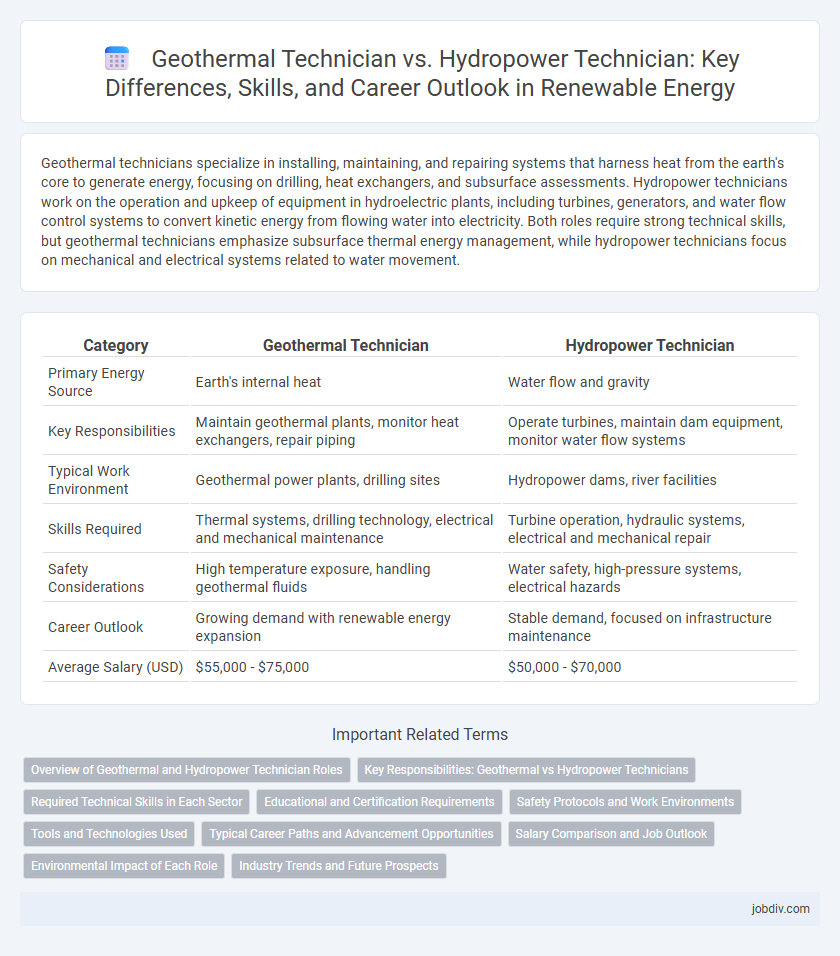
Geothermal technicians specialize in installing, maintaining, and repairing systems that harness heat from the earth's core to generate energy, focusing on drilling, heat exchangers, and subsurface assessments. Hydropower technicians work on the operation and upkeep of equipment in hydroelectric plants, including turbines, generators, and water flow control systems to convert kinetic energy from flowing water into electricity. Both roles require strong technical skills, but geothermal technicians emphasize subsurface thermal energy management, while hydropower technicians focus on mechanical and electrical systems related to water movement.
Table of Comparison
| Category | Geothermal Technician | Hydropower Technician |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Energy Source | Earth's internal heat | Water flow and gravity |
| Key Responsibilities | Maintain geothermal plants, monitor heat exchangers, repair piping | Operate turbines, maintain dam equipment, monitor water flow systems |
| Typical Work Environment | Geothermal power plants, drilling sites | Hydropower dams, river facilities |
| Skills Required | Thermal systems, drilling technology, electrical and mechanical maintenance | Turbine operation, hydraulic systems, electrical and mechanical repair |
| Safety Considerations | High temperature exposure, handling geothermal fluids | Water safety, high-pressure systems, electrical hazards |
| Career Outlook | Growing demand with renewable energy expansion | Stable demand, focused on infrastructure maintenance |
| Average Salary (USD) | $55,000 - $75,000 | $50,000 - $70,000 |
Overview of Geothermal and Hydropower Technician Roles
Geothermal Technicians specialize in installing and maintaining systems that harness heat from the Earth's core to generate electricity and provide heating solutions. Hydropower Technicians focus on the operation, repair, and maintenance of equipment used in water-based power plants, managing turbines and generators that convert flowing water into energy. Both roles require technical expertise in renewable energy systems but differ in energy source management and site-specific operational challenges.
