Lobbyists specialize in influencing government policies and legislation by directly engaging with lawmakers and regulators, while public relations specialists manage the public image and communication strategies of organizations to enhance their reputation. Lobbyists rely heavily on political connections and a deep understanding of regulatory environments, whereas public relations specialists focus on media relations, content creation, and crisis management. Both roles require strong communication skills but differ significantly in their target audiences and objectives.
Table of Comparison
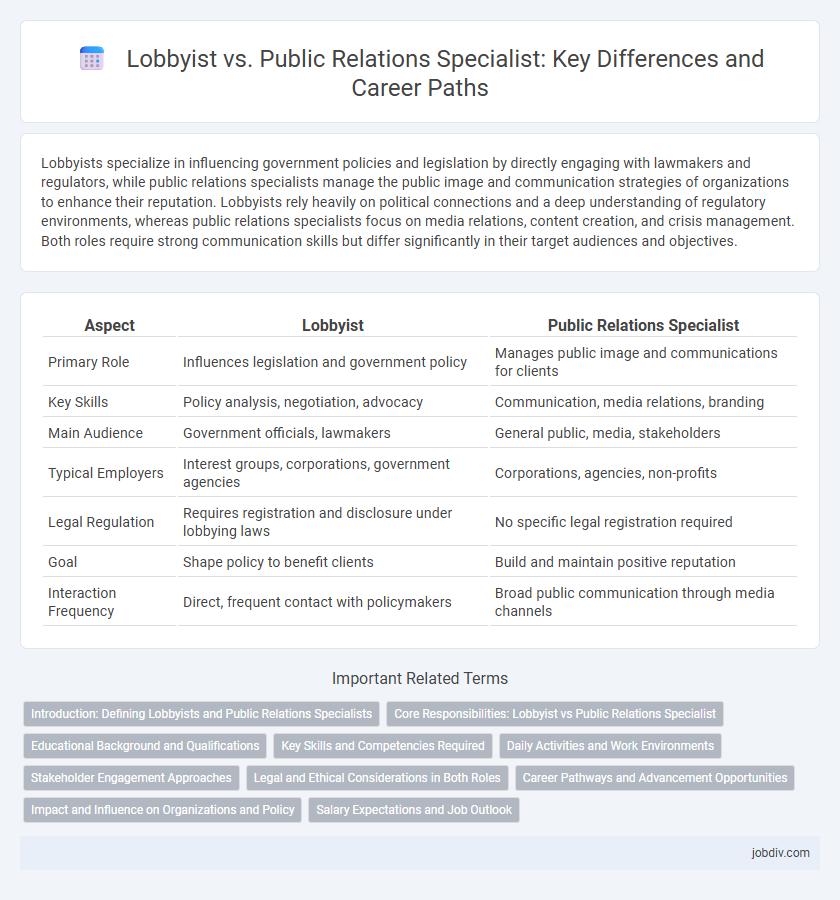
| Aspect | Lobbyist | Public Relations Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Influences legislation and government policy | Manages public image and communications for clients |
| Key Skills | Policy analysis, negotiation, advocacy | Communication, media relations, branding |
| Main Audience | Government officials, lawmakers | General public, media, stakeholders |
| Typical Employers | Interest groups, corporations, government agencies | Corporations, agencies, non-profits |
| Legal Regulation | Requires registration and disclosure under lobbying laws | No specific legal registration required |
| Goal | Shape policy to benefit clients | Build and maintain positive reputation |
| Interaction Frequency | Direct, frequent contact with policymakers | Broad public communication through media channels |
Introduction: Defining Lobbyists and Public Relations Specialists
Lobbyists are professionals who influence government decisions by advocating for specific policies or legislation on behalf of clients, often corporations or interest groups. Public relations specialists manage communication between organizations and the public, shaping their image and handling media relations to build reputation and trust. Both roles require strategic communication skills but differ in focus, with lobbyists targeting policymakers and public relations specialists engaging a broader audience.
