Data Wranglers specialize in cleaning, transforming, and preparing raw data for analysis, ensuring accuracy and usability. Data Modelers design and create database structures by defining relationships, rules, and data flows to support business requirements. Both roles are critical for effective data management but focus on different stages of the data lifecycle.
Table of Comparison
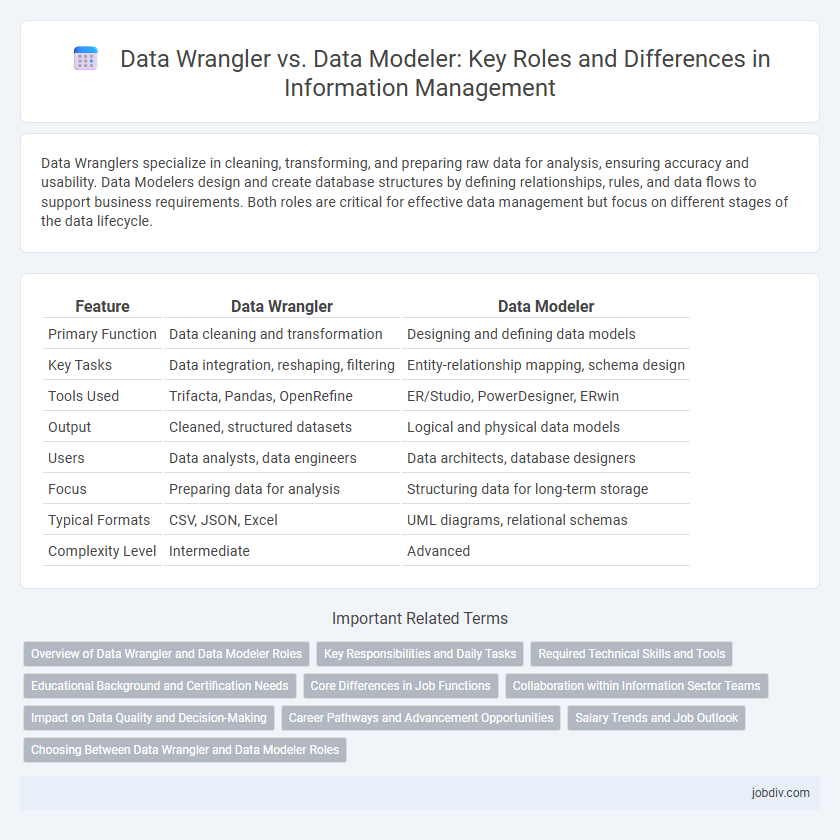
| Feature | Data Wrangler | Data Modeler |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Data cleaning and transformation | Designing and defining data models |
| Key Tasks | Data integration, reshaping, filtering | Entity-relationship mapping, schema design |
| Tools Used | Trifacta, Pandas, OpenRefine | ER/Studio, PowerDesigner, ERwin |
| Output | Cleaned, structured datasets | Logical and physical data models |
| Users | Data analysts, data engineers | Data architects, database designers |
| Focus | Preparing data for analysis | Structuring data for long-term storage |
| Typical Formats | CSV, JSON, Excel | UML diagrams, relational schemas |
| Complexity Level | Intermediate | Advanced |
Overview of Data Wrangler and Data Modeler Roles
Data Wrangler roles center on cleaning, transforming, and preparing raw data for analysis, ensuring data quality and consistency. Data Modelers focus on designing and structuring databases, creating data schemas and models that represent business processes and support analytics. Both roles are critical in the data pipeline, with Data Wranglers handling data preprocessing and Data Modelers optimizing data architecture for efficient storage and retrieval.
Key Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
Data Wranglers specialize in cleaning, transforming, and organizing raw data from diverse sources to ensure it is analysis-ready, typically handling data extraction, normalization, and quality checks daily. Data Modelers focus on designing and optimizing data structures, creating logical and physical data models to support database architecture and business requirements. While Data Wranglers manage the preparation and preprocessing of data, Data Modelers develop frameworks that enable efficient data storage, retrieval, and integration.
