Gillnetters use vertical nets to catch fish by entangling them, making this method effective for targeting specific species but often resulting in higher bycatch. Longliners deploy extensive lines with numerous baited hooks, allowing for selective fishing and reducing unwanted catch, but they require more equipment and effort. Both techniques impact marine ecosystems differently, with careful management essential to minimize environmental harm.
Table of Comparison
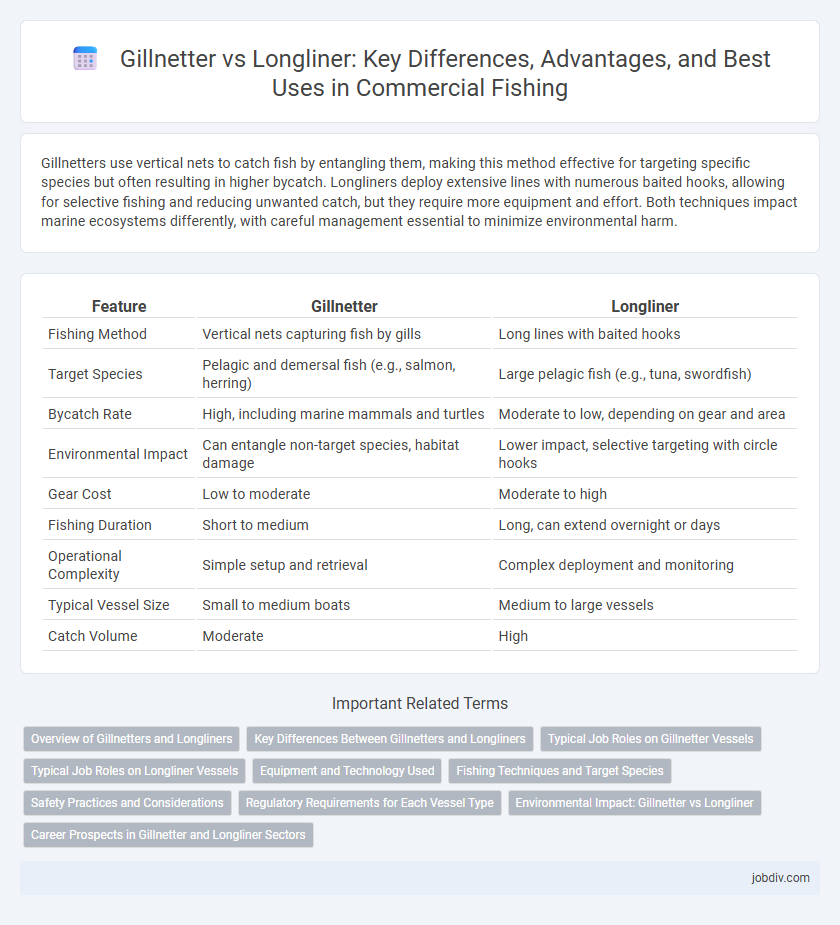
| Feature | Gillnetter | Longliner |
|---|---|---|
| Fishing Method | Vertical nets capturing fish by gills | Long lines with baited hooks |
| Target Species | Pelagic and demersal fish (e.g., salmon, herring) | Large pelagic fish (e.g., tuna, swordfish) |
| Bycatch Rate | High, including marine mammals and turtles | Moderate to low, depending on gear and area |
| Environmental Impact | Can entangle non-target species, habitat damage | Lower impact, selective targeting with circle hooks |
| Gear Cost | Low to moderate | Moderate to high |
| Fishing Duration | Short to medium | Long, can extend overnight or days |
| Operational Complexity | Simple setup and retrieval | Complex deployment and monitoring |
| Typical Vessel Size | Small to medium boats | Medium to large vessels |
| Catch Volume | Moderate | High |
Overview of Gillnetters and Longliners
Gillnetters use vertical panels of netting that trap fish by their gills, targeting species like salmon and herring in coastal waters. Longliners deploy extensive lines with baited hooks designed to catch pelagic species such as tuna and swordfish across deep ocean areas. Both methods vary in selectivity and environmental impact, with gillnetting often associated with bycatch of non-target species and longlining linked to seabird and turtle interactions.
