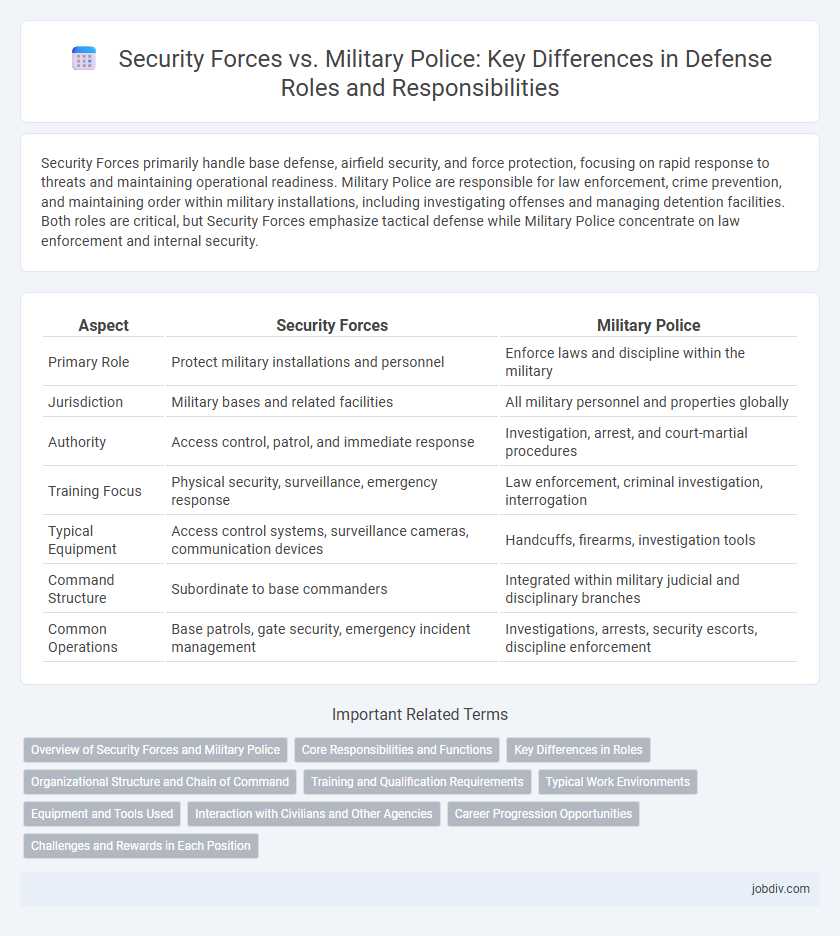
Security Forces primarily handle base defense, airfield security, and force protection, focusing on rapid response to threats and maintaining operational readiness. Military Police are responsible for law enforcement, crime prevention, and maintaining order within military installations, including investigating offenses and managing detention facilities. Both roles are critical, but Security Forces emphasize tactical defense while Military Police concentrate on law enforcement and internal security.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Security Forces | Military Police |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Protect military installations and personnel | Enforce laws and discipline within the military |
| Jurisdiction | Military bases and related facilities | All military personnel and properties globally |
| Authority | Access control, patrol, and immediate response | Investigation, arrest, and court-martial procedures |
| Training Focus | Physical security, surveillance, emergency response | Law enforcement, criminal investigation, interrogation |
| Typical Equipment | Access control systems, surveillance cameras, communication devices | Handcuffs, firearms, investigation tools |
| Command Structure | Subordinate to base commanders | Integrated within military judicial and disciplinary branches |
| Common Operations | Base patrols, gate security, emergency incident management | Investigations, arrests, security escorts, discipline enforcement |
Overview of Security Forces and Military Police
Security Forces are specialized units responsible for safeguarding military installations, personnel, and critical assets through comprehensive perimeter defense, access control, and rapid response capabilities. Military Police perform law enforcement within military jurisdictions, focusing on maintaining discipline, investigating crimes, managing prisoners of war, and traffic control on military property. Both entities play integral roles in operational security, with Security Forces emphasizing external protection and Military Police concentrating on internal order and legal enforcement.
