Information Retrieval Specialists focus on developing systems and algorithms to efficiently locate and access relevant data from large datasets or databases based on user queries. Information Extraction Specialists concentrate on identifying and structuring specific pieces of information from unstructured or semi-structured sources to convert raw data into usable formats. Both roles are critical in managing and processing data, but Information Retrieval emphasizes search functionality while Information Extraction emphasizes data transformation.
Table of Comparison
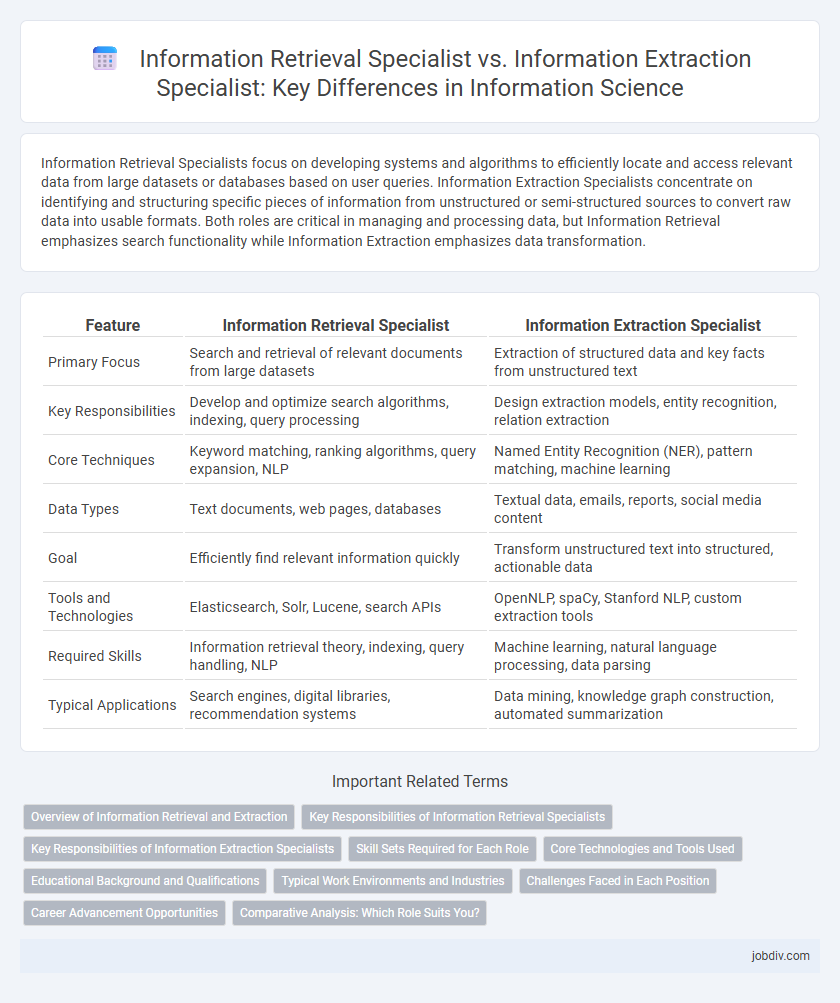
| Feature | Information Retrieval Specialist | Information Extraction Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Search and retrieval of relevant documents from large datasets | Extraction of structured data and key facts from unstructured text |
| Key Responsibilities | Develop and optimize search algorithms, indexing, query processing | Design extraction models, entity recognition, relation extraction |
| Core Techniques | Keyword matching, ranking algorithms, query expansion, NLP | Named Entity Recognition (NER), pattern matching, machine learning |
| Data Types | Text documents, web pages, databases | Textual data, emails, reports, social media content |
| Goal | Efficiently find relevant information quickly | Transform unstructured text into structured, actionable data |
| Tools and Technologies | Elasticsearch, Solr, Lucene, search APIs | OpenNLP, spaCy, Stanford NLP, custom extraction tools |
| Required Skills | Information retrieval theory, indexing, query handling, NLP | Machine learning, natural language processing, data parsing |
| Typical Applications | Search engines, digital libraries, recommendation systems | Data mining, knowledge graph construction, automated summarization |
Overview of Information Retrieval and Extraction
Information retrieval specialists focus on designing systems that efficiently search, index, and retrieve relevant documents or data from large datasets or databases based on user queries. Information extraction specialists develop algorithms to automatically identify and extract structured information, such as entities, relationships, and events, from unstructured text sources. Both fields leverage natural language processing techniques but differ in their goals: retrieval aims at finding and ranking whole documents, while extraction targets granular data for detailed analysis.
