A Digital Imaging Technician (DIT) manages on-set digital workflow, ensuring image quality and data integrity during shooting, while a Colorist specializes in post-production, enhancing and adjusting color to achieve the desired visual style. The DIT bridges the gap between camera and post, working closely with cinematographers to maintain consistent imagery, whereas the Colorist focuses on creative color grading to finalize the look of the project. Both roles are essential in digital filmmaking, with the DIT handling technical image management and the Colorist providing artistic color enhancement.
Table of Comparison
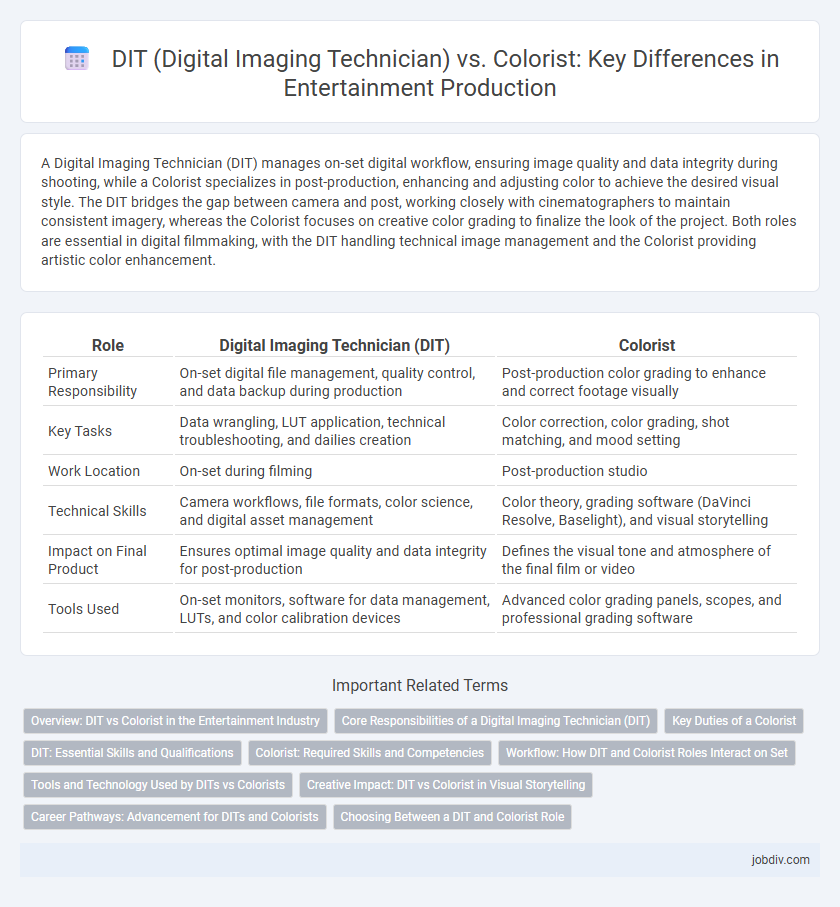
| Role | Digital Imaging Technician (DIT) | Colorist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Responsibility | On-set digital file management, quality control, and data backup during production | Post-production color grading to enhance and correct footage visually |
| Key Tasks | Data wrangling, LUT application, technical troubleshooting, and dailies creation | Color correction, color grading, shot matching, and mood setting |
| Work Location | On-set during filming | Post-production studio |
| Technical Skills | Camera workflows, file formats, color science, and digital asset management | Color theory, grading software (DaVinci Resolve, Baselight), and visual storytelling |
| Impact on Final Product | Ensures optimal image quality and data integrity for post-production | Defines the visual tone and atmosphere of the final film or video |
| Tools Used | On-set monitors, software for data management, LUTs, and color calibration devices | Advanced color grading panels, scopes, and professional grading software |
Overview: DIT vs Colorist in the Entertainment Industry
The Digital Imaging Technician (DIT) manages on-set digital workflows, ensuring image quality, data integrity, and real-time color correction during filming. In contrast, the Colorist works in post-production, manipulating the color palette to enhance mood, continuity, and visual storytelling. Both roles are essential in the entertainment industry for achieving the director's visual vision, yet they operate at different stages of the production pipeline.