Core Responsibilities and Functions
Security Forces specialize in base defense, force protection, and combat arms operations, ensuring overall installation security and rapid response to threats. Military Police focus on law enforcement, criminal investigations, and maintaining order within military installations through patrols and detainee operations. Both entities collaborate to uphold safety and discipline, but their core functions distinctly address external defense versus internal security enforcement.
Key Differences in Roles
Security Forces primarily handle the protection of critical infrastructure, perform law enforcement duties on military installations, and ensure force security during deployment. Military Police focus on law enforcement, criminal investigations, detainee operations, and maintaining order within the armed forces. While both units support military operations, Security Forces are centered on base defense and external threats, whereas Military Police emphasize internal law enforcement and discipline.
Organizational Structure and Chain of Command
Security Forces operate within a broader defense organizational structure emphasizing base security, force protection, and law enforcement duties, typically under an Air Force or similar service branch. Military Police are specialized units within the Army or other military branches with responsibilities including battlefield law enforcement, detainee operations, and convoy security. The chain of command for Security Forces often falls under a base or installation commander with operational control centralized at the service branch level, while Military Police maintain a dual chain of command involving both military law enforcement leadership and operational commanders in deployed environments.
Training and Qualification Requirements
Security Forces personnel undergo comprehensive training emphasizing base defense, force protection, and law enforcement tasks tailored to safeguard critical military assets, while Military Police receive rigorous instruction in criminal investigations, detainee operations, and law enforcement authority on installations. Security Forces training programs often include weapons proficiency, tactical response, and emergency management to prepare members for combat support roles, whereas Military Police focus more extensively on legal procedures, evidence handling, and jurisdictional enforcement. Both forces require physical fitness standards and continuous professional development, but Military Police must also attain certifications related to military law and order maintenance.
Typical Work Environments
Security Forces typically operate in fixed installations such as air bases, military compounds, and critical infrastructure sites, ensuring perimeter security and access control. Military Police are often deployed in diverse environments including active combat zones, military operational areas, and detention facilities, focusing on law enforcement, investigations, and detainee management. Both forces maintain operational readiness but differ in their primary settings and specific mission scopes within defense structures.
Equipment and Tools Used
Security Forces utilize a broad range of tactical gear including advanced surveillance systems, assault rifles, and non-lethal crowd control tools designed for versatile operational environments. Military Police are equipped with standard-issue sidearms, riot control equipment, and communication devices tailored for law enforcement and detention facility operations. Both forces employ body armor and vehicle-mounted support systems, but Security Forces prioritize combat readiness while Military Police focus on maintaining order and discipline within military installations.
Interaction with Civilians and Other Agencies
Security forces prioritize community engagement and maintain public order through continuous interaction with civilians, fostering trust and cooperation. Military police operate primarily within military environments, enforcing discipline and law among service members while coordinating with civilian law enforcement during joint operations. Collaboration between security forces and military police ensures seamless communication and effective responses in both civilian and military contexts.
Career Progression Opportunities
Security Forces personnel often experience more diverse career progression opportunities within combat support and specialized operational roles, enhancing skills in cybersecurity, crisis response, and base defense management. Military Police careers typically advance through law enforcement leadership, criminal investigation expertise, and corrections management, providing pathways to senior management and federal law enforcement integration. Both paths offer structured promotion systems, but Security Forces emphasize tactical and technical proficiency, while Military Police focus on legal enforcement and investigative competencies.
Challenges and Rewards in Each Position
Security Forces personnel face challenges such as maintaining base perimeter security and responding to diverse threats that require constant vigilance and rapid decision-making, demanding physical endurance and adaptability. Military Police encounter complex law enforcement duties including investigations, detainee operations, and enforcing military law under high-stress situations, which develop critical judgment and leadership skills. Both positions offer rewards in terms of specialized training, career advancement opportunities, and the fulfillment derived from protecting personnel and assets within the defense community.
Security Forces vs Military Police Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com