Required Technical Skills and Tools
Data Wranglers need strong proficiency in data cleaning and transformation using tools like Python, R, and ETL platforms such as Talend or Alteryx. Data Modelers require expertise in database design, normalization, and ER modeling, often leveraging tools like ER/Studio, IBM InfoSphere Data Architect, or Microsoft Visio. Both roles demand knowledge of SQL, but Data Wranglers focus more on raw data manipulation while Data Modelers emphasize structured schema development.
Educational Background and Certification Needs
Data Wranglers typically hold degrees in computer science, data science, or related fields, emphasizing skills in data cleaning, transformation, and preprocessing. Data Modelers often have backgrounds in database management, information systems, or software engineering, with expertise in designing and structuring data architectures. Certifications such as Certified Data Management Professional (CDMP) benefit Data Modelers, while Data Wranglers may pursue credentials like Microsoft Certified: Data Analyst Associate to validate their technical proficiency.
Core Differences in Job Functions
Data Wranglers specialize in cleaning, transforming, and preparing raw data for analysis, ensuring data quality and usability. Data Modelers design and create data structures and schemas that define how data is stored, accessed, and related within databases and systems. While Data Wranglers focus on data preprocessing and handling inconsistencies, Data Modelers concentrate on database architecture and optimizing data organization for efficient querying.
Collaboration within Information Sector Teams
Data Wranglers and Data Modelers collaborate closely within information sector teams to streamline data processing and structure development. Data Wranglers focus on cleaning, transforming, and preparing raw datasets for analysis, ensuring data quality and consistency. Data Modelers design logical and physical data structures, enabling seamless integration and efficient data flow, which supports collaborative decision-making and innovation.
Impact on Data Quality and Decision-Making
Data Wranglers enhance data quality by cleaning, transforming, and integrating raw datasets, ensuring accuracy and consistency for reliable analysis. Data Modelers improve decision-making by designing structured data architectures that enable efficient data retrieval and interpretation, supporting strategic insights. Together, they optimize data workflows, increasing the overall effectiveness of data-driven decisions.
Career Pathways and Advancement Opportunities
Data Wrangler roles emphasize extracting, cleaning, and transforming raw data into usable formats, serving as a crucial foundation for data analysis and enabling entry-level professionals to develop technical skills in data manipulation tools like Python, SQL, and ETL processes. Data Modelers focus on designing and optimizing data structures and databases, requiring expertise in data architecture, normalization, and business rules, thus offering advanced career pathways toward database administration, data architecture, and enterprise data management leadership roles. Career advancement for Data Wranglers often leads to specialization in data engineering or analytics, while Data Modelers have opportunities to transition into strategic roles involving data governance and system design.
Salary Trends and Job Outlook
Data Wrangler salaries typically range from $65,000 to $95,000 annually, reflecting strong demand for skills in data cleaning and transformation across industries. Data Modelers often command higher salaries, averaging between $85,000 and $120,000, due to their expertise in designing complex database structures and analytics frameworks. Job outlook for both roles remains positive, with Data Wranglers growing rapidly in tech-driven sectors and Data Modelers becoming increasingly essential for strategic data management in enterprise environments.
Choosing Between Data Wrangler and Data Modeler Roles
Choosing between a Data Wrangler and a Data Modeler depends on the project's focus: Data Wranglers specialize in cleaning, transforming, and preparing raw data for analysis, making them essential in early data pipeline stages. Data Modelers design and implement data structures and schemas optimized for storage and retrieval, crucial for database architecture and long-term data management. Organizations prioritize Data Wranglers for agility in handling diverse datasets, while Data Modelers drive strategic planning for scalable, efficient data systems.
Data Wrangler vs Data Modeler Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com