Key Responsibilities: Geothermal vs Hydropower Technicians
Geothermal technicians specialize in maintaining and repairing equipment that extracts heat from the earth, such as geothermal pumps and heat exchangers, ensuring efficient energy transfer and system stability. Hydropower technicians focus on the operation, inspection, and maintenance of turbines, generators, and control systems in hydroelectric power plants to optimize water flow and electricity production. Both roles require expertise in mechanical and electrical systems, but geothermal technicians emphasize subsurface energy management while hydropower technicians prioritize fluid dynamics and hydraulic machinery.
Required Technical Skills in Each Sector
Geothermal technicians require expertise in subsurface heat extraction methods, including drilling operations, thermal fluid management, and the maintenance of binary cycle power plants. Hydropower technicians specialize in turbine operation, hydraulic system maintenance, and electrical grid integration for converting water flow into electricity efficiently. Both roles demand proficiency in mechanical systems, electrical troubleshooting, and safety protocols specific to their renewable energy sectors.
Educational and Certification Requirements
Geothermal technicians typically require specialized training in geothermal systems and may hold certifications such as the Geothermal Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) Certification or credentials from the International Ground Source Heat Pump Association (IGSHPA). Hydropower technicians often need education in electrical or mechanical engineering fields and certifications like the Hydropower Operations Technician Certification or licenses in turbine maintenance and safety protocols. Both roles demand strong technical skills, but geothermal technicians focus more on earth science and thermal energy systems, whereas hydropower technicians emphasize fluid mechanics and electrical generation equipment.
Safety Protocols and Work Environments
Geothermal technicians operate in high-temperature, high-pressure environments requiring strict adherence to safety protocols such as monitoring for toxic gases and ensuring proper protective gear to prevent burns and respiratory hazards. Hydropower technicians work in aquatic and mechanical settings, emphasizing fall protection, electrical safety, and lockout/tagout procedures to manage risks associated with water flow and heavy machinery. Both roles demand rigorous safety training, but the specific hazards and environmental conditions shape distinct safety measures tailored to geothermal steam systems versus hydropower turbines.
Tools and Technologies Used
Geothermal Technicians primarily utilize specialized drilling rigs, temperature sensors, and heat exchangers to access and manage subterranean heat sources, alongside software for monitoring geothermal reservoir performance. Hydropower Technicians rely heavily on turbines, generators, and control systems to harness energy from flowing water, integrating SCADA systems and predictive maintenance tools to optimize plant efficiency. Both roles demand proficiency with diagnostic instruments and data analysis software to ensure sustainable energy production and operational safety.
Typical Career Paths and Advancement Opportunities
Geothermal technicians often begin their careers as field operators or maintenance technicians, advancing to roles in system design, project management, or specialized geothermal resource assessment. Hydropower technicians typically start with hands-on experience in turbine operation and maintenance, progressing to positions such as control room supervisors, facilities managers, or hydroelectric project engineers. Both careers offer advancement through technical certifications and experience in renewable energy technologies, with hydropower technicians frequently moving into large-scale infrastructure management and geothermal technicians focusing on sustainable energy system optimization.
Salary Comparison and Job Outlook
Geothermal technicians earn an average annual salary ranging from $50,000 to $70,000, driven by growing geothermal energy projects and rising demand for sustainable heating solutions. Hydropower technicians typically receive salaries between $45,000 and $65,000, influenced by the maintenance needs of existing hydroelectric plants and modernization efforts. Job outlook for both roles is positive, with geothermal technician positions expected to grow faster due to expanding renewable energy investments, while hydropower technicians benefit from stable employment in long-established infrastructure.
Environmental Impact of Each Role
Geothermal technicians manage subsurface heat extraction systems that produce renewable energy with minimal carbon emissions and limited land usage but carry risks of induced seismicity and water contamination. Hydropower technicians maintain dam and turbine infrastructure, generating clean electricity with low greenhouse gas emissions, though their work can disrupt aquatic ecosystems and affect fish migration patterns. Both roles contribute to sustainable energy production, yet geothermal technology has a smaller ecological footprint compared to potential habitat alterations caused by hydropower projects.
Industry Trends and Future Prospects
Geothermal technicians are increasingly in demand due to the global push for sustainable energy sources and advancements in enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) technology, which promise higher efficiency and broader application. Hydropower technicians face steady growth driven by modernization of existing infrastructure and small-scale hydro projects that align with environmental regulations and decentralized energy models. Both fields show strong future prospects, but geothermal technology benefits from rising investments in deep-earth resource exploration and reduced carbon footprint initiatives.
Geothermal Technician vs Hydropower Technician Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com