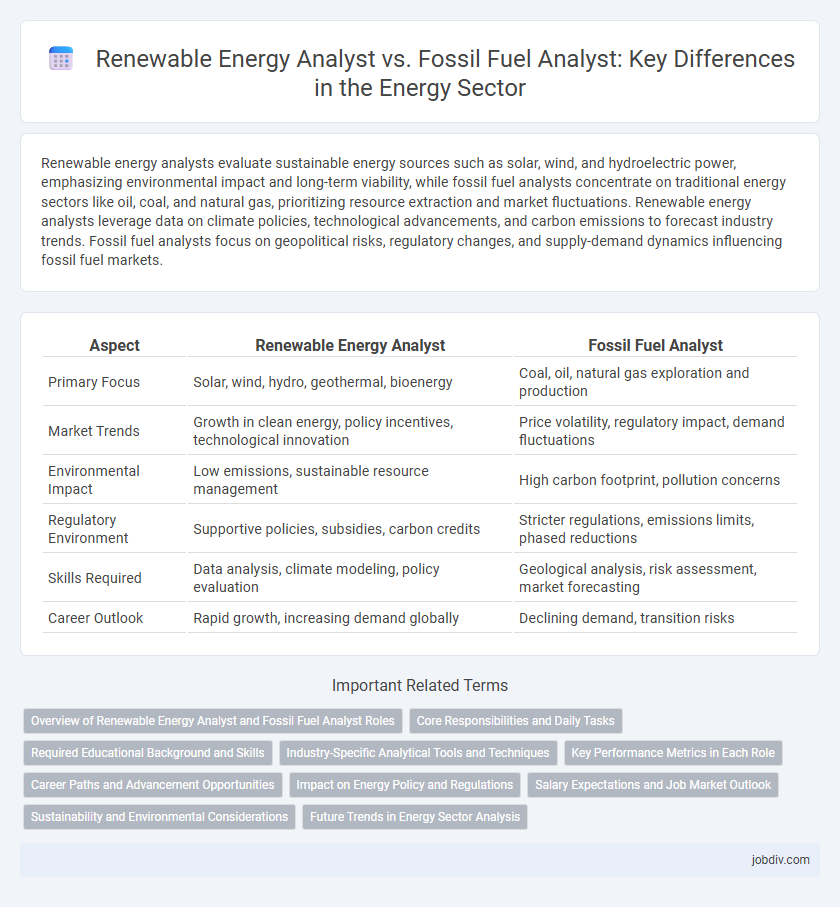
Renewable energy analysts evaluate sustainable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, emphasizing environmental impact and long-term viability, while fossil fuel analysts concentrate on traditional energy sectors like oil, coal, and natural gas, prioritizing resource extraction and market fluctuations. Renewable energy analysts leverage data on climate policies, technological advancements, and carbon emissions to forecast industry trends. Fossil fuel analysts focus on geopolitical risks, regulatory changes, and supply-demand dynamics influencing fossil fuel markets.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Renewable Energy Analyst | Fossil Fuel Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, bioenergy | Coal, oil, natural gas exploration and production |
| Market Trends | Growth in clean energy, policy incentives, technological innovation | Price volatility, regulatory impact, demand fluctuations |
| Environmental Impact | Low emissions, sustainable resource management | High carbon footprint, pollution concerns |
| Regulatory Environment | Supportive policies, subsidies, carbon credits | Stricter regulations, emissions limits, phased reductions |
| Skills Required | Data analysis, climate modeling, policy evaluation | Geological analysis, risk assessment, market forecasting |
| Career Outlook | Rapid growth, increasing demand globally | Declining demand, transition risks |
Overview of Renewable Energy Analyst and Fossil Fuel Analyst Roles
Renewable Energy Analysts specialize in evaluating sustainable energy sources such as solar, wind, and bioenergy, focusing on market trends, policy impacts, and technological advancements to support clean energy investments. Fossil Fuel Analysts analyze coal, oil, and natural gas markets, assessing supply-demand dynamics, regulatory environments, and price fluctuations to guide traditional energy sector decisions. Both roles require strong financial modeling skills but differ in their emphasis on environmental impacts and regulatory frameworks.
