Curriculum developers focus on creating comprehensive educational frameworks and learning objectives that align with academic standards, ensuring a cohesive progression across courses. Instructional designers specialize in designing engaging, interactive learning materials and assessments tailored to diverse learning styles and technologies. Both roles collaborate closely to enhance the effectiveness and accessibility of educational programs.
Table of Comparison
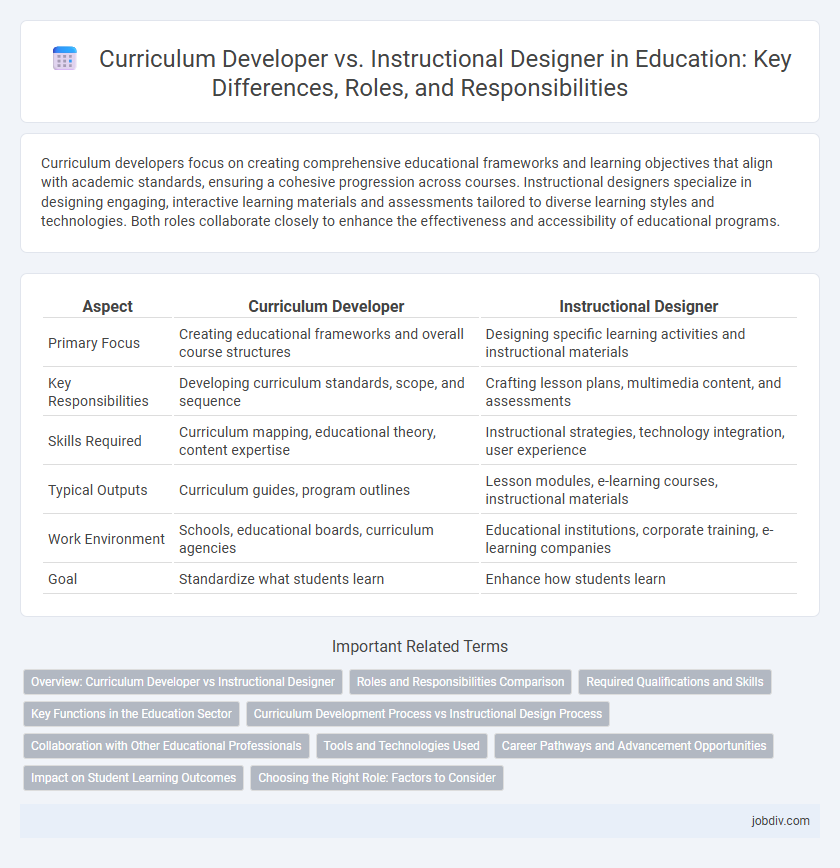
| Aspect | Curriculum Developer | Instructional Designer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Creating educational frameworks and overall course structures | Designing specific learning activities and instructional materials |
| Key Responsibilities | Developing curriculum standards, scope, and sequence | Crafting lesson plans, multimedia content, and assessments |
| Skills Required | Curriculum mapping, educational theory, content expertise | Instructional strategies, technology integration, user experience |
| Typical Outputs | Curriculum guides, program outlines | Lesson modules, e-learning courses, instructional materials |
| Work Environment | Schools, educational boards, curriculum agencies | Educational institutions, corporate training, e-learning companies |
| Goal | Standardize what students learn | Enhance how students learn |
Overview: Curriculum Developer vs Instructional Designer
Curriculum developers design comprehensive educational programs that establish learning objectives, content scope, and assessment strategies to ensure alignment with academic standards. Instructional designers create specific learning materials and experiences using pedagogical theories and technology, focusing on enhancing learner engagement and knowledge retention. Both roles collaborate to optimize educational outcomes, with curriculum developers focusing on macro-level program architecture and instructional designers targeting micro-level course delivery.
Roles and Responsibilities Comparison
Curriculum developers design and organize educational content, aligning learning objectives with standards, while instructional designers create engaging learning experiences using multimedia and technology to enhance knowledge retention. Curriculum developers focus on the blueprint and structure of courses, ensuring coherence across grade levels or training sessions, whereas instructional designers emphasize course delivery methods and learner interaction. Both roles collaborate to improve educational effectiveness but differ in their specialization on content creation versus instructional strategies.
Required Qualifications and Skills
Curriculum developers require deep expertise in subject matter, strong analytical skills, and advanced degrees in education or specialized fields to design comprehensive academic programs. Instructional designers must possess proficiency in educational technology, multimedia development, and pedagogical theories, often holding certificates or degrees in instructional design or educational technology. Both roles demand excellent communication, creativity, and project management abilities to create effective, learner-centered educational materials.
Key Functions in the Education Sector
Curriculum Developers design comprehensive educational frameworks by outlining learning objectives, content sequencing, and assessment strategies tailored for specific academic standards. Instructional Designers focus on creating engaging, technology-integrated learning experiences using multimedia tools and pedagogical theories to enhance student comprehension and retention. Both roles collaborate to ensure alignment between curriculum goals and instructional methods, optimizing the overall educational effectiveness in schools and higher education institutions.
Curriculum Development Process vs Instructional Design Process
The curriculum development process involves designing and sequencing educational content and learning objectives to create a comprehensive academic program, emphasizing alignment with standards and learner needs. Instructional design focuses on developing engaging, effective learning experiences and materials through analysis, design, development, implementation, and evaluation phases. While curriculum developers establish the overarching framework and goals, instructional designers translate these into practical instructional strategies and resources for optimal learner engagement.
Collaboration with Other Educational Professionals
Curriculum developers collaborate closely with subject matter experts, teachers, and school administrators to design comprehensive educational programs aligned with standards and learning outcomes. Instructional designers work alongside educators, multimedia specialists, and technology experts to create engaging, interactive learning materials using instructional technologies and pedagogical frameworks. Both roles require strong communication and teamwork skills to ensure educational content meets diverse learner needs and institutional goals.
Tools and Technologies Used
Curriculum developers primarily utilize tools like curriculum mapping software, content management systems, and assessment platforms to create structured educational frameworks aligned with standards. Instructional designers focus on e-learning authoring tools such as Articulate Storyline, Adobe Captivate, and Learning Management Systems (LMS) to design interactive and engaging online learning experiences. Both roles leverage data analytics tools to assess learner outcomes and optimize instructional effectiveness.
Career Pathways and Advancement Opportunities
Curriculum Developers typically advance by gaining expertise in subject matter and educational standards, progressing to roles such as Senior Curriculum Specialist or Education Program Manager. Instructional Designers enhance their career paths through mastery of learning technologies and user experience design, often moving into positions like Learning Experience Designer Lead or Director of Instructional Design. Both professions offer pathways into higher education administration, corporate training leadership, and consultancy roles, emphasizing specialized skills for career growth and leadership opportunities.
Impact on Student Learning Outcomes
Curriculum developers create comprehensive frameworks that align educational standards with measurable learning objectives, ensuring coherence across grade levels and subjects, which directly enhances student achievement. Instructional designers focus on developing engaging and effective learning experiences through multimedia and technology integration, improving knowledge retention and skill acquisition. Both roles contribute significantly to student learning outcomes by addressing content relevance and instructional quality.
Choosing the Right Role: Factors to Consider
Choosing between a curriculum developer and an instructional designer depends on factors such as project scope, target audience, and educational goals. Curriculum developers focus on creating comprehensive educational frameworks and aligning content with standards, while instructional designers specialize in developing interactive learning experiences and instructional materials. Consider the specific needs of your educational program, including content structure and delivery methods, to determine the most suitable role.
Curriculum Developer vs Instructional Designer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com