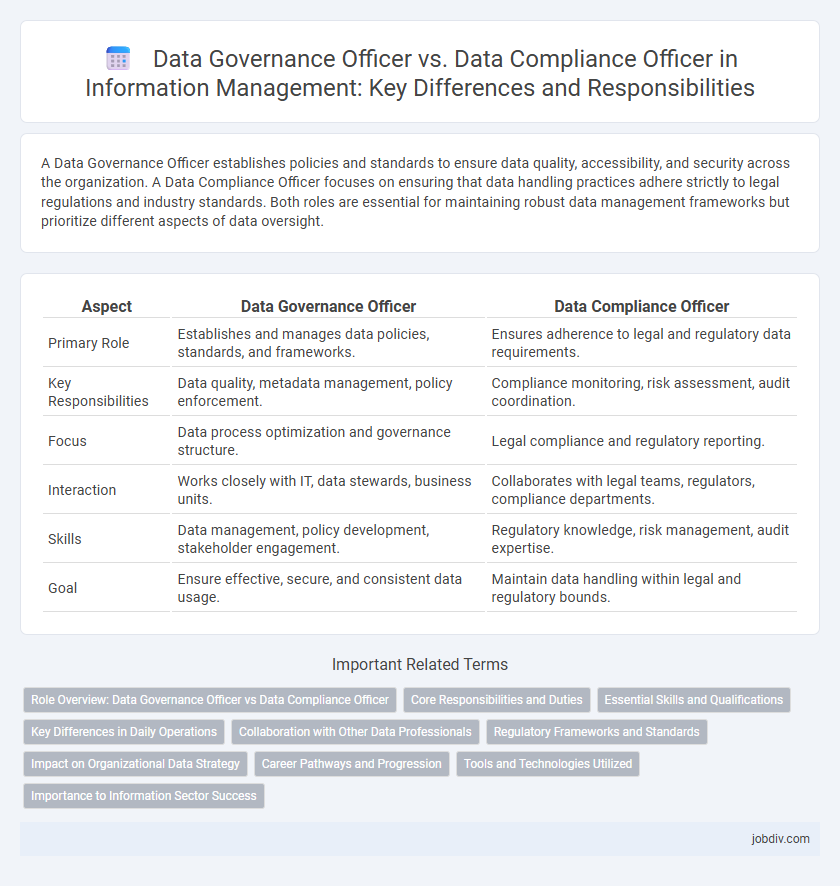
A Data Governance Officer establishes policies and standards to ensure data quality, accessibility, and security across the organization. A Data Compliance Officer focuses on ensuring that data handling practices adhere strictly to legal regulations and industry standards. Both roles are essential for maintaining robust data management frameworks but prioritize different aspects of data oversight.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Data Governance Officer | Data Compliance Officer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Establishes and manages data policies, standards, and frameworks. | Ensures adherence to legal and regulatory data requirements. |
| Key Responsibilities | Data quality, metadata management, policy enforcement. | Compliance monitoring, risk assessment, audit coordination. |
| Focus | Data process optimization and governance structure. | Legal compliance and regulatory reporting. |
| Interaction | Works closely with IT, data stewards, business units. | Collaborates with legal teams, regulators, compliance departments. |
| Skills | Data management, policy development, stakeholder engagement. | Regulatory knowledge, risk management, audit expertise. |
| Goal | Ensure effective, secure, and consistent data usage. | Maintain data handling within legal and regulatory bounds. |
Role Overview: Data Governance Officer vs Data Compliance Officer
A Data Governance Officer oversees the establishment and enforcement of data policies, ensuring data quality, integrity, and accessibility across an organization. In contrast, a Data Compliance Officer focuses on adherence to legal regulations and industry standards, managing risk related to data privacy and security compliance. Both roles collaborate to align data management practices with organizational goals and regulatory requirements.
Core Responsibilities and Duties
A Data Governance Officer focuses on establishing policies, standards, and frameworks that ensure the effective management and quality of enterprise data assets. A Data Compliance Officer centers on monitoring adherence to data protection regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and industry-specific laws, ensuring organizational compliance and risk mitigation. Both roles collaborate to align data practices with legal requirements and internal governance objectives.
Essential Skills and Qualifications
Data Governance Officers require strong expertise in data management frameworks, policy development, and risk assessment to ensure organizational data integrity and accessibility. Data Compliance Officers must possess in-depth knowledge of regulatory requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, and industry-specific standards, along with skills in auditing, monitoring, and enforcement of compliance protocols. Both roles benefit from proficiency in data analysis tools, communication skills, and the ability to align data practices with corporate governance and legal mandates.
Key Differences in Daily Operations
Data Governance Officers primarily focus on establishing data policies, standards, and frameworks to ensure data quality and usability across the organization. In contrast, Data Compliance Officers concentrate on monitoring adherence to legal regulations and industry standards, enforcing data privacy and security requirements. Daily operations for Data Governance Officers involve data stewardship and policy development, while Data Compliance Officers perform audits, risk assessments, and compliance reporting.
Collaboration with Other Data Professionals
Data Governance Officers collaborate closely with data stewards, architects, and analysts to establish and enforce data policies, ensuring data quality and consistency across the organization. Data Compliance Officers work alongside legal teams, risk managers, and auditors to ensure adherence to regulatory requirements and mitigate compliance risks. Both roles require seamless coordination to balance governance frameworks with regulatory mandates, fostering a unified data management strategy.
Regulatory Frameworks and Standards
Data Governance Officers develop and enforce internal policies aligned with regulatory frameworks like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA to ensure data quality and security. Data Compliance Officers specialize in monitoring and auditing compliance with these standards, focusing on legal adherence and risk mitigation. Both roles collaborate to maintain organizational data integrity while meeting evolving regulatory requirements.
Impact on Organizational Data Strategy
A Data Governance Officer drives the development and implementation of data policies, ensuring data quality, consistency, and accessibility across the organization to support strategic decision-making. In contrast, a Data Compliance Officer focuses on adherence to regulatory requirements, minimizing legal risks related to data privacy and protection. Both roles impact organizational data strategy by balancing data utilization with compliance, but the Governance Officer aligns data management practices with business goals while the Compliance Officer safeguards against regulatory penalties.
Career Pathways and Progression
Data Governance Officers typically advance by developing expertise in data management frameworks, policy creation, and aligning data strategy with business objectives, often progressing to roles such as Chief Data Officer or Head of Data Governance. Data Compliance Officers focus on regulatory requirements, risk management, and ensuring organizational adherence to data privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA, positioning themselves for senior roles in compliance, risk management, or legal advisory. Both career pathways demand continuous skills development in data privacy, security, and regulatory landscapes, with progression influenced by industry trends and organizational data maturity.
Tools and Technologies Utilized
Data Governance Officers primarily utilize data cataloging tools, metadata management systems, and data quality platforms to ensure data accuracy, lineage, and consistency across the organization. Data Compliance Officers rely heavily on compliance management software, regulatory reporting tools, and automated audit solutions to monitor adherence to legal standards and data privacy regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA. Both roles increasingly integrate advanced analytics and AI-driven platforms to streamline data oversight and risk management processes efficiently.
Importance to Information Sector Success
Data Governance Officers establish frameworks ensuring data quality, security, and accessibility, directly impacting decision-making and operational efficiency in the information sector. Data Compliance Officers focus on adherence to regulations like GDPR and HIPAA, mitigating legal risks and protecting organizational reputation. Both roles are crucial for information sector success by balancing robust data management with strict regulatory compliance.
Data Governance Officer vs Data Compliance Officer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com