Oil & Gas Engineers specialize in the exploration, extraction, and production of fossil fuels, employing advanced drilling techniques and reservoir management to optimize hydrocarbon recovery. Bioenergy Engineers focus on developing renewable energy solutions by converting organic materials into sustainable fuels and power, emphasizing environmental impact reduction and energy efficiency. Both roles require expertise in energy systems but differ fundamentally in resource focus, environmental goals, and technological approaches.
Table of Comparison
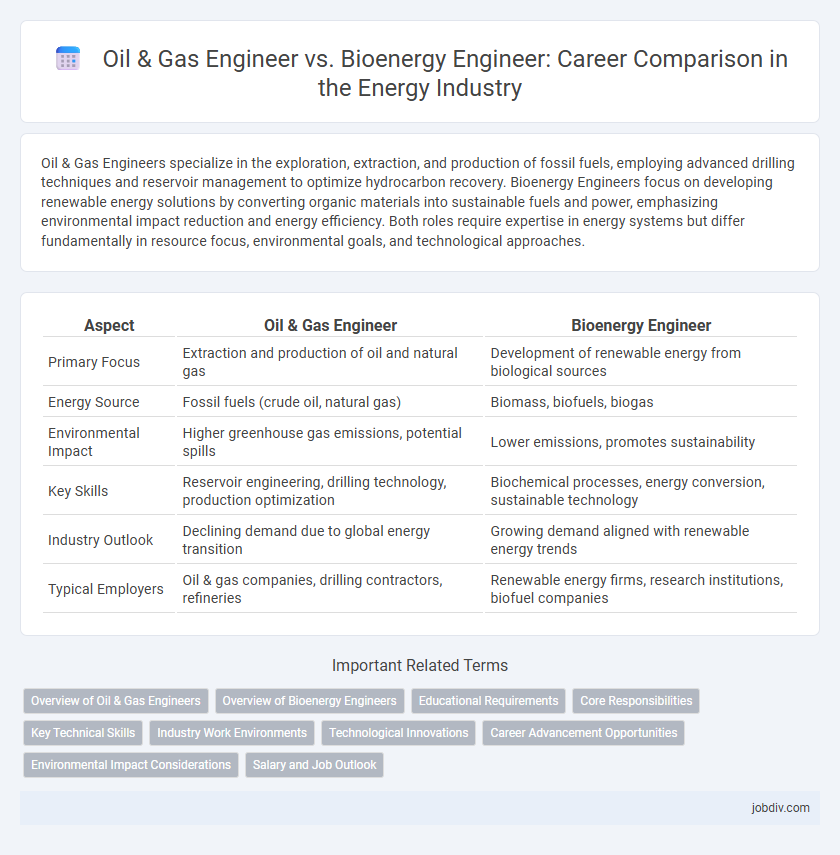
| Aspect | Oil & Gas Engineer | Bioenergy Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Extraction and production of oil and natural gas | Development of renewable energy from biological sources |
| Energy Source | Fossil fuels (crude oil, natural gas) | Biomass, biofuels, biogas |
| Environmental Impact | Higher greenhouse gas emissions, potential spills | Lower emissions, promotes sustainability |
| Key Skills | Reservoir engineering, drilling technology, production optimization | Biochemical processes, energy conversion, sustainable technology |
| Industry Outlook | Declining demand due to global energy transition | Growing demand aligned with renewable energy trends |
| Typical Employers | Oil & gas companies, drilling contractors, refineries | Renewable energy firms, research institutions, biofuel companies |
Overview of Oil & Gas Engineers
Oil & Gas Engineers design and oversee the extraction and production of petroleum resources, utilizing advanced technologies for drilling, reservoir management, and pipeline systems. They specialize in optimizing hydrocarbon recovery while ensuring safety and environmental compliance in complex geological settings. Expertise in geophysics, thermodynamics, and fluid mechanics enables them to innovate within a capital-intensive industry focused on fossil fuel energy supply.
Overview of Bioenergy Engineers
Bioenergy engineers specialize in developing sustainable energy solutions by converting organic materials such as biomass, agricultural residues, and waste into biofuels and bioenergy products. Their expertise includes optimizing biochemical and thermochemical processes to enhance energy efficiency and reduce environmental impact compared to traditional fossil fuel extraction methods used by oil and gas engineers. Advanced knowledge in renewable resource management and environmental engineering distinguishes bioenergy engineers in the transition toward greener energy systems.
