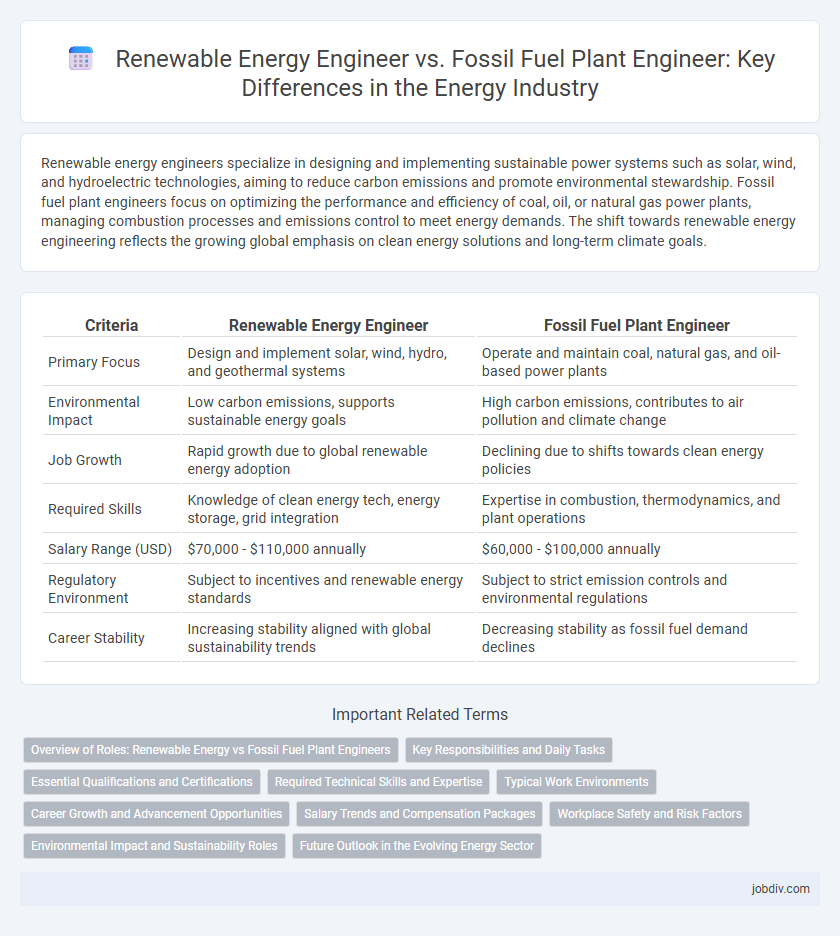
Renewable energy engineers specialize in designing and implementing sustainable power systems such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric technologies, aiming to reduce carbon emissions and promote environmental stewardship. Fossil fuel plant engineers focus on optimizing the performance and efficiency of coal, oil, or natural gas power plants, managing combustion processes and emissions control to meet energy demands. The shift towards renewable energy engineering reflects the growing global emphasis on clean energy solutions and long-term climate goals.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Renewable Energy Engineer | Fossil Fuel Plant Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Design and implement solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal systems | Operate and maintain coal, natural gas, and oil-based power plants |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon emissions, supports sustainable energy goals | High carbon emissions, contributes to air pollution and climate change |
| Job Growth | Rapid growth due to global renewable energy adoption | Declining due to shifts towards clean energy policies |
| Required Skills | Knowledge of clean energy tech, energy storage, grid integration | Expertise in combustion, thermodynamics, and plant operations |
| Salary Range (USD) | $70,000 - $110,000 annually | $60,000 - $100,000 annually |
| Regulatory Environment | Subject to incentives and renewable energy standards | Subject to strict emission controls and environmental regulations |
| Career Stability | Increasing stability aligned with global sustainability trends | Decreasing stability as fossil fuel demand declines |
Overview of Roles: Renewable Energy vs Fossil Fuel Plant Engineers
Renewable Energy Engineers design, develop, and implement sustainable energy systems such as solar, wind, and bioenergy technologies to reduce carbon emissions and promote environmental conservation. Fossil Fuel Plant Engineers focus on operating and maintaining power plants that rely on coal, natural gas, or oil, ensuring efficiency and compliance with safety regulations while managing greenhouse gas impacts. Both roles require expertise in energy systems and engineering principles, but their objectives diverge sharply toward sustainable innovation versus traditional energy production.
