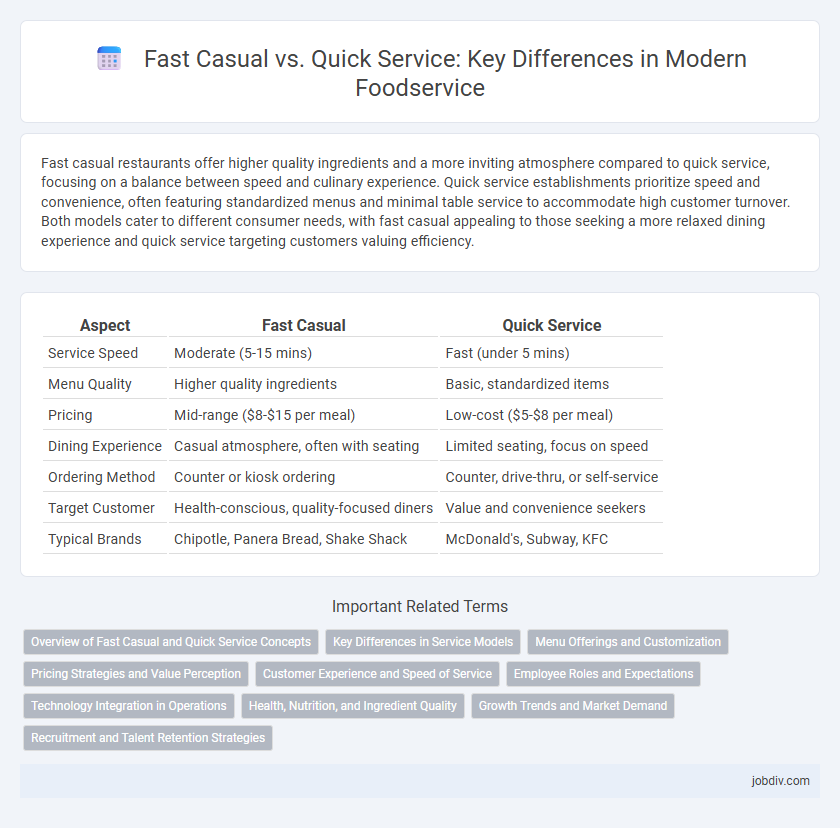
Fast casual restaurants offer higher quality ingredients and a more inviting atmosphere compared to quick service, focusing on a balance between speed and culinary experience. Quick service establishments prioritize speed and convenience, often featuring standardized menus and minimal table service to accommodate high customer turnover. Both models cater to different consumer needs, with fast casual appealing to those seeking a more relaxed dining experience and quick service targeting customers valuing efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fast Casual | Quick Service |
|---|---|---|
| Service Speed | Moderate (5-15 mins) | Fast (under 5 mins) |
| Menu Quality | Higher quality ingredients | Basic, standardized items |
| Pricing | Mid-range ($8-$15 per meal) | Low-cost ($5-$8 per meal) |
| Dining Experience | Casual atmosphere, often with seating | Limited seating, focus on speed |
| Ordering Method | Counter or kiosk ordering | Counter, drive-thru, or self-service |
| Target Customer | Health-conscious, quality-focused diners | Value and convenience seekers |
| Typical Brands | Chipotle, Panera Bread, Shake Shack | McDonald's, Subway, KFC |
Overview of Fast Casual and Quick Service Concepts
Fast Casual restaurants combine the speed of quick service with higher-quality ingredients and a more upscale dining environment, targeting customers who seek convenience without sacrificing food quality. Quick Service establishments prioritize rapid service, low prices, and high efficiency, catering to customers looking for fast, affordable meals. Both concepts utilize streamlined operations but differ significantly in menu offerings, price points, and overall customer experience.
