A butcher specializes in preparing and selling various cuts of meat from land animals, ensuring precise slicing and proper meat handling techniques. A fishmonger focuses exclusively on fresh seafood, offering expert knowledge in selecting, cleaning, and filleting fish and shellfish. Both professionals play crucial roles in the foodservice industry by supplying quality protein options tailored to diverse culinary needs.
Table of Comparison
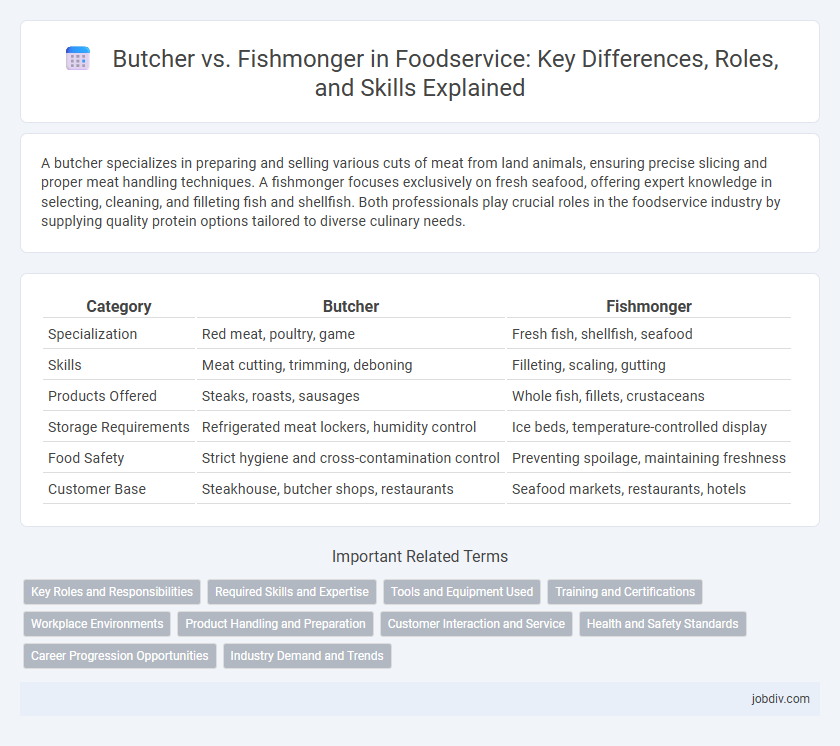
| Category | Butcher | Fishmonger |
|---|---|---|
| Specialization | Red meat, poultry, game | Fresh fish, shellfish, seafood |
| Skills | Meat cutting, trimming, deboning | Filleting, scaling, gutting |
| Products Offered | Steaks, roasts, sausages | Whole fish, fillets, crustaceans |
| Storage Requirements | Refrigerated meat lockers, humidity control | Ice beds, temperature-controlled display |
| Food Safety | Strict hygiene and cross-contamination control | Preventing spoilage, maintaining freshness |
| Customer Base | Steakhouse, butcher shops, restaurants | Seafood markets, restaurants, hotels |
Key Roles and Responsibilities
A butcher specializes in meat preparation, including cutting, trimming, and curing various types of meats to ensure quality and safety for foodservice establishments. A fishmonger focuses on selecting, gutting, filleting, and preserving fresh seafood to maintain optimal flavor and freshness. Both roles require expert knowledge of product handling, hygiene standards, and customer service within the foodservice industry.
Required Skills and Expertise
A butcher requires expertise in meat cutting, knowledge of animal anatomy, and proficiency in handling various knives and machinery to prepare and portion meat products accurately. A fishmonger specializes in seafood, needing skills in filleting, scaling, and recognizing freshness indicators, as well as understanding sustainable sourcing practices. Both roles demand strong hygiene standards, customer service abilities, and product knowledge to ensure quality and safety in foodservice environments.
Tools and Equipment Used
Butchers rely on heavy-duty knives, cleavers, meat grinders, and bone saws to cut, trim, and process various types of meat with precision. Fishmongers use specialized tools such as fillet knives, fish scalers, bone tweezers, and gutting spoons designed to handle delicate fish and seafood without damaging the flesh. Both professionals utilize sharpening steels and cutting boards tailored to their specific needs, ensuring hygiene and efficiency in food preparation.
Training and Certifications
Butchers typically undergo formal apprenticeships or vocational training programs focusing on meat cutting, food safety, and hygiene, often earning certifications such as ServSafe or Certified Meat Cutter. Fishmongers, on the other hand, receive specialized training in seafood handling, filleting, and preservation techniques, with certifications like HACCP Seafood or Fish Handling Safety courses being essential. Both professions require knowledge of regulatory standards and practical skills to ensure quality, safety, and customer satisfaction in foodservice environments.
Workplace Environments
Butchers typically work in environments like meat processing plants, butcher shops, or supermarket meat departments, where temperature control and sanitation are critical to handle raw meat safely. Fishmongers operate in specialized fish markets, seafood counters, or fish processing facilities, requiring cold storage and swift turnover to maintain seafood freshness. Both professions demand precise hygiene standards and equipment designed for their specific protein types to ensure food safety and quality.
Product Handling and Preparation
Butchers specialize in handling and preparing various cuts of meat, employing techniques such as trimming, deboning, and portioning to ensure optimal quality and freshness for cooking. Fishmongers focus on selecting, cleaning, filleting, and sometimes curing or smoking fish and seafood, emphasizing delicate handling to preserve texture and flavor. Both professions require extensive knowledge of food safety standards and proper storage temperatures to maintain product integrity in the foodservice industry.
Customer Interaction and Service
Butchers and fishmongers both provide specialized customer interaction by offering expert advice tailored to their respective products, whether meat or seafood. Butchers often assist customers in selecting cuts, suggesting cooking methods, and customizing orders, while fishmongers emphasize freshness, seasonal availability, and sustainable sourcing. Exceptional service in both roles builds trust, enhances customer satisfaction, and encourages repeat business in the foodservice industry.
Health and Safety Standards
Butchers and fishmongers both adhere to strict health and safety standards to prevent contamination and ensure food quality. Butchers focus on proper meat handling, maintaining clean cutting surfaces, and controlling temperatures to inhibit bacterial growth, while fishmongers prioritize preventing cross-contamination by using separate tools and refrigerated displays to keep fish fresh. Compliance with HACCP guidelines and regular inspections is critical in both professions to maintain safe foodservice environments.
Career Progression Opportunities
Career progression opportunities in foodservice differ significantly between butchers and fishmongers, with butchers often advancing to roles such as meat department managers, quality control supervisors, or supply chain coordinators due to the broader demand for meat processing expertise. Fishmongers can evolve into seafood specialists, quality assurance managers, or seafood procurement officers, capitalizing on the growing consumer demand for sustainable and fresh seafood. Both careers benefit from advanced training in food safety and product knowledge, but butchers generally access a wider range of positions in retail chains and meat production facilities.
Industry Demand and Trends
The foodservice industry is experiencing a rising demand for both butchers and fishmongers due to increasing consumer preference for fresh, high-quality protein. Butchers are adapting to trends by offering sustainably sourced, ethically raised meats, while fishmongers focus on providing wild-caught and farm-raised seafood with traceability. Market growth in specialty meats and seafood highlights the critical role these skilled professionals play in meeting evolving culinary and health-conscious consumer demands.
Butcher vs Fishmonger Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com