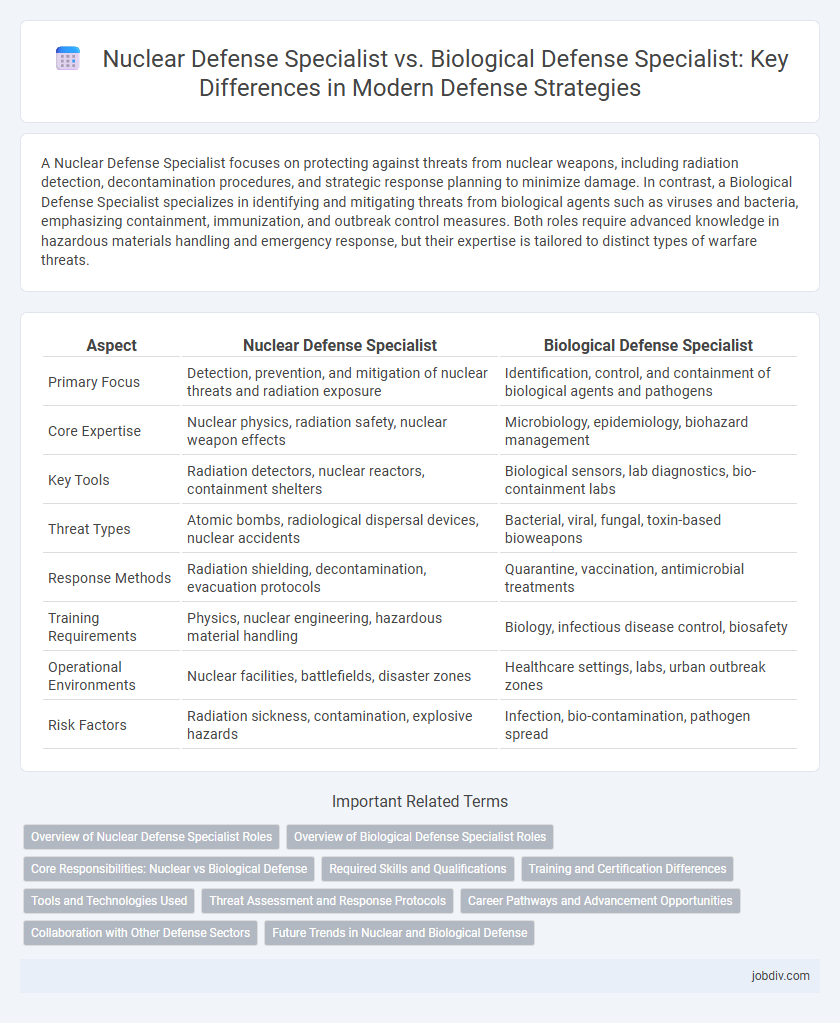
A Nuclear Defense Specialist focuses on protecting against threats from nuclear weapons, including radiation detection, decontamination procedures, and strategic response planning to minimize damage. In contrast, a Biological Defense Specialist specializes in identifying and mitigating threats from biological agents such as viruses and bacteria, emphasizing containment, immunization, and outbreak control measures. Both roles require advanced knowledge in hazardous materials handling and emergency response, but their expertise is tailored to distinct types of warfare threats.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Nuclear Defense Specialist | Biological Defense Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Detection, prevention, and mitigation of nuclear threats and radiation exposure | Identification, control, and containment of biological agents and pathogens |
| Core Expertise | Nuclear physics, radiation safety, nuclear weapon effects | Microbiology, epidemiology, biohazard management |
| Key Tools | Radiation detectors, nuclear reactors, containment shelters | Biological sensors, lab diagnostics, bio-containment labs |
| Threat Types | Atomic bombs, radiological dispersal devices, nuclear accidents | Bacterial, viral, fungal, toxin-based bioweapons |
| Response Methods | Radiation shielding, decontamination, evacuation protocols | Quarantine, vaccination, antimicrobial treatments |
| Training Requirements | Physics, nuclear engineering, hazardous material handling | Biology, infectious disease control, biosafety |
| Operational Environments | Nuclear facilities, battlefields, disaster zones | Healthcare settings, labs, urban outbreak zones |
| Risk Factors | Radiation sickness, contamination, explosive hazards | Infection, bio-contamination, pathogen spread |
Overview of Nuclear Defense Specialist Roles
Nuclear Defense Specialists are responsible for detecting, analyzing, and mitigating threats related to nuclear weapons and radiological materials, ensuring national security against potential nuclear attacks or accidents. Their expertise includes radiation detection technologies, nuclear forensics, emergency response coordination, and implementation of defense protocols to protect military personnel and civilians. These specialists work closely with intelligence agencies, military units, and emergency management teams to develop strategies for nuclear threat prevention and response.
