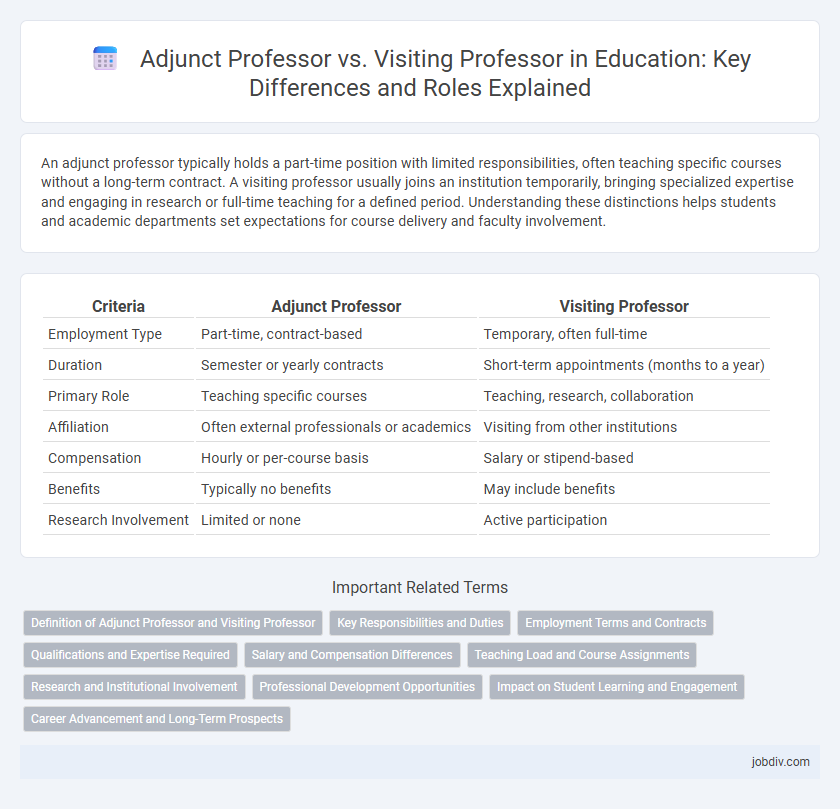
An adjunct professor typically holds a part-time position with limited responsibilities, often teaching specific courses without a long-term contract. A visiting professor usually joins an institution temporarily, bringing specialized expertise and engaging in research or full-time teaching for a defined period. Understanding these distinctions helps students and academic departments set expectations for course delivery and faculty involvement.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Adjunct Professor | Visiting Professor |
|---|---|---|
| Employment Type | Part-time, contract-based | Temporary, often full-time |
| Duration | Semester or yearly contracts | Short-term appointments (months to a year) |
| Primary Role | Teaching specific courses | Teaching, research, collaboration |
| Affiliation | Often external professionals or academics | Visiting from other institutions |
| Compensation | Hourly or per-course basis | Salary or stipend-based |
| Benefits | Typically no benefits | May include benefits |
| Research Involvement | Limited or none | Active participation |
Definition of Adjunct Professor and Visiting Professor
An Adjunct Professor is a part-time instructor hired on a contractual basis, typically without tenure, who brings specialized expertise to complement full-time faculty. A Visiting Professor is a temporary faculty member, often from another institution, appointed for a limited period to teach or conduct research, usually possessing substantial academic credentials. Both roles enhance educational offerings but differ in employment terms and duration.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
Adjunct Professors typically teach part-time courses with a primary focus on delivering specialized knowledge and practical skills, often bringing industry experience to the classroom without engaging in extensive research or administrative duties. Visiting Professors are usually appointed temporarily to contribute specific expertise, conduct research, and participate in academic collaboration, while often playing a more active role in curriculum development and faculty committees. Both roles enhance educational offerings, but Visiting Professors carry broader responsibilities beyond instruction, including mentoring students and advancing institutional research goals.
Employment Terms and Contracts
Adjunct Professors typically work part-time with contracts based on course-by-course or semester-to-semester agreements, often lacking long-term job security and benefits. Visiting Professors are usually appointed for a fixed term, such as one academic year, with full-time or part-time contracts that may include salary and institutional privileges similar to regular faculty. Employment terms for visiting professors often emphasize temporary research or teaching assignments funded by the host institution, contrasting with the contingent status and limited contractual duration of adjunct positions.
Qualifications and Expertise Required
Adjunct Professors typically hold a master's or doctoral degree and possess specialized industry experience, allowing them to teach part-time while maintaining professional careers outside academia. Visiting Professors are usually full-time faculty members from other institutions with established academic credentials, often including published research and advanced scholarly expertise, appointed temporarily to bring specialized knowledge to the host university. Both roles require subject-matter proficiency, but Visiting Professors often demonstrate a higher level of academic distinction and research accomplishments.
Salary and Compensation Differences
Adjunct professors typically receive lower salaries and limited benefits compared to visiting professors, often paid on a per-course basis without long-term job security. Visiting professors usually receive a fixed salary with additional compensation such as research stipends, housing allowances, and sometimes health benefits, reflecting their temporary but full-time roles. Salary differences are influenced by contract length, institution type, and academic field, with visiting professors generally earning more due to their specialized expertise and temporary appointments.
Teaching Load and Course Assignments
Adjunct Professors typically balance a heavier teaching load with multiple course assignments across semesters, often working part-time without research obligations. Visiting Professors usually have a lighter teaching load focused on specialized courses aligned with their expertise, often for a limited term or sabbatical replacement. Course assignments for adjuncts lean toward general curriculum needs, while visiting professors contribute to advanced or niche subjects within their academic field.
Research and Institutional Involvement
Adjunct Professors primarily focus on teaching with limited involvement in institutional research projects or administrative duties, often maintaining external professional commitments. Visiting Professors engage more deeply in institutional research activities, collaborating with faculty on ongoing projects and contributing to the academic community through seminars and workshops during their temporary appointments. Research output and integration within the university's scholarly environment typically distinguish Visiting Professors from Adjunct Professors.
Professional Development Opportunities
Adjunct Professors often balance teaching with other professional roles, limiting their access to extensive professional development programs compared to Visiting Professors, who are typically appointed for fixed terms and engage more deeply in academic activities such as research collaborations and workshops. Visiting Professors benefit from institutional resources that enhance their expertise and contribute to their scholarly network, while Adjunct Professors may have fewer opportunities for funded conferences or specialized training. Universities prioritize professional development for Visiting Professors to foster academic growth and integration into the campus community, influencing long-term career advancement.
Impact on Student Learning and Engagement
Adjunct professors often bring practical, real-world experience that enhances student learning through applied knowledge and industry insights, fostering engagement with current professional practices. Visiting professors contribute fresh perspectives and specialized expertise from diverse academic environments, enriching the curriculum and stimulating intellectual curiosity. Both roles impact student engagement by providing varied teaching styles and expanding access to expert knowledge beyond the core faculty.
Career Advancement and Long-Term Prospects
An adjunct professor typically holds a part-time, contract-based role with limited opportunities for career advancement or tenure, often balancing multiple positions to maintain steady income. In contrast, a visiting professor usually occupies a temporary full-time position often associated with research or specialized teaching, offering more visibility and stronger prospects for long-term academic appointments. Career advancement for visiting professors is more likely due to institutional recognition and networking potential within the academic community.
Adjunct Professor vs Visiting Professor Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com