Educational Requirements
Oil & Gas Engineers typically require a bachelor's degree in petroleum engineering, mechanical engineering, or chemical engineering, often supplemented by specialized courses in reservoir engineering and drilling technology. Bioenergy Engineers usually hold degrees in bioengineering, environmental engineering, or renewable energy engineering, emphasizing coursework in biomass conversion, sustainable energy systems, and bioprocessing. Both fields benefit from advanced technical training, but Bioenergy Engineers often pursue interdisciplinary education combining biology, chemistry, and engineering principles to innovate in renewable energy technologies.
Core Responsibilities
Oil & Gas Engineers specialize in designing drilling operations, managing reservoir performance, and ensuring efficient extraction of hydrocarbons from subsurface formations. Bioenergy Engineers focus on developing sustainable energy solutions by converting biomass into biofuels and optimizing bioprocesses for renewable energy production. Both roles involve technical expertise but differ significantly in resource type, environmental impact, and innovation approach within the energy sector.
Key Technical Skills
Oil & Gas Engineers specialize in reservoir modeling, drilling operations, and hydrocarbon production optimization, utilizing skills in fluid mechanics, thermodynamics, and geological analysis. Bioenergy Engineers focus on biochemical conversion processes, biomass feedstock assessment, and renewable energy system design, with expertise in enzyme technology, bio-reactor design, and sustainable resource management. Both disciplines require proficiency in process simulation software and environmental impact assessment tailored to their specific energy sectors.
Industry Work Environments
Oil & Gas Engineers typically work in offshore platforms, refineries, and drilling sites, where they manage extraction and production processes under high-risk conditions. Bioenergy Engineers are commonly employed in research laboratories, biomass processing plants, and renewable energy facilities, focusing on developing sustainable fuel technologies. Both professions require specialized expertise, but their work environments differ significantly in terms of safety protocols, operational scale, and environmental impact considerations.
Technological Innovations
Oil & Gas Engineers drive advancements in drilling automation, reservoir simulation, and enhanced oil recovery technologies, optimizing fossil fuel extraction and minimizing environmental impact. Bioenergy Engineers specialize in developing biofuels, biomass conversion processes, and genetic engineering of microorganisms to increase renewable energy yield and sustainability. Both fields leverage cutting-edge techniques in digital modeling, sensor integration, and process innovation to meet evolving global energy demands efficiently.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Oil & Gas Engineers benefit from established global infrastructure and high demand in traditional energy markets, providing access to extensive training programs, international projects, and leadership roles in multinational companies. Bioenergy Engineers experience rapid growth in renewable energy sectors, with expanding opportunities in research and development, policy advising, and sustainability initiatives that align with global climate goals. Both fields offer distinct career advancement paths, with Oil & Gas focusing on operational expertise and Bioenergy emphasizing innovation and environmental impact.
Environmental Impact Considerations
Oil & Gas Engineers primarily address environmental challenges related to fossil fuel extraction, including greenhouse gas emissions, oil spills, and habitat disruption, demanding rigorous mitigation strategies and regulatory compliance. Bioenergy Engineers concentrate on producing renewable energy from biomass, emphasizing sustainable feedstock sourcing, lifecycle carbon footprint reduction, and minimizing land-use change impacts. Both roles require advanced understanding of environmental impact assessments but differ in their approaches to balancing energy production with ecological preservation.
Salary and Job Outlook
Oil & Gas Engineers typically command higher average salaries, often ranging from $90,000 to $130,000 annually, reflecting the industry's scale and capital intensity, while Bioenergy Engineers earn between $70,000 and $100,000, driven by growing renewable energy investments. The job outlook for Oil & Gas Engineers is expected to grow modestly at around 5% over the next decade due to fluctuating fossil fuel demand and regulatory challenges. In contrast, Bioenergy Engineers face robust growth projections exceeding 10% annually, fueled by increased global emphasis on sustainable energy solutions and climate change mitigation efforts.
Oil & Gas Engineer vs Bioenergy Engineer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com