An Operations Manager in a nonprofit pet organization ensures the smooth functioning of daily activities, including volunteer coordination, event planning, and facility management to improve animal care services. A Finance Manager focuses on budgeting, financial reporting, and grant management to secure and allocate funds effectively for the nonprofit's sustainability. Both roles are essential for balancing operational efficiency with fiscal responsibility in advancing the nonprofit's mission.
Table of Comparison
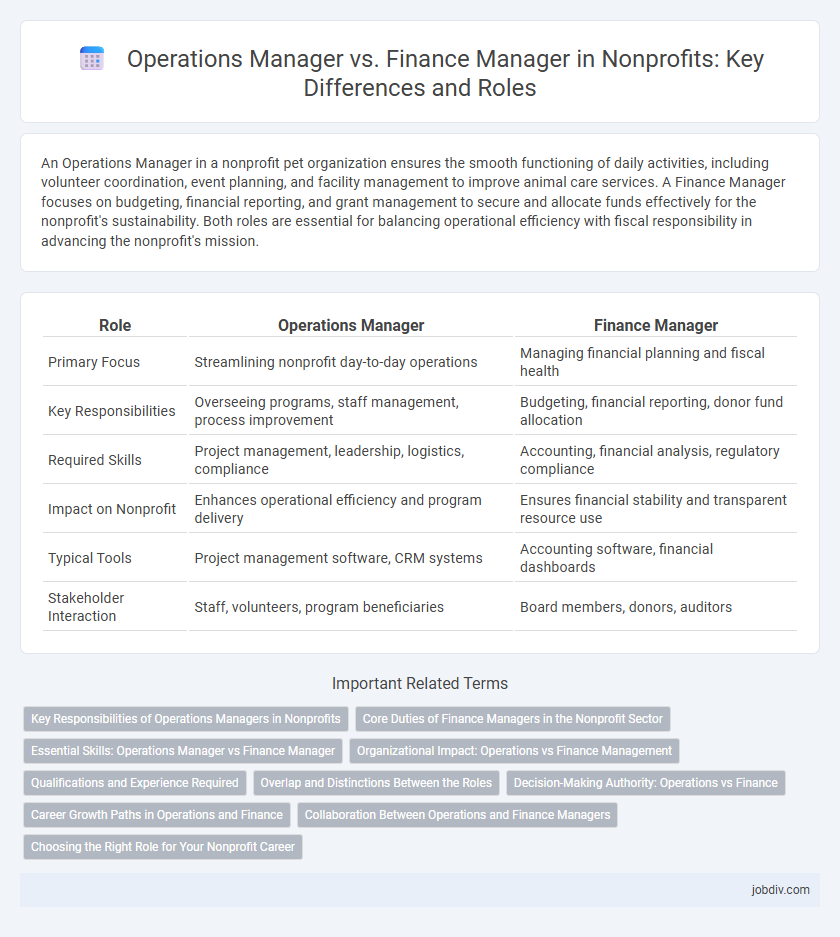
| Role | Operations Manager | Finance Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Streamlining nonprofit day-to-day operations | Managing financial planning and fiscal health |
| Key Responsibilities | Overseeing programs, staff management, process improvement | Budgeting, financial reporting, donor fund allocation |
| Required Skills | Project management, leadership, logistics, compliance | Accounting, financial analysis, regulatory compliance |
| Impact on Nonprofit | Enhances operational efficiency and program delivery | Ensures financial stability and transparent resource use |
| Typical Tools | Project management software, CRM systems | Accounting software, financial dashboards |
| Stakeholder Interaction | Staff, volunteers, program beneficiaries | Board members, donors, auditors |
Key Responsibilities of Operations Managers in Nonprofits
Operations Managers in nonprofits oversee daily organizational functions, including program implementation, staff coordination, and resource allocation to ensure mission alignment and operational efficiency. They manage logistics, maintain compliance with regulations, and collaborate with department heads to optimize workflows and performance metrics. Their role is critical in sustaining nonprofit capacity and enabling effective service delivery to target communities.