Key Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
Renewable Energy Engineers design, develop, and implement sustainable energy systems such as solar, wind, and bioenergy, with daily tasks including site assessment, system optimization, and integration of advanced technologies to maximize efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Fossil Fuel Plant Engineers oversee the operation, maintenance, and safety of coal, oil, or gas power plants, focusing on equipment reliability, emissions control, and compliance with regulatory standards to ensure stable energy production. Both roles require strong technical expertise, but Renewable Energy Engineers emphasize innovation in clean technologies, whereas Fossil Fuel Plant Engineers prioritize operational stability and emission management.
Essential Qualifications and Certifications
Renewable Energy Engineers require a strong foundation in electrical, mechanical, or environmental engineering, often holding certifications such as LEED Accredited Professional (LEED AP) or Certified Energy Manager (CEM) to validate expertise in sustainable technologies. Fossil Fuel Plant Engineers typically possess degrees in mechanical or chemical engineering with certifications like Professional Engineer (PE) license and specialized training in combustion systems, thermodynamics, and safety protocols specific to coal, oil, or gas plants. Both roles emphasize proficiency in industry-relevant software and adherence to environmental regulations, but renewable energy positions prioritize knowledge in solar, wind, or bioenergy systems.
Required Technical Skills and Expertise
Renewable Energy Engineers require expertise in solar panel design, wind turbine technology, and energy storage systems, with proficiency in CAD software and knowledge of sustainable materials. Fossil Fuel Plant Engineers must possess strong skills in thermodynamics, combustion processes, and equipment maintenance, alongside experience with pollution control technologies. Both roles demand solid understanding of electrical and mechanical engineering principles, yet Renewable Energy Engineers focus more on emerging clean energy innovations while Fossil Fuel Plant Engineers specialize in optimizing conventional power plant operations.
Typical Work Environments
Renewable Energy Engineers typically work in research facilities, wind farms, solar power plants, and urban development projects focused on sustainable infrastructure. Fossil Fuel Plant Engineers usually operate within coal, natural gas, or oil-fired power plants, often in industrial zones with heavy machinery and strict safety protocols. Both roles require collaboration with environmental scientists, technicians, and regulatory bodies to ensure efficient energy production and compliance with environmental standards.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Renewable energy engineers experience rapid career growth driven by global investments in solar, wind, and battery technologies, with opportunities expanding in research, project management, and policy development. Fossil fuel plant engineers face limited advancement prospects due to industry decline and regulatory constraints, though expertise in plant optimization and emissions control remains valuable. The shift toward decarbonization accelerates demand for renewable specialists, offering more dynamic and sustainable long-term career paths.
Salary Trends and Compensation Packages
Renewable Energy Engineers typically see rising salary trends due to growing investments in sustainable technologies and government incentives promoting clean energy adoption, with average salaries ranging from $70,000 to $110,000 annually. Fossil Fuel Plant Engineers, while traditionally commanding higher starting salaries around $80,000 to $120,000, face stagnating or slightly declining compensation as the industry shifts toward decarbonization. Compensation packages for renewable roles often include bonuses linked to project milestones and stock options in green technology firms, whereas fossil fuel positions emphasize retirement benefits and union-negotiated pay scales.
Workplace Safety and Risk Factors
Renewable Energy Engineers work in environments with lower exposure to hazardous chemicals and combustion-related risks, contributing to safer workplace conditions compared to Fossil Fuel Plant Engineers who face dangers from toxic emissions, high-pressure equipment, and fire hazards. Safety protocols for Fossil Fuel Plant Engineers are more stringent due to the increased risk of accidents such as explosions and chronic exposure to pollutants. The shift towards renewable energy reduces long-term health risks and environmental liabilities for engineers by minimizing exposure to fossil fuel combustion byproducts.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Roles
Renewable Energy Engineers drive the integration of solar, wind, and hydro technologies, significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting carbon neutrality. Fossil Fuel Plant Engineers focus on optimizing coal, oil, or natural gas systems, often managing pollution control but maintaining reliance on finite resources with higher environmental footprints. Sustainability roles in renewable energy emphasize lifecycle carbon reduction and ecosystem preservation, contrasting with fossil fuel engineering which prioritizes efficiency improvements within more environmentally harmful frameworks.
Future Outlook in the Evolving Energy Sector
Renewable Energy Engineers are poised for significant growth due to the global shift toward sustainable power sources, driven by government policies targeting carbon neutrality and technological advancements in solar, wind, and energy storage systems. Fossil Fuel Plant Engineers face a declining job market as coal, oil, and natural gas plants are phased out to meet climate goals and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The evolving energy sector prioritizes innovation in green technologies, creating more opportunities in renewables with higher demand for expertise in grid integration and clean energy solutions.
Renewable Energy Engineer vs Fossil Fuel Plant Engineer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com