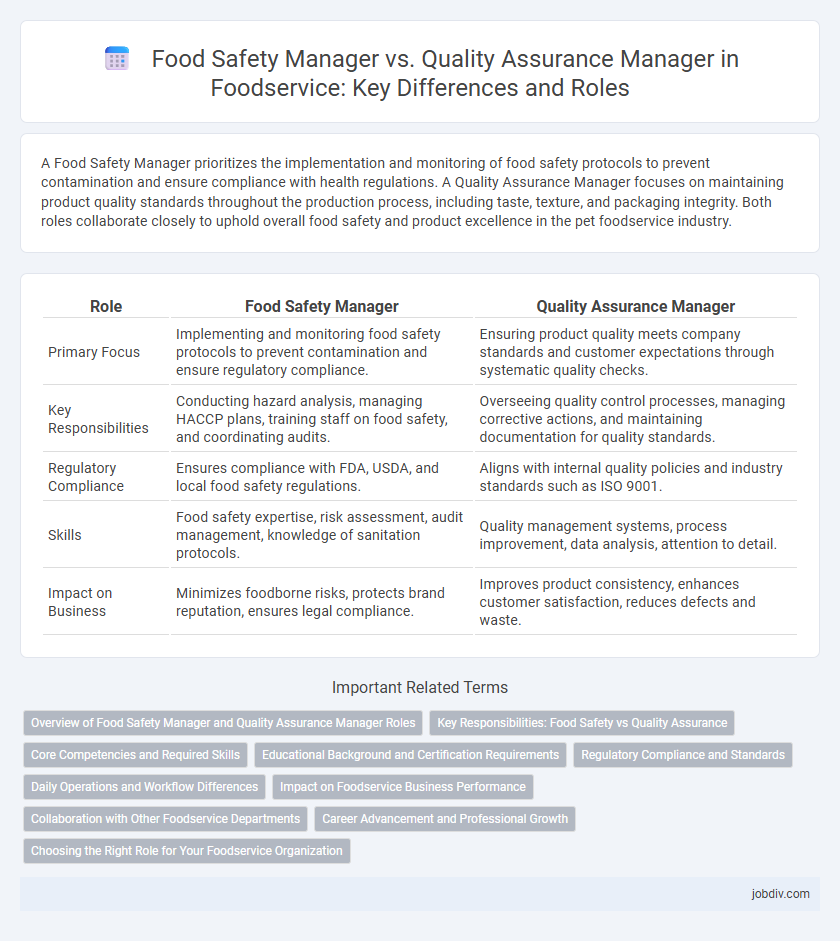
A Food Safety Manager prioritizes the implementation and monitoring of food safety protocols to prevent contamination and ensure compliance with health regulations. A Quality Assurance Manager focuses on maintaining product quality standards throughout the production process, including taste, texture, and packaging integrity. Both roles collaborate closely to uphold overall food safety and product excellence in the pet foodservice industry.
Table of Comparison
| Role | Food Safety Manager | Quality Assurance Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Implementing and monitoring food safety protocols to prevent contamination and ensure regulatory compliance. | Ensuring product quality meets company standards and customer expectations through systematic quality checks. |
| Key Responsibilities | Conducting hazard analysis, managing HACCP plans, training staff on food safety, and coordinating audits. | Overseeing quality control processes, managing corrective actions, and maintaining documentation for quality standards. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Ensures compliance with FDA, USDA, and local food safety regulations. | Aligns with internal quality policies and industry standards such as ISO 9001. |
| Skills | Food safety expertise, risk assessment, audit management, knowledge of sanitation protocols. | Quality management systems, process improvement, data analysis, attention to detail. |
| Impact on Business | Minimizes foodborne risks, protects brand reputation, ensures legal compliance. | Improves product consistency, enhances customer satisfaction, reduces defects and waste. |
Overview of Food Safety Manager and Quality Assurance Manager Roles
Food Safety Managers oversee compliance with food safety regulations and implement hazard analysis control measures to prevent contamination and ensure consumer safety. Quality Assurance Managers focus on maintaining product quality standards through systematic testing, documentation, and continuous improvement processes within food production. Both roles are critical in the foodservice industry to uphold regulatory compliance and deliver safe, high-quality products to customers.