Core Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
Renewable Energy Analysts evaluate solar, wind, and hydroelectric projects through data modeling, market trend analysis, and policy impact assessment to drive sustainable energy adoption. Fossil Fuel Analysts focus on coal, oil, and natural gas markets by monitoring commodity prices, regulatory changes, and supply-demand dynamics to optimize resource extraction and profitability. Both roles require expertise in energy economics, but Renewable Energy Analysts emphasize environmental impact and innovation while Fossil Fuel Analysts prioritize operational efficiency and risk management.
Required Educational Background and Skills
Renewable Energy Analysts typically require a background in environmental science, engineering, or sustainable energy, with strong skills in data analysis, policy evaluation, and knowledge of solar, wind, and bioenergy technologies. Fossil Fuel Analysts often hold degrees in geology, petroleum engineering, or energy economics, with expertise in market trends, reserve estimation, and regulatory compliance related to oil, coal, and natural gas. Both roles demand proficiency in quantitative analysis, risk assessment, and familiarity with industry-specific software tools.
Industry-Specific Analytical Tools and Techniques
Renewable Energy Analysts leverage advanced GIS mapping, satellite data analysis, and energy yield simulation tools to assess solar, wind, and hydroelectric potential, enabling precise forecasting and optimization of clean energy projects. Fossil Fuel Analysts utilize seismic imaging, reservoir modeling software, and production forecasting algorithms to evaluate hydrocarbon reserves and enhance extraction efficiency in oil and gas fields. Both roles demand expertise in industry-specific analytics platforms, with renewable practitioners prioritizing sustainability metrics and carbon footprint modeling, while fossil fuel experts focus on resource depletion rates and market price volatility analysis.
Key Performance Metrics in Each Role
Renewable Energy Analysts prioritize metrics such as carbon emission reductions, energy yield from solar and wind installations, and cost per kilowatt-hour to assess sustainability and economic viability. Fossil Fuel Analysts focus on production volumes, reserve replacement ratios, and volatility in commodity prices to evaluate operational efficiency and market risks. Both roles require detailed data analysis but emphasize distinct environmental and financial performance indicators reflective of their energy sectors.
Career Paths and Advancement Opportunities
Renewable Energy Analysts focus on technologies like solar, wind, and bioenergy, with career advancement often leading to roles in sustainability consulting, project management, or policy development as demand for clean energy grows. Fossil Fuel Analysts specialize in coal, oil, and natural gas markets, typically advancing toward strategic planning, risk assessment, or executive roles within conventional energy companies. The renewable energy sector offers faster growth potential and diverse opportunities aligned with global decarbonization goals, while fossil fuel careers may involve navigating fluctuating market dynamics and regulatory pressures.
Impact on Energy Policy and Regulations
Renewable energy analysts influence energy policy by advocating for increased investment in sustainable technologies, shaping regulations that promote clean energy adoption and carbon reduction targets. Fossil fuel analysts often impact policy through assessing the implications of continued hydrocarbon dependence, influencing regulatory measures related to emissions, extraction, and energy security. The contrasting insights from both analysts drive balanced energy policies that aim to meet environmental goals while addressing economic and reliability concerns.
Salary Expectations and Job Market Outlook
Renewable energy analysts typically earn salaries ranging from $65,000 to $95,000 annually, reflecting the growing demand for expertise in solar, wind, and other clean energy sectors. Fossil fuel analysts often have salaries between $70,000 and $100,000 but face a declining job market due to regulatory pressures and the global shift towards sustainability. The renewable energy job market is expanding rapidly, driven by policy incentives and corporate commitments to net-zero emissions, whereas fossil fuel analysis roles are contracting in response to decreasing industry investments.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Renewable Energy Analysts prioritize sustainability by evaluating energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, assessing their environmental impact and potential to reduce carbon emissions. Fossil Fuel Analysts focus on traditional energy sources like coal, oil, and natural gas, analyzing extraction efficiency and market trends while addressing environmental regulations and carbon footprint mitigation. The growing demand for clean energy solutions places Renewable Energy Analysts at the forefront of promoting environmentally responsible practices and combating climate change.
Future Trends in Energy Sector Analysis
Renewable energy analysts forecast significant growth in solar, wind, and battery storage technologies, driven by global decarbonization policies and advancements in grid integration. Fossil fuel analysts are increasingly focused on declining oil and coal demand projections, carbon capture utilization, and the economic impacts of transitioning economies toward cleaner alternatives. Emerging trends highlight a shift in investment patterns favoring renewables, with sophisticated data models assessing policy risks and market volatility shaping the energy sector's future landscape.
Renewable Energy Analyst vs Fossil Fuel Analyst Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com