Baristas specialize in crafting coffee beverages, mastering espresso machines, and creating latte art, ensuring a personalized cafe experience. Bartenders focus on mixing, garnishing, and serving alcoholic drinks while maintaining a lively and social atmosphere at the bar. Both roles require excellent customer service skills but differ significantly in their drink preparation techniques and workplace environments.
Table of Comparison
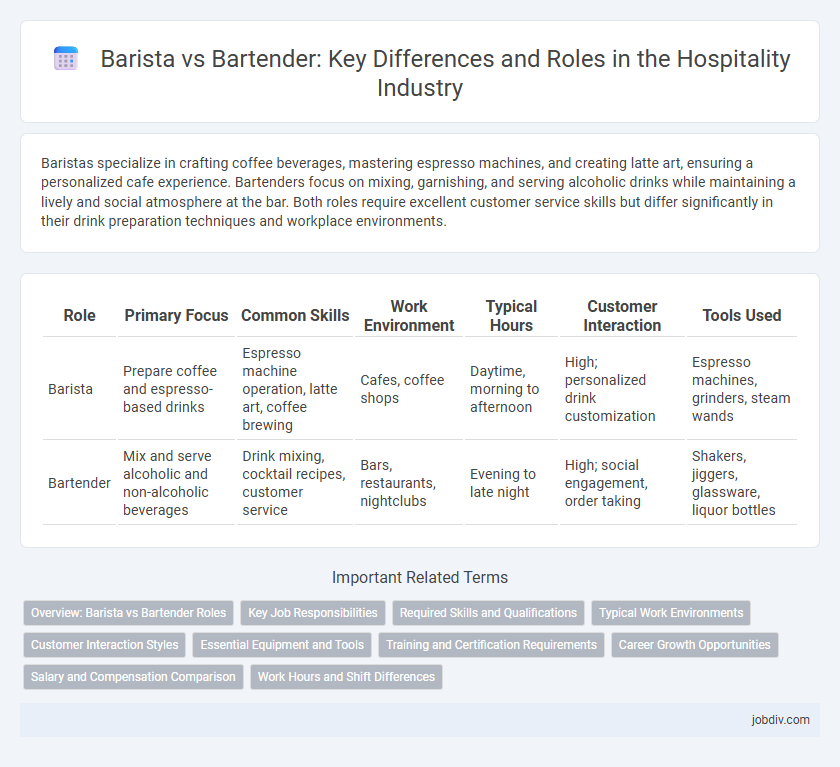
| Role | Primary Focus | Common Skills | Work Environment | Typical Hours | Customer Interaction | Tools Used |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barista | Prepare coffee and espresso-based drinks | Espresso machine operation, latte art, coffee brewing | Cafes, coffee shops | Daytime, morning to afternoon | High; personalized drink customization | Espresso machines, grinders, steam wands |
| Bartender | Mix and serve alcoholic and non-alcoholic beverages | Drink mixing, cocktail recipes, customer service | Bars, restaurants, nightclubs | Evening to late night | High; social engagement, order taking | Shakers, jiggers, glassware, liquor bottles |
Overview: Barista vs Bartender Roles
Baristas specialize in crafting espresso-based beverages and managing coffee equipment, prioritizing precise brewing techniques and customer customization. Bartenders focus on mixing, garnishing, and serving alcoholic and non-alcoholic drinks, often requiring knowledge of cocktail recipes, spirits, and bar inventory management. Both roles demand strong customer service skills, but baristas emphasize coffee preparation while bartenders handle a broader range of drink types and social interaction settings.
Key Job Responsibilities
Baristas expertly brew and serve coffee and espresso-based beverages while maintaining high standards of cleanliness and customer service in cafes. Bartenders skillfully mix, garnish, and serve alcoholic and non-alcoholic drinks, manage bar inventory, and ensure compliance with licensing laws in pubs or nightlife venues. Both roles require strong interpersonal skills, product knowledge, and the ability to work efficiently in fast-paced environments.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Baristas must possess expert coffee brewing skills, deep knowledge of espresso machines, and exceptional customer service abilities to craft personalized beverages efficiently. Bartenders require proficiency in mixology, knowledge of a wide range of alcoholic beverages, and strong multitasking skills to manage high-volume service and create creative cocktails. Both roles benefit from excellent communication skills, attention to detail, and the ability to work in fast-paced hospitality environments.
Typical Work Environments
Baristas typically work in coffee shops, cafes, and specialty coffee retailers focused on crafting espresso-based beverages and maintaining high-quality coffee standards. Bartenders are commonly found in bars, pubs, restaurants, and nightclubs, where they mix drinks, serve alcohol, and engage with customers in a fast-paced setting. Both roles demand excellent customer service skills but differ significantly in ambiance, work hours, and the nature of beverage preparation.
Customer Interaction Styles
Baristas emphasize personalized, friendly interactions by engaging customers in conversations about coffee preferences, brewing methods, and flavor profiles, creating a warm and inviting atmosphere. Bartenders adopt a dynamic and conversational style, balancing socializing with multiple patrons while efficiently mixing drinks and managing orders in a lively environment. Both professions require strong interpersonal skills, but baristas tend to foster one-on-one connections, whereas bartenders excel in multitasking and entertaining larger groups.
Essential Equipment and Tools
Baristas rely on espresso machines, grinders, frothers, and tampers designed specifically for coffee preparation, ensuring precision in brewing and milk texturing. Bartenders use shakers, strainers, muddlers, jiggers, and pour spouts to mix and serve cocktails efficiently. Both roles require tools tailored to their beverage focus, emphasizing the importance of specialized equipment for optimal service in hospitality.
Training and Certification Requirements
Baristas typically undergo specialized training in coffee brewing techniques, latte art, and espresso machine operation, with certifications offered by organizations like the Specialty Coffee Association (SCA). Bartenders require training in mixology, drink recipes, and responsible alcohol service, often earning certification through programs such as the Alcohol Server Education (ASE) or TIPS certification. Both roles emphasize hands-on experience and customer service skills, but bartending certifications frequently include legal knowledge about alcohol laws and safety procedures.
Career Growth Opportunities
Baristas often advance their careers by specializing in coffee craftsmanship, opening their own cafes, or transitioning into roles such as coffee roasters and trainers within the specialty coffee industry. Bartenders can develop expertise in mixology, progress to bar management, or become beverage directors in upscale hospitality venues, expanding their influence on menu design and customer experience. Both careers offer distinct pathways, with bartending typically providing faster access to leadership positions in diverse beverage settings while barista roles emphasize product knowledge and customer service in coffee-focused environments.
Salary and Compensation Comparison
Baristas typically earn an hourly wage ranging from $11 to $15, with additional income potential through tips averaging $2 to $5 per hour, depending on location and establishment type. Bartenders often receive higher base pay, between $12 and $18 per hour, plus tips that can significantly increase total compensation, sometimes doubling the hourly rate in busy venues. Overall, bartenders generally have a higher earning potential than baristas due to greater tipping opportunities and premium service environments.
Work Hours and Shift Differences
Baristas typically work early morning to mid-afternoon shifts, catering to breakfast and lunch crowds in coffee shops or cafes, with peak hours between 6 AM and 2 PM. Bartenders often have later shifts, starting in the late afternoon and continuing into the night, especially in bars or restaurants, covering peak hours from 5 PM to 2 AM. The difference in work hours reflects the varying customer demand patterns, with baristas aligned to daytime business hours and bartenders to evening and late-night social activities.
Barista vs Bartender Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com