Core Responsibilities of a Digital Imaging Technician (DIT)
A Digital Imaging Technician (DIT) manages on-set digital workflows, ensuring the integrity and organization of footage through real-time data backup and quality control. Their core responsibilities include color correction to approximate the director's vision, metadata management, and coordinating with the camera and post-production teams to optimize image quality. This role is critical for maintaining the technical accuracy and smooth transition of footage from the camera to post-production.
Key Duties of a Colorist
A colorist specializes in enhancing the visual tone and mood of a film by adjusting color balance, contrast, and saturation to achieve the director's artistic vision. They work primarily during post-production using advanced color grading software like DaVinci Resolve to ensure consistent color continuity across scenes. Unlike a Digital Imaging Technician (DIT), who manages on-set data and ensures footage quality during filming, the colorist's key duties focus on the creative manipulation of color to evoke emotion and narrative coherence.
DIT: Essential Skills and Qualifications
A Digital Imaging Technician (DIT) plays a crucial role on set by managing data workflow, ensuring image quality, and collaborating closely with the cinematographer to maintain the director's visual intent. Essential skills for a DIT include proficiency in camera systems, color grading software like DaVinci Resolve, data management protocols, and a strong understanding of post-production processes. Qualifications often combine technical expertise in digital imaging, experience with on-set workflows, and problem-solving abilities to handle real-time image adjustments and data integrity.
Colorist: Required Skills and Competencies
A Colorist must possess advanced knowledge of color theory, digital grading software such as DaVinci Resolve, and an acute eye for detail to enhance the visual tone and mood of a film or television project. Expertise in LUTs (Look-Up Tables), color calibration, and understanding of camera profiles is essential for achieving consistent and compelling imagery. Strong collaboration skills are required to interpret the director's vision while maintaining technical precision in post-production workflows.
Workflow: How DIT and Colorist Roles Interact on Set
The Digital Imaging Technician (DIT) manages on-set data management, ensuring the integrity and quality of footage through color grading previews and LUT application before the footage reaches post-production. The Colorist works post-shoot, refining the footage's color balance, contrast, and mood to achieve the director's vision, building upon the DIT's initial work. Their workflow interaction enhances efficiency by allowing real-time color feedback on set, streamlining the transition from raw footage capture to final color grading.
Tools and Technology Used by DITs vs Colorists
Digital Imaging Technicians (DITs) utilize specialized tools such as LUT management software, on-set color grading monitors, and data wrangling applications to ensure camera footage integrity and consistency during production. Colorists primarily work with advanced color grading suites like DaVinci Resolve or Baselight, employing sophisticated color correction panels and software to enhance visual storytelling in post-production. The technology used by DITs focuses on real-time monitoring and data management, while colorists leverage precision grading tools to achieve the desired cinematic look.
Creative Impact: DIT vs Colorist in Visual Storytelling
A Digital Imaging Technician (DIT) ensures technical precision by managing data integrity, on-set color calibration, and immediate image adjustments, directly influencing the foundational quality of the footage. The Colorist transforms this base by applying sophisticated color grading techniques, enhancing mood, tone, and emotional resonance to shape the film's visual narrative. Together, their creative impact drives compelling storytelling, with the DIT safeguarding the image's fidelity and the Colorist defining its artistic expression.
Career Pathways: Advancement for DITs and Colorists
Career pathways for Digital Imaging Technicians (DITs) often lead to advanced roles in on-set image management, post-production supervision, or transitioning into color grading specialists, given their foundational expertise in digital workflow and color science. Colorists typically advance by mastering complex grading techniques, moving into senior colorist positions, or branching into creative consultation and color workflow management for major film or television productions. Both careers benefit from continuous skill development in emerging color grading software and technology, offering opportunities for leadership in digital post-production environments.
Choosing Between a DIT and Colorist Role
Choosing between a Digital Imaging Technician (DIT) and a Colorist role depends on your career focus within post-production workflows; DITs manage on-set data integrity, color correction groundwork, and technical troubleshooting, while Colorists specialize in enhancing the final image aesthetically during color grading. DITs require strong technical expertise in camera systems, LUTs, and color science, whereas Colorists must master creative color grading tools and software such as DaVinci Resolve to craft the visual tone. Understanding the responsibilities and skill sets of each role helps in aligning career goals with industry demands in film and television production.
DIT (Digital Imaging Technician) vs Colorist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com