Overview of Biological Defense Specialist Roles
Biological Defense Specialists focus on detecting, monitoring, and responding to biological threats such as pathogens and biotoxins, ensuring public safety through advanced surveillance and containment strategies. They develop and implement biosecurity measures, coordinate with health agencies, and conduct research on biodefense technologies to mitigate risks posed by biological warfare. Their expertise encompasses epidemic modeling, rapid diagnostics, and emergency preparedness to protect military personnel and civilian populations from biological hazards.
Core Responsibilities: Nuclear vs Biological Defense
Nuclear Defense Specialists focus on detecting, preventing, and mitigating nuclear threats, including radiological monitoring, nuclear weapon threat assessment, and blast impact analysis. Biological Defense Specialists concentrate on identifying, containing, and countering biological hazards through pathogen detection, epidemic modeling, and biosecurity protocol implementation. Both roles require expertise in threat assessment and emergency response but differ in the nature of their specialized containment and mitigation techniques.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Nuclear Defense Specialists require expertise in radiological science, nuclear physics, and radiation detection technologies, alongside certifications in hazardous material handling and emergency response protocols. Biological Defense Specialists must have a strong background in microbiology, epidemiology, and biohazard containment, with qualifications in biosafety levels and infectious disease control. Both fields demand rigorous training in defense strategies, risk assessment, and coordination with government agencies for effective threat mitigation.
Training and Certification Differences
Nuclear Defense Specialists undergo rigorous training in radiation safety, nuclear weapons effects, and emergency response protocols, often requiring certifications like the Nuclear Certified Professional (NCP) and Nuclear Emergency Response Operator (NERO). Biological Defense Specialists focus on pathogen identification, biosafety levels, and biohazard containment procedures, with certifications such as Certified Biological Safety Professional (CBSP) and training in detection technologies for bioterrorism threats. The key distinction lies in nuclear specialists emphasizing radiological hazard mitigation, while biological specialists concentrate on microbial threat management and containment.
Tools and Technologies Used
Nuclear Defense Specialists utilize advanced radiation detection instruments, such as Geiger counters and spectrometers, alongside nuclear forensics tools to identify and mitigate radiological threats. Biological Defense Specialists deploy biosensors, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) machines, and advanced immunoassay technologies to detect and analyze pathogenic agents rapidly. Both fields heavily rely on protective gear, specialized containment units, and real-time monitoring systems tailored to their specific threat environments.
Threat Assessment and Response Protocols
Nuclear Defense Specialists concentrate on threat assessment involving radiological dispersion devices, nuclear weapon development intelligence, and electromagnetic pulse impacts, implementing response protocols that prioritize radiation containment, evacuation, and decontamination measures. Biological Defense Specialists analyze pathogenic threat vectors, bioagent dissemination tactics, and incubation periods, deploying response protocols focused on quarantine enforcement, mass prophylaxis, and medical countermeasure distribution. Both roles require continuous intelligence integration and coordination with national security agencies to adapt defense strategies against evolving nuclear and biological threats.
Career Pathways and Advancement Opportunities
Nuclear Defense Specialists often follow career pathways that include roles in nuclear threat assessment, radiation monitoring, and strategic defense planning, with advancement opportunities in government agencies like the Department of Defense and the Nuclear Regulatory Commission. Biological Defense Specialists typically advance through careers involving biohazard risk analysis, infectious disease containment, and bioterrorism response, progressing to senior positions within organizations such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Department of Homeland Security. Both specialties require continuous education and certifications, with leadership roles demanding expertise in emerging technologies and interdisciplinary collaboration.
Collaboration with Other Defense Sectors
Nuclear Defense Specialists collaborate extensively with cyber defense teams and emergency response units to ensure integrated threat detection and rapid containment of radiological hazards. Biological Defense Specialists engage closely with public health agencies and environmental monitoring units to coordinate early warning systems and effective outbreak mitigation strategies. Cross-sector collaboration enhances overall national security by combining expertise in nuclear and biological threat management.
Future Trends in Nuclear and Biological Defense
Future trends in nuclear defense emphasize advanced detection technologies, such as AI-powered radiation sensors and space-based early warning systems, enhancing threat identification and response speed. In biological defense, innovations focus on rapid pathogen detection through genomic sequencing and AI-driven predictive modeling to anticipate outbreaks and develop countermeasures. Integration of cyber-physical systems and cross-domain intelligence sharing is becoming critical in both fields to improve resilience against evolving nuclear and biological threats.
Nuclear Defense Specialist vs Biological Defense Specialist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com