emergency response, directly influencing the implementation of domestic security measures. National Defense Specialists focus on military strategy, defense policy, and international threat assessment, shaping broader defense initiatives and strategic military operations. Both roles are essential for a comprehensive national security strategy, integrating internal safety measures with external defense preparedness.
Homeland Security Specialist vs National Defense Specialist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com