Key Responsibilities: Food Safety vs Quality Assurance
Food Safety Managers are responsible for developing and implementing food safety programs, conducting hazard analysis, and ensuring compliance with FDA and USDA regulations to prevent contamination and foodborne illnesses. Quality Assurance Managers focus on maintaining product consistency, monitoring quality control processes, and managing audits to meet industry standards like ISO 22000 and HACCP certifications. Both roles collaborate to enhance food safety culture while driving continuous improvement in foodservice operations.
Core Competencies and Required Skills
Food Safety Managers specialize in hazard analysis, regulatory compliance, and contamination prevention to ensure safe food handling and production processes. Quality Assurance Managers focus on product quality standards, process optimization, and continuous improvement methodologies such as Six Sigma and ISO standards. Both roles demand strong analytical skills, attention to detail, and proficiency in risk management software, but Food Safety Managers prioritize food safety protocols while Quality Assurance Managers emphasize quality control and customer satisfaction.
Educational Background and Certification Requirements
Food Safety Managers typically hold degrees in food science, microbiology, or public health, with certifications such as the Certified Food Safety Manager (CFSM) or ServSafe Manager. Quality Assurance Managers often possess educational backgrounds in food technology, engineering, or quality management, complemented by certifications like Certified Quality Auditor (CQA) or Six Sigma Green Belt. Both roles demand specialized training, but Food Safety Managers emphasize hazard control and regulatory compliance, whereas Quality Assurance Managers focus on process optimization and product consistency.
Regulatory Compliance and Standards
Food Safety Managers ensure strict adherence to regulatory compliance by implementing food safety standards such as HACCP, FDA, and USDA guidelines to prevent contamination and foodborne illnesses. Quality Assurance Managers oversee product quality control processes and certify that food products meet industry standards and customer specifications while aligning with regulatory requirements. Both roles are critical in maintaining compliance, but Food Safety Managers focus more on hazard prevention and safety regulations, whereas Quality Assurance Managers emphasize quality consistency and standard protocol adherence.
Daily Operations and Workflow Differences
Food Safety Managers focus on daily operations by ensuring compliance with health regulations, conducting hazard analyses, and implementing sanitation protocols to prevent contamination. Quality Assurance Managers oversee workflow by monitoring product standards, managing quality control processes, and coordinating corrective actions to maintain consistent food quality. Both roles require detailed documentation, but Food Safety emphasizes risk prevention while Quality Assurance prioritizes product consistency and customer satisfaction.
Impact on Foodservice Business Performance
Food Safety Managers ensure compliance with health regulations and implement protocols that prevent contamination and foodborne illnesses, directly reducing risks of costly recalls and reputational damage in foodservice operations. Quality Assurance Managers focus on maintaining product consistency, optimizing processes, and meeting customer expectations, which enhances operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. The combined efforts of both managers significantly improve foodservice business performance by fostering trust, ensuring legal compliance, and driving sustainable growth.
Collaboration with Other Foodservice Departments
Food Safety Managers collaborate closely with kitchen staff, procurement, and sanitation teams to enforce hygiene protocols and prevent contamination risks throughout food preparation and storage. Quality Assurance Managers work alongside product development, supply chain, and customer service departments to ensure consistent quality standards and compliance with regulatory requirements. Both roles require seamless communication and coordinated efforts to maintain overall foodservice safety and quality integrity.
Career Advancement and Professional Growth
Food Safety Managers specialize in implementing regulatory compliance and hazard analysis protocols, making them crucial for risk management and operational safety in foodservice environments. Quality Assurance Managers oversee product consistency and process improvements, driving standards that enhance customer satisfaction and brand reputation. Career advancement in food safety often leads to roles in regulatory affairs or risk management, while quality assurance professionals may progress into supply chain leadership or product development, both pathways offering ample opportunities for professional growth.
Choosing the Right Role for Your Foodservice Organization
Food Safety Managers prioritize compliance with health regulations and implement protocols to prevent contamination, essential for maintaining public trust and avoiding costly recalls. Quality Assurance Managers concentrate on systematic testing and continuous improvement of products and processes to ensure consistent food quality and customer satisfaction. Selecting the right role depends on whether your foodservice organization needs stricter regulatory adherence or enhanced product reliability to meet consumer demands.
Food Safety Manager vs Quality Assurance Manager Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com