Key Differences Between Gillnetters and Longliners
Gillnetters use vertical panels of netting that entangle fish by their gills, targeting species like salmon and herring, while longliners deploy extensive lines with baited hooks to catch fish such as tuna and swordfish. Gillnetting is often associated with higher bycatch rates and habitat impact, whereas longlining allows for selective targeting but may still pose risks to seabirds and turtles. Vessel size and gear deployment methods also differ significantly, influencing operational range and catch efficiency.
Typical Job Roles on Gillnetter Vessels
Gillnetter vessels typically employ deckhands responsible for setting and retrieving gillnets designed to entangle fish by their gills, alongside captains who navigate and ensure optimal net placement in targeted fishing zones. Crew members also handle gear maintenance, sorting catch, and monitoring bycatch to comply with regulatory standards. These roles contrast with longliner operations, where specialized skills focus on deploying long fishing lines equipped with numerous baited hooks to catch species like tuna and swordfish.
Typical Job Roles on Longliner Vessels
Typical job roles on longliner vessels include the skipper, who oversees vessel operations and fishing strategies; deckhands, responsible for setting and retrieving longlines, handling catch, and maintaining gear; and the engineer, who manages the engine and mechanical systems essential for efficient vessel performance. Crew members often specialize in bait preparation, hook setting, and fish processing to maximize catch quality. These roles ensure the longliner operates smoothly while targeting species such as tuna, swordfish, and halibut in offshore waters.
Equipment and Technology Used
Gillnetters use large vertical nets made of monofilament or multifilament lines designed to entangle fish by their gills, often equipped with floaters and weights to maintain the net's position in the water column. Longliners deploy extensive lines with baited hooks spaced at intervals, utilizing specialized reels, hydraulic systems, and GPS technology for precise placement and retrieval. Both methods incorporate advanced sonar and fish-finding equipment to optimize catch efficiency while minimizing bycatch.
Fishing Techniques and Target Species
Gillnetters utilize vertical nets suspended in the water column to entangle fish by their gills, targeting species such as salmon, herring, and cod often found in nearshore waters. Longliners employ a mainline with numerous baited hooks spread over long distances, primarily catching large pelagic species like tuna, swordfish, and halibut in deep oceanic environments. These distinct fishing techniques directly influence the selectivity, bycatch rates, and habitat impact associated with each gear type.
Safety Practices and Considerations
Gillnetters require strict adherence to safety protocols due to the risk of entanglement in large, nearly invisible nets, including the use of personal flotation devices and regular equipment inspections. Longliners must manage hazards related to heavy gear and baited hooks, emphasizing proper handling techniques and secure storage to prevent injuries. Both fishing methods demand rigorous emergency preparedness and crew training to ensure safe operations in harsh marine environments.
Regulatory Requirements for Each Vessel Type
Gillnetters must comply with specific mesh size regulations and seasonal restrictions to prevent overfishing and protect juvenile fish, often requiring the use of biodegradable materials to reduce ghost fishing. Longliners face stringent rules on hook types, bait usage, and mandatory bird-scaring devices to minimize bycatch, particularly of seabirds and turtles, alongside vessel monitoring system requirements for tracking and data reporting. Both vessel types are subject to national and international fisheries management plans aimed at sustainable harvest levels and ecosystem preservation.
Environmental Impact: Gillnetter vs Longliner
Gillnetters often contribute to higher bycatch rates, entangling non-target species such as dolphins, sea turtles, and seabirds, which disrupts marine biodiversity. Longliners, while also causing bycatch, tend to have more selective targeting capabilities through hook design and setting strategies, reducing unintended marine life capture. Both methods impact ocean ecosystems, but longlining generally presents a lower overall environmental footprint when managed with sustainable practices.
Career Prospects in Gillnetter and Longliner Sectors
Career prospects in the Gillnetter sector emphasize steady demand for operators skilled in setting and retrieving gillnets to catch species like salmon and herring, often offering seasonal employment with potential for advancement to supervisory roles. The Longliner sector presents opportunities for professionals experienced in deploying longlines targeting high-value species such as tuna and swordfish, generally providing higher income potential and extended voyages that require advanced navigation and fish handling skills. Both sectors demand adherence to sustainability practices and regulatory compliance, influencing job stability and career growth within fisheries management and conservation initiatives.
Gillnetter vs Longliner Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com