Aquaculture technicians specialize in breeding and raising fish in controlled environments, ensuring sustainable population growth and health management. Wild catch harvesters focus on capturing fish from natural habitats, relying on traditional fishing methods and knowledge of ecosystem dynamics. Both roles require expertise in fish biology, but aquaculture emphasizes cultivation while wild catch centers on extraction.
Table of Comparison
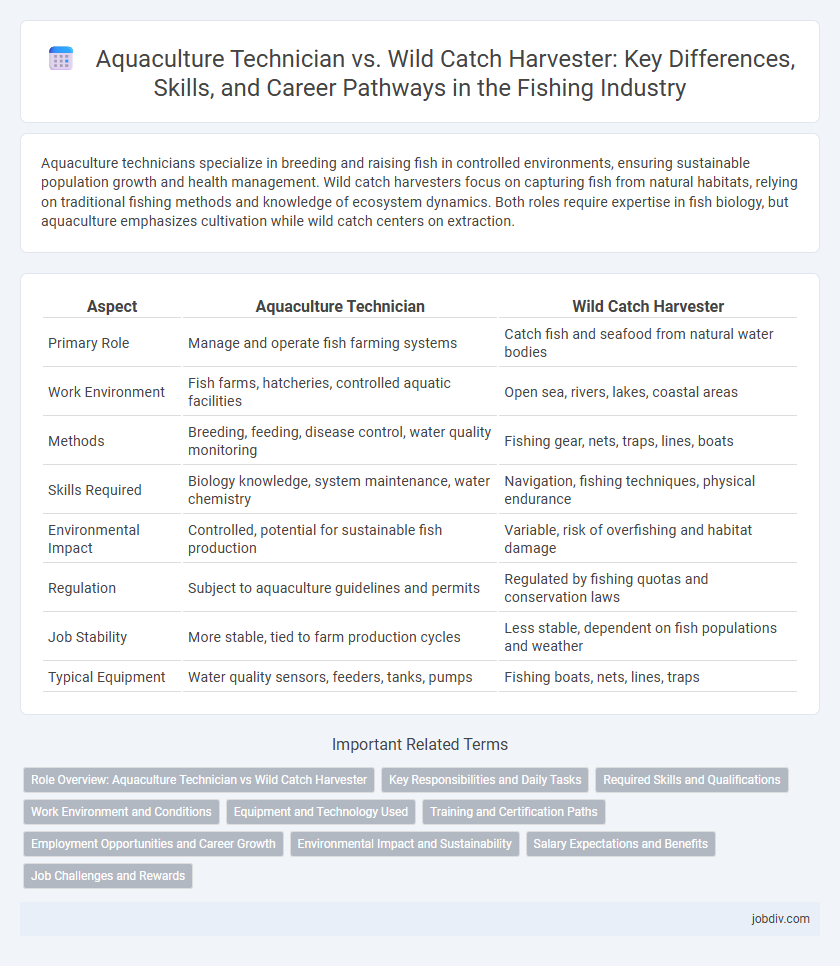
| Aspect | Aquaculture Technician | Wild Catch Harvester |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Manage and operate fish farming systems | Catch fish and seafood from natural water bodies |
| Work Environment | Fish farms, hatcheries, controlled aquatic facilities | Open sea, rivers, lakes, coastal areas |
| Methods | Breeding, feeding, disease control, water quality monitoring | Fishing gear, nets, traps, lines, boats |
| Skills Required | Biology knowledge, system maintenance, water chemistry | Navigation, fishing techniques, physical endurance |
| Environmental Impact | Controlled, potential for sustainable fish production | Variable, risk of overfishing and habitat damage |
| Regulation | Subject to aquaculture guidelines and permits | Regulated by fishing quotas and conservation laws |
| Job Stability | More stable, tied to farm production cycles | Less stable, dependent on fish populations and weather |
| Typical Equipment | Water quality sensors, feeders, tanks, pumps | Fishing boats, nets, lines, traps |
Role Overview: Aquaculture Technician vs Wild Catch Harvester
Aquaculture Technicians manage the breeding, rearing, and health of aquatic organisms in controlled environments, ensuring optimal water quality and habitat conditions to maximize production efficiency. Wild Catch Harvesters specialize in capturing fish and other marine species from natural habitats using nets, traps, or lines, relying on knowledge of fish behavior and ecosystem dynamics for sustainable harvesting. Both roles demand expertise in aquatic biology, but Aquaculture Technicians emphasize cultivation processes, while Wild Catch Harvesters focus on extraction techniques.