Core Duties of Finance Managers in the Nonprofit Sector
Finance Managers in the nonprofit sector are responsible for budgeting, ensuring compliance with financial regulations, and managing grants and donor funds to maintain transparency and accountability. They oversee financial reporting, monitor cash flow, and coordinate audits to safeguard the organization's assets. Accurate financial data provided by Finance Managers supports strategic planning and mission-driven decision-making.
Essential Skills: Operations Manager vs Finance Manager
Operations Managers in nonprofits excel in project management, process optimization, and team leadership to ensure efficient program delivery and organizational workflow. Finance Managers specialize in budgeting, financial reporting, regulatory compliance, and risk management to maintain fiscal responsibility and transparency. Both roles require strong analytical abilities and communication skills, but Operations Managers focus more on operational efficiency while Finance Managers emphasize financial accuracy and sustainability.
Organizational Impact: Operations vs Finance Management
Operations Managers in nonprofits drive organizational efficiency by streamlining processes and optimizing resource allocation, directly enhancing program delivery and stakeholder engagement. Finance Managers ensure fiscal responsibility through budgeting, financial reporting, and compliance, safeguarding the organization's sustainability and enabling strategic decision-making. Both roles are crucial, with Operations focusing on daily workflow optimization while Finance maintains financial health to support mission-driven activities.
Qualifications and Experience Required
Operations Managers in nonprofits generally require a background in project management, process optimization, and team leadership, often with a bachelor's degree in business administration or nonprofit management and 3-5 years of experience in operational roles. Finance Managers need strong expertise in accounting, budgeting, financial reporting, and compliance, typically holding a degree in finance, accounting, or a related field, along with certifications such as CPA or CMA and at least 5 years of financial management experience. Both roles demand proficiency in nonprofit-specific regulations and software, but Finance Managers emphasize fiscal stewardship while Operations Managers focus on organizational efficiency.
Overlap and Distinctions Between the Roles
Operations Managers in nonprofits oversee daily organizational functions, ensuring programs run efficiently, while Finance Managers focus on budgeting, financial reporting, and compliance. Both roles require strategic planning and resource management but differ as Operations Managers prioritize operational workflows and staff coordination, whereas Finance Managers specialize in financial analysis and fiscal health. Collaboration occurs in areas like budget implementation and performance tracking, highlighting their complementary functions within nonprofit management.
Decision-Making Authority: Operations vs Finance
Operations Managers in nonprofits hold decision-making authority over daily organizational functions, resource allocation, and program implementation, ensuring efficient service delivery and mission fulfillment. Finance Managers wield authority over budgeting, financial planning, and fiduciary oversight, guiding fiscal responsibility and regulatory compliance to sustain organizational health. The distinct decision-making domains emphasize operational efficiency versus financial stewardship, both critical for nonprofit strategic success.
Career Growth Paths in Operations and Finance
Operations Managers in nonprofits often progress toward executive roles such as Director of Operations or Chief Operating Officer, developing skills in program management, logistics, and team leadership. Finance Managers typically advance to positions like Finance Director or Chief Financial Officer, emphasizing expertise in budgeting, financial reporting, and compliance with nonprofit regulations. Both career paths offer opportunities for strategic influence and cross-departmental collaboration, critical for organizational sustainability and growth.
Collaboration Between Operations and Finance Managers
Operations Managers and Finance Managers in nonprofit organizations collaborate closely to ensure efficient resource allocation and financial transparency. The Operations Manager oversees daily workflows and program implementation, while the Finance Manager monitors budgets, financial reporting, and compliance. Their partnership drives strategic decision-making, aligns operational activities with financial goals, and strengthens overall organizational sustainability.
Choosing the Right Role for Your Nonprofit Career
Choosing the right role for your nonprofit career depends on your skills and interests; Operations Managers focus on streamlining organizational processes, overseeing program delivery, and managing staff logistics to ensure mission effectiveness. Finance Managers specialize in budgeting, financial reporting, grant management, and compliance, safeguarding the nonprofit's fiscal health. Aligning your expertise with these core responsibilities helps maximize your impact within the nonprofit sector.
Operations Manager vs Finance Manager Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com