Key Responsibilities of Information Retrieval Specialists
Information Retrieval Specialists primarily focus on designing and implementing systems that efficiently locate relevant information from large datasets, utilizing techniques like indexing, query processing, and relevance ranking. They optimize search algorithms to improve accuracy and speed, often working with databases, search engines, and metadata frameworks. Their key responsibilities include evaluating retrieval performance, managing information storage structures, and ensuring seamless user interaction with search interfaces.
Key Responsibilities of Information Extraction Specialists
Information Extraction Specialists focus on identifying and extracting structured data from unstructured text sources using natural language processing techniques and machine learning algorithms. Their key responsibilities include developing and optimizing extraction models, annotating datasets for training purposes, and ensuring high accuracy in transforming raw text into meaningful entities and relationships. They collaborate closely with data scientists and engineers to integrate extracted information into knowledge bases and enhance data accessibility for analysis.
Skill Sets Required for Each Role
Information Retrieval Specialists require strong skills in query formulation, indexing algorithms, and database management to effectively locate relevant data across vast repositories. Information Extraction Specialists focus on expertise in natural language processing (NLP), pattern recognition, and machine learning techniques to automatically identify and extract structured information from unstructured text. Both roles demand proficiency in programming languages such as Python or Java, but the emphasis differs: retrieval specialists prioritize search engine optimization and metadata analysis, while extraction specialists concentrate on semantic parsing and entity recognition.
Core Technologies and Tools Used
Information Retrieval Specialists primarily utilize search engines, indexing algorithms, and natural language processing tools like Elasticsearch and Apache Lucene to efficiently locate and rank relevant documents from large datasets. Information Extraction Specialists focus on tools such as Named Entity Recognition (NER), OpenIE, and machine learning frameworks like spaCy and Stanford NLP to extract structured data and relationships from unstructured text. Both roles rely heavily on Python programming and deep learning libraries, but their core technologies diverge by emphasizing search and retrieval versus detailed content extraction.
Educational Background and Qualifications
An Information Retrieval Specialist typically holds degrees in computer science, library science, or information technology, emphasizing skills in database management, search algorithms, and user interface design. In contrast, an Information Extraction Specialist often has a background in computational linguistics, natural language processing, or data science, focusing on machine learning techniques and text mining to automatically extract meaningful data from unstructured content. Both roles require strong analytical and programming skills, but their educational paths diverge to support different aspects of handling and processing information.
Typical Work Environments and Industries
Information Retrieval Specialists commonly work in academic institutions, libraries, and tech companies, focusing on designing algorithms to locate and organize data from vast digital repositories. Information Extraction Specialists often find their roles in sectors like healthcare, finance, and defense, where they develop systems to automatically extract structured information from unstructured texts, such as medical records or financial reports. Both specialists frequently collaborate with data science teams and operate in environments that emphasize artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing technologies.
Challenges Faced in Each Position
Information Retrieval Specialists face challenges in efficiently indexing and searching vast amounts of unstructured data while ensuring high relevance and accuracy in query results. Information Extraction Specialists struggle with accurately identifying and extracting structured data from diverse and noisy text sources, often contending with ambiguities, incomplete data, and varied document formats. Both roles require advanced techniques in natural language processing and machine learning to overcome data heterogeneity and maintain system scalability.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Information Retrieval Specialists benefit from career advancement through roles such as data scientist, search architect, and knowledge engineer, leveraging expertise in query processing and indexing techniques. Information Extraction Specialists can progress to positions like natural language processing (NLP) engineer, machine learning specialist, and data analyst by focusing on entity recognition, text mining, and pattern extraction. Both career paths offer growth in tech companies, research institutions, and industries emphasizing big data and artificial intelligence applications.
Comparative Analysis: Which Role Suits You?
An Information Retrieval Specialist focuses on designing systems that efficiently locate relevant data from vast databases using algorithms and search techniques, whereas an Information Extraction Specialist develops methods to automatically pull structured information from unstructured sources like text or images. Information Retrieval is ideal for those interested in search engines, indexing, and query optimization, while Information Extraction suits professionals passionate about natural language processing, data mining, and machine learning. Choosing between these roles depends on whether you prefer optimizing access to existing data or transforming raw data into structured formats for analysis.
Information Retrieval Specialist vs Information Extraction Specialist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com