Key Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
Aquaculture Technicians manage the breeding, rearing, and health monitoring of fish and other aquatic species in controlled environments, ensuring optimal water quality and feed efficiency. Wild Catch Harvesters focus on locating, capturing, and processing fish from natural habitats using various fishing techniques while complying with regulatory and sustainability guidelines. Both roles demand knowledge of aquatic ecosystems, but Aquaculture Technicians emphasize cultivation and maintenance, whereas Wild Catch Harvesters prioritize harvesting and environmental adaptation.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Aquaculture Technicians require knowledge of aquatic biology, water quality management, and the ability to operate specialized equipment for breeding and raising fish in controlled environments. Wild Catch Harvesters need skills in navigation, understanding marine ecosystems, and proficiency with fishing gear and vessels to safely and efficiently capture fish in natural habitats. Both roles demand physical stamina, knowledge of safety protocols, and adherence to environmental regulations, but Aquaculture Technicians often hold certifications in aquaculture or marine science.
Work Environment and Conditions
Aquaculture Technicians typically work in controlled environments such as fish farms, hatcheries, or aquatic laboratories, where conditions are stable and equipment maintenance is crucial. Wild Catch Harvesters operate in open waters, facing unpredictable weather, rough seas, and physical demands while capturing fish in natural habitats. Both roles require knowledge of marine ecosystems but differ significantly in workplace safety, routine, and exposure to environmental hazards.
Equipment and Technology Used
Aquaculture technicians utilize advanced monitoring systems, automated feeders, and water quality sensors to maintain controlled environments for fish farming, ensuring optimal growth and health. Wild catch harvesters rely primarily on traditional nets, trawlers equipped with sonar technology, and GPS navigation to locate and capture fish in open waters. Modern aquaculture increasingly integrates IoT devices and robotics, contrasting with wild catch methods that emphasize durable, vessel-based equipment for dynamic, large-scale ocean harvesting.
Training and Certification Paths
Aquaculture Technicians typically undergo specialized training in marine biology, water quality management, and breeding techniques, often earning certifications such as Certified Aquaculture Technician (CAT) or aquaculture-specific credentials from accredited institutions. Wild Catch Harvesters require knowledge in sustainable fishing practices, navigation, and safety protocols, with certifications including Commercial Fishing Licenses and specialized training in fish identification and seafood safety standards. Both career paths emphasize hands-on experience, but Aquaculture Technicians focus more on controlled environments, while Wild Catch Harvesters prioritize field expertise and regulatory compliance.
Employment Opportunities and Career Growth
Aquaculture technicians have growing employment opportunities driven by the expansion of sustainable seafood production and technological advancements in fish farming, offering career growth in research, management, and environmental monitoring. Wild catch harvesters face fluctuating job availability influenced by fish stock regulations and ecological factors, with advancement often tied to gaining experience and obtaining specialized certifications. The aquaculture sector typically provides more stable and diverse career paths compared to the unpredictable nature of wild catch harvesting.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Aquaculture technicians cultivate fish and seafood in controlled environments, reducing pressures on wild populations and enabling sustainable resource management. Wild catch harvesters collect fish directly from natural habitats, which can lead to overfishing and ecosystem disruption if not properly regulated. Advances in aquaculture technology promote environmental benefits by minimizing habitat degradation and supporting biodiversity conservation compared to traditional wild fishing methods.
Salary Expectations and Benefits
Aquaculture technicians typically earn an average salary ranging from $35,000 to $55,000 annually, with benefits often including health insurance, retirement plans, and opportunities for skill development in sustainable fish farming. Wild catch harvesters usually have variable incomes based on catch volume and market demand, with annual earnings between $30,000 and $60,000, and benefits are less consistent, often limited to seasonal work protections and equipment allowances. The stability of income and comprehensive benefits packages generally favor aquaculture technician roles over the more fluctuating and physically demanding wild catch harvester positions.
Job Challenges and Rewards
Aquaculture Technicians face challenges such as maintaining water quality, preventing disease outbreaks, and ensuring sustainable breeding practices while benefiting from steady employment and contributing to food security. Wild Catch Harvesters contend with unpredictable weather, fluctuating fish populations, and regulatory restrictions but gain the reward of direct interaction with diverse marine ecosystems and potentially higher immediate earnings. Both roles require specialized skills, physical endurance, and a commitment to sustainable fishing practices for long-term industry viability.
Aquaculture Technician vs Wild Catch Harvester Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com