Key Differences in Service Models
Fast Casual restaurants offer higher quality food and a more inviting dining environment than Quick Service establishments, with an emphasis on customization and made-to-order meals. Quick Service models focus on speed and efficiency, often utilizing pre-prepared ingredients to serve customers rapidly, typically featuring drive-thru or counter service. The pricing in Fast Casual tends to be moderately higher, reflecting fresher ingredients and enhanced customer experience, while Quick Service prioritizes affordability and convenience.
Menu Offerings and Customization
Fast Casual restaurants offer diverse, chef-inspired menu offerings with fresh, high-quality ingredients that emphasize customization to cater to individual dietary preferences and trends such as plant-based or gluten-free options. Quick Service establishments prioritize speed and efficiency with standardized menus featuring limited customization, focusing on core items designed for rapid preparation and turnover. The level of menu customization directly influences customer experience and operational complexity, making Fast Casual appealing for personalized dining while Quick Service excels in convenience and consistency.
Pricing Strategies and Value Perception
Fast casual restaurants implement tiered pricing strategies that emphasize fresh ingredients and customizable menu options, fostering a higher perceived value compared to quick service establishments. Quick service pricing focuses on affordability and speed, often using value meals and promotional discounts to attract cost-conscious consumers. Consumer perception of value in fast casual centers on quality and experience, while quick service appeals primarily through convenience and low prices.
Customer Experience and Speed of Service
Fast Casual restaurants prioritize a higher-quality customer experience with fresh ingredients and customizable menu options, often featuring modern dining environments that encourage longer visits. Quick Service establishments emphasize speed of service and convenience, delivering food within minutes through streamlined ordering and preparation processes designed for high customer turnover. Balancing speed and experience, Fast Casual appeals to customers seeking flavor and ambiance, while Quick Service targets those needing rapid meals during busy schedules.
Employee Roles and Expectations
Fast casual restaurants require employees to balance customer interaction with food preparation, emphasizing personalized service and higher culinary skills. Quick service roles prioritize speed and efficiency, focusing on order accuracy and rapid service to manage high customer volume. Employee expectations in fast casual include multitasking with a focus on quality, while quick service demands consistent performance under fast-paced conditions.
Technology Integration in Operations
Fast Casual restaurants leverage advanced technology integration such as table-top ordering systems and mobile app customization to enhance customer experience and streamline order accuracy. Quick Service establishments prioritize rapid transaction technologies including self-service kiosks and contactless payment methods to minimize wait times and increase throughput. Both models utilize data analytics for inventory management and personalized marketing, optimizing operational efficiency and customer engagement in the foodservice industry.
Health, Nutrition, and Ingredient Quality
Fast casual restaurants prioritize higher-quality ingredients, often featuring organic, locally sourced produce and hormone-free meats, enhancing nutritional value compared to quick service chains. Nutritional transparency is typically greater in fast casual venues, enabling customers to make health-conscious decisions with access to detailed calorie counts and allergen information. Quick service establishments emphasize speed and convenience but often rely on processed ingredients and higher sodium, fat, and sugar content, impacting overall health outcomes.
Growth Trends and Market Demand
Fast casual restaurants are experiencing a significant growth trend driven by consumer demand for higher-quality ingredients and customizable menu options, capturing a larger share of the foodservice market. Quick service establishments continue to maintain strong market demand due to their convenience, affordability, and speed, particularly in urban and high-traffic areas. Industry reports project fast casual growth at an annual rate of 8-10%, outpacing quick service expansion which hovers around 3-5%, reflecting evolving consumer preferences towards premium and health-conscious dining experiences.
Recruitment and Talent Retention Strategies
Fast Casual restaurants emphasize hiring skilled culinary and customer service professionals by offering competitive benefits and clear career growth pathways to enhance talent retention. Quick Service establishments focus on high-volume recruitment and fast onboarding processes, utilizing incentives and flexible scheduling to reduce turnover rates. Data shows that companies investing in employee development programs experience up to 25% higher retention in both Foodservice segments.
Fast Casual vs Quick Service Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com