Core Responsibilities: Lobbyist vs Public Relations Specialist
Lobbyists primarily focus on influencing legislation and government policies by directly interacting with lawmakers and regulatory agencies to advocate for specific interests or causes. Public Relations Specialists manage the public image of organizations by crafting strategic communication campaigns, handling media relations, and shaping public perception to build and maintain a positive reputation. While lobbyists concentrate on policy advocacy and regulatory impact, public relations specialists emphasize brand awareness and stakeholder engagement across various media platforms.
Educational Background and Qualifications
Lobbyists typically hold degrees in political science, law, or public administration, with many possessing advanced certifications like the Registered Lobbyist designation to navigate legislative processes effectively. Public Relations Specialists usually have a background in communications, journalism, or marketing, often supplemented by certifications such as the Accreditation in Public Relations (APR) to enhance strategic media relations skills. Both professions benefit from strong interpersonal skills, but their educational pathways emphasize distinct areas aligned with advocacy and media communication respectively.
Key Skills and Competencies Required
Lobbyists require expertise in legislative processes, negotiation, and policy analysis to influence governmental decisions effectively. Public relations specialists excel in communication, media relations, and strategic messaging to shape public perception and manage brand reputation. Both roles demand strong interpersonal skills, critical thinking, and the ability to build and maintain relationships with diverse stakeholders.
Daily Activities and Work Environments
Lobbyists typically engage in direct interaction with government officials and policymakers, conducting research on legislation, drafting policy proposals, and attending hearings to advocate for specific interests. Public Relations Specialists focus on managing an organization's public image by crafting press releases, organizing media events, and monitoring public sentiment across various platforms. Lobbyists often work in governmental or legislative offices, law firms, and advocacy organizations, while Public Relations Specialists are commonly employed in corporations, non-profits, and media agencies.
Stakeholder Engagement Approaches
Lobbyists employ targeted advocacy strategies to influence policymakers and government officials, leveraging direct communication and legislative expertise to advance specific interests. Public relations specialists focus on cultivating broad stakeholder relationships through strategic messaging, media relations, and reputation management to shape public perception. Both roles prioritize tailored engagement but differ in audience focus, with lobbyists emphasizing regulatory bodies and PR specialists addressing diverse stakeholder groups.
Legal and Ethical Considerations in Both Roles
Lobbyists must navigate strict regulatory frameworks including registration, disclosure of financial activities, and adherence to anti-corruption laws to maintain transparency and legality. Public Relations Specialists are bound by ethical codes such as honesty, avoiding misinformation, and respecting client confidentiality to uphold public trust and professional integrity. Both roles require vigilance to prevent conflicts of interest and ensure compliance with industry-specific legal standards to protect organizational reputation and stakeholder interests.
Career Pathways and Advancement Opportunities
Lobbyists often leverage government relations and policy expertise to influence legislation, advancing by building strong networks within political and regulatory circles. Public relations specialists focus on managing communication strategies and media relations, progressing through roles that highlight strategic messaging and brand reputation management. Career advancement for lobbyists typically involves senior advisory or consultancy positions, while public relations specialists may move into director-level roles or corporate communications leadership.
Impact and Influence on Organizations and Policy
Lobbyists strategically engage with lawmakers to directly shape legislation and regulatory policies that affect organizational interests, leveraging in-depth expertise and personal connections within government sectors. Public relations specialists cultivate a favorable public image and stakeholder trust through targeted communication campaigns, indirectly influencing policy environments by shaping public opinion and media narratives. The combined impact of these roles enhances organizational power by aligning public perception with legislative advocacy, driving both policy outcomes and reputation management effectively.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Lobbyists typically earn a median salary ranging from $65,000 to $110,000 annually, with experienced professionals in major markets exceeding $130,000, driven by their role in influencing legislation and government policies. Public Relations Specialists have a median salary of about $62,000 per year, with a job outlook projected to grow 6% over the next decade, reflecting steady demand for media management and corporate communication expertise. Lobbyists often face higher salary volatility tied to political climates, while Public Relations Specialists experience more consistent employment growth across various industries.
Lobbyist vs Public Relations Specialist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com