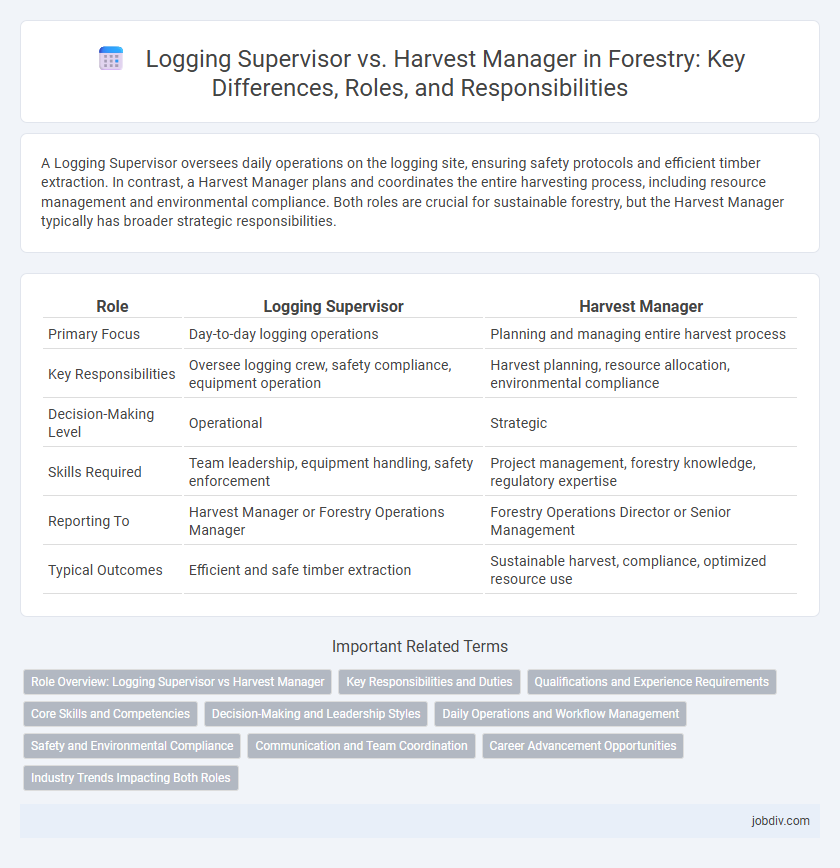
A Logging Supervisor oversees daily operations on the logging site, ensuring safety protocols and efficient timber extraction. In contrast, a Harvest Manager plans and coordinates the entire harvesting process, including resource management and environmental compliance. Both roles are crucial for sustainable forestry, but the Harvest Manager typically has broader strategic responsibilities.
Table of Comparison
| Role | Logging Supervisor | Harvest Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Day-to-day logging operations | Planning and managing entire harvest process |
| Key Responsibilities | Oversee logging crew, safety compliance, equipment operation | Harvest planning, resource allocation, environmental compliance |
| Decision-Making Level | Operational | Strategic |
| Skills Required | Team leadership, equipment handling, safety enforcement | Project management, forestry knowledge, regulatory expertise |
| Reporting To | Harvest Manager or Forestry Operations Manager | Forestry Operations Director or Senior Management |
| Typical Outcomes | Efficient and safe timber extraction | Sustainable harvest, compliance, optimized resource use |
Role Overview: Logging Supervisor vs Harvest Manager
Logging Supervisors oversee daily timber harvesting operations, ensuring worker safety, equipment functionality, and compliance with environmental regulations on-site. Harvest Managers plan and coordinate entire harvesting projects, managing budgets, scheduling, and liaising with stakeholders to optimize forest resource utilization. Both roles require strong leadership and knowledge of sustainable forestry practices but differ in scope, with Logging Supervisors focusing on field execution and Harvest Managers on strategic oversight.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
Logging Supervisors oversee on-site logging operations, ensuring safety compliance, equipment maintenance, and direct worker supervision to maximize productivity. Harvest Managers plan and coordinate the entire timber harvest process, including scheduling, resource allocation, and regulatory adherence to optimize sustainable yield. Both roles require strong leadership, but Harvest Managers focus more on strategic planning and environmental stewardship, while Logging Supervisors handle day-to-day operational tasks.
