Graphic designers specialize in creating visuals that communicate messages through typography, imagery, and layout, often focusing on print and digital media. Visual designers emphasize the overall aesthetic and user experience of digital interfaces, integrating branding elements with functionality to create cohesive designs. Both roles require creativity and technical skills, but visual designers typically engage more with user interface and interaction design aspects.
Table of Comparison
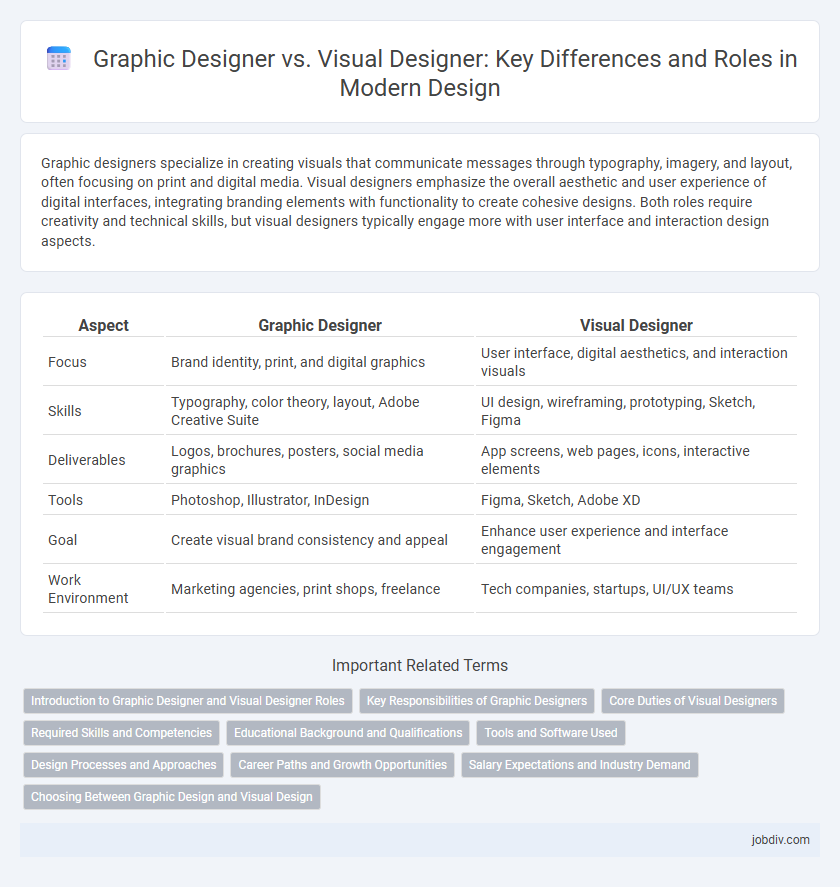
| Aspect | Graphic Designer | Visual Designer |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Brand identity, print, and digital graphics | User interface, digital aesthetics, and interaction visuals |
| Skills | Typography, color theory, layout, Adobe Creative Suite | UI design, wireframing, prototyping, Sketch, Figma |
| Deliverables | Logos, brochures, posters, social media graphics | App screens, web pages, icons, interactive elements |
| Tools | Photoshop, Illustrator, InDesign | Figma, Sketch, Adobe XD |
| Goal | Create visual brand consistency and appeal | Enhance user experience and interface engagement |
| Work Environment | Marketing agencies, print shops, freelance | Tech companies, startups, UI/UX teams |
Introduction to Graphic Designer and Visual Designer Roles
Graphic designers create visual content using typography, imagery, and color to communicate messages effectively across print and digital media. Visual designers focus on the overall aesthetics and user interface of digital products, integrating branding, layout, and interactive elements to enhance user experience. Both roles require strong design principles but differ in their emphasis on static visuals versus interactive digital environments.