Qualifications and Experience Requirements
Logging Supervisors typically require hands-on experience in timber harvesting, safety management certifications, and knowledge of equipment operation, emphasizing practical skills in crew coordination and on-site decision-making. Harvest Managers often hold advanced degrees in forestry or natural resource management, coupled with extensive experience in strategic planning, regulatory compliance, and sustainable resource management practices. Both roles demand strong leadership abilities, but Harvest Managers focus more on long-term operational planning and environmental impact assessment.
Core Skills and Competencies
Logging Supervisors excel in operational oversight, crew management, and safety compliance, ensuring efficient timber extraction while adhering to environmental regulations. Harvest Managers demonstrate strategic planning, resource allocation, and sustainability practices, optimizing harvest schedules and ecosystem impact assessments. Both roles require strong communication, leadership, and knowledge of forestry equipment and regulations to drive productive and compliant forestry operations.
Decision-Making and Leadership Styles
Logging Supervisors prioritize operational efficiency and safety by making tactical decisions on-site, emphasizing direct leadership and immediate problem-solving with crew members. Harvest Managers adopt a strategic approach, integrating sustainable forestry practices and long-term resource management, guiding multiple teams through collaborative leadership and cross-functional coordination. Effective decision-making in these roles hinges on balancing real-time operational control with overarching environmental and business objectives.
Daily Operations and Workflow Management
Logging Supervisors coordinate daily field operations, ensuring compliance with safety protocols and optimizing crew productivity during timber harvesting. Harvest Managers oversee comprehensive workflow management, integrating planning, resource allocation, and logistics to maximize efficiency and sustainability across multiple logging sites. Both roles require adaptive decision-making and effective communication to maintain smooth operational progress in forestry projects.
Safety and Environmental Compliance
Logging Supervisors directly manage on-site operations, ensuring that logging crews adhere to strict safety protocols such as proper equipment use and hazard communication to minimize workplace accidents. Harvest Managers oversee the entire timber harvest process, integrating environmental compliance measures like erosion control, wildlife habitat preservation, and sustainable harvesting practices to meet regulatory standards. Both roles require comprehensive knowledge of OSHA regulations and local environmental laws to effectively balance productivity with safety and ecological responsibility.
Communication and Team Coordination
Logging Supervisors oversee daily logging operations, ensuring clear communication between field crews and equipment operators to maintain safety and efficiency. Harvest Managers coordinate broader team efforts by planning harvest schedules, optimizing resource allocation, and facilitating interdepartmental communication to achieve sustainable forestry goals. Effective communication and team coordination in both roles are critical for minimizing operational downtime and maximizing productivity in timber harvesting.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Logging Supervisors typically handle on-site operations and crew management, serving as a critical step in gaining practical field experience essential for progressing in forestry careers. Harvest Managers oversee broader planning and resource allocation, positioning themselves for strategic leadership roles within forest management or operations. Transitioning from Logging Supervisor to Harvest Manager represents a significant career advancement by expanding responsibility from tactical execution to organizational oversight.
Industry Trends Impacting Both Roles
Emerging industry trends such as increased automation, sustainable harvesting practices, and stricter regulatory compliance significantly impact both Logging Supervisors and Harvest Managers, demanding advanced skills in technology integration and environmental stewardship. Logging Supervisors must adapt to real-time data analytics and equipment automation to optimize operational efficiency, while Harvest Managers focus on strategic planning that aligns with conservation policies and market demands. Both roles are influenced by the growing emphasis on sustainable forest management and climate change mitigation efforts, requiring continuous updates in training and operational protocols.
Logging Supervisor vs Harvest Manager Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com