Key Responsibilities of Graphic Designers
Graphic designers focus on creating compelling visual content by combining typography, images, and color to communicate messages effectively across print and digital media. They develop branding materials, marketing collateral, brochures, logos, and advertisements tailored to target audiences. Expertise in software such as Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, and InDesign is essential for producing high-quality graphics that align with client objectives and enhance brand identity.
Core Duties of Visual Designers
Visual designers primarily focus on creating cohesive visual elements that enhance user experience through typography, color theory, and layout design. They translate complex ideas into visually appealing interfaces, balancing aesthetics with functionality to support branding and user engagement. Their core duties include designing user interface components, ensuring consistency across digital platforms, and collaborating closely with UX designers to refine interaction flows.
Required Skills and Competencies
Graphic designers excel in visual communication through mastery of typography, color theory, and software like Adobe Photoshop and Illustrator, emphasizing print and digital media. Visual designers combine graphic design skills with user experience (UX) knowledge, requiring competencies in wireframing, prototyping, and understanding user interface (UI) principles to create cohesive digital product aesthetics. Proficiency in creativity, attention to detail, and collaboration with marketing and development teams is essential for both roles to ensure impactful design solutions.
Educational Background and Qualifications
Graphic Designers typically hold degrees in graphic design, visual communication, or related fields, emphasizing skills in typography, color theory, and software like Adobe Creative Suite. Visual Designers often possess a broader educational background that includes graphic design, UI/UX design, or multimedia arts, combining traditional design principles with interactive and digital media knowledge. Certifications in user experience, prototyping tools, and web technologies further enhance a visual designer's qualifications, aligning them with both aesthetic and functional design requirements.
Tools and Software Used
Graphic designers primarily use Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, and InDesign to create logos, brochures, and print materials, emphasizing pixel-based and vector graphics. Visual designers incorporate these tools but also rely heavily on UX/UI software like Sketch, Figma, and Adobe XD to design interactive digital interfaces and enhance user experience. Mastery of both traditional graphic tools and modern web design platforms differentiates visual designers from graphic designers in their approach to digital and print media.
Design Processes and Approaches
Graphic designers primarily focus on creating visual content through typography, imagery, and color to communicate specific messages, employing a process rooted in concept development and brand alignment. Visual designers adopt a broader approach that integrates user experience principles, interactive elements, and digital interfaces, emphasizing clarity and functionality across multiple platforms. Both roles utilize iterative design processes, wireframing, and prototyping, but visual designers often incorporate user research and usability testing to refine their solutions.
Career Paths and Growth Opportunities
Graphic designers typically focus on creating visual content for print and digital media, specializing in branding, advertising, and layout design, which offers diverse career opportunities in agencies, publishing, and marketing departments. Visual designers emphasize user interface and experience design for digital platforms, often progressing towards roles in UX/UI design, product design, or creative direction within tech companies and startups. Both career paths offer growth through skill expansion in software tools, industry trends, and interdisciplinary collaboration, with visual design increasingly emphasizing digital proficiency and user-centered approaches.
Salary Expectations and Industry Demand
Graphic designers typically earn between $45,000 and $65,000 annually, reflecting steady demand in advertising, publishing, and digital media sectors. Visual designers command higher salaries, ranging from $60,000 to $85,000, due to their broader skill set in user interface and brand experience design, driving strong demand in tech and e-commerce industries. Industry projections indicate a 10% growth for graphic designers and a 13% growth for visual designers over the next decade, highlighting increased investment in digital user engagement and visual storytelling.
Choosing Between Graphic Design and Visual Design
Choosing between graphic design and visual design depends on project goals and skill sets; graphic design emphasizes creating visual content for print and digital media, focusing on typography, color theory, and branding. Visual design encompasses broader elements like user interface, interaction, and overall user experience, integrating graphic design principles with digital functionality. Understanding these distinctions aids professionals and clients in selecting the right designer to enhance communication and engagement through tailored visual solutions.
Graphic Designer vs Visual Designer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com