Payroll Specialists manage employee payment processing, ensuring accuracy in wage calculations, tax deductions, and compliance with relevant laws. Compensation Analysts evaluate market salary data and company pay structures to develop competitive and equitable compensation programs that attract and retain talent. Both roles are critical in maintaining organizational financial health, with Payroll Specialists focusing on transactional accuracy and Compensation Analysts driving strategic pay decisions.
Table of Comparison
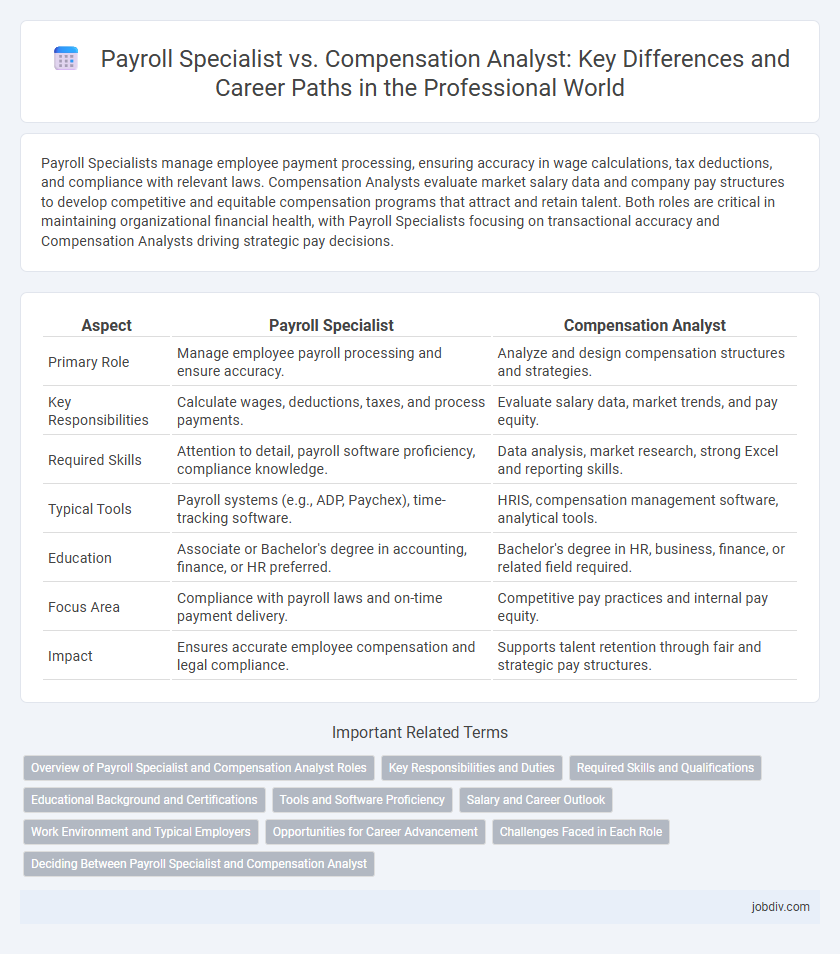
| Aspect | Payroll Specialist | Compensation Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Manage employee payroll processing and ensure accuracy. | Analyze and design compensation structures and strategies. |
| Key Responsibilities | Calculate wages, deductions, taxes, and process payments. | Evaluate salary data, market trends, and pay equity. |
| Required Skills | Attention to detail, payroll software proficiency, compliance knowledge. | Data analysis, market research, strong Excel and reporting skills. |
| Typical Tools | Payroll systems (e.g., ADP, Paychex), time-tracking software. | HRIS, compensation management software, analytical tools. |
| Education | Associate or Bachelor's degree in accounting, finance, or HR preferred. | Bachelor's degree in HR, business, finance, or related field required. |
| Focus Area | Compliance with payroll laws and on-time payment delivery. | Competitive pay practices and internal pay equity. |
| Impact | Ensures accurate employee compensation and legal compliance. | Supports talent retention through fair and strategic pay structures. |
Overview of Payroll Specialist and Compensation Analyst Roles
Payroll Specialists manage employee compensation by processing payroll, ensuring compliance with tax regulations, and maintaining accurate payment records. Compensation Analysts evaluate market salary data, design competitive pay structures, and support organizational compensation strategies to attract and retain talent. Both roles are essential in managing employee compensation but focus on different aspects of payroll administration and strategic pay planning.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
Payroll Specialists manage employee compensation processing, ensuring accurate salary payments, tax withholdings, benefits deductions, and compliance with payroll laws and regulations. Compensation Analysts conduct market research, analyze salary data, and develop competitive compensation structures aligned with organizational goals and budget constraints. Both roles require strong attention to detail and collaboration with HR and finance departments to maintain fair and timely employee compensation systems.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Payroll Specialists require proficiency in payroll software, attention to detail, and knowledge of tax regulations to ensure accurate employee compensation processing. Compensation Analysts need strong analytical abilities, experience with market salary data, and expertise in designing compensation structures aligned with organizational goals. Both roles demand excellent communication skills and understanding of labor laws, but Compensation Analysts typically require advanced statistical and financial modeling skills.
Educational Background and Certifications
Payroll Specialists typically hold a bachelor's degree in accounting, finance, or business administration, with certifications such as the Certified Payroll Professional (CPP) enhancing their expertise in payroll processing and compliance. Compensation Analysts often possess degrees in human resources, business, or economics, and benefit from certifications like Certified Compensation Professional (CCP) that deepen their knowledge of compensation strategies, market analysis, and salary structures. Both roles require an understanding of employment laws and data analysis, but their educational pathways and certifications reflect their distinct focus on payroll execution versus compensation planning.
Tools and Software Proficiency
Payroll Specialists excel in payroll processing systems such as ADP, Paychex, and QuickBooks Payroll, ensuring accurate salary disbursement and tax compliance. Compensation Analysts primarily utilize HR analytics platforms like SAP SuccessFactors, Workday, and Excel for data modeling and salary benchmarking. Both roles demand proficiency in payroll and HRIS software but differ in focus, with Payroll Specialists emphasizing transactional tools and Compensation Analysts leveraging analytical software for strategic pay analysis.
Salary and Career Outlook
Payroll Specialists typically earn an average salary ranging from $45,000 to $60,000 annually, while Compensation Analysts command higher pay, often between $65,000 and $85,000 due to their advanced expertise in market salary trends and pay structure design. The career outlook for Payroll Specialists shows steady demand driven by compliance and payroll processing needs, whereas Compensation Analysts experience faster growth prospects linked to strategic workforce planning and competitive compensation strategies. Employers increasingly value Compensation Analysts for their role in optimizing employee retention and organizational compensation frameworks, reflecting their higher salary potential and dynamic career trajectory.
Work Environment and Typical Employers
Payroll Specialists often work in accounting firms, corporate finance departments, and payroll service companies, usually operating in structured office settings with routine tasks processing employee compensation. Compensation Analysts typically find employment in human resources departments of large corporations, government agencies, and consulting firms, engaging in strategic roles within collaborative, dynamic office environments focused on salary benchmarking and benefits analysis. Both roles require attention to detail and confidentiality but differ in their interaction levels, with Payroll Specialists emphasizing transactional accuracy and Compensation Analysts focusing on compensation strategy development.
Opportunities for Career Advancement
Payroll Specialists can advance by moving into payroll management or HR roles that require deep expertise in compliance and data accuracy. Compensation Analysts often transition into total rewards or strategic compensation management positions, leveraging their ability to design and analyze pay structures. Both career paths offer opportunities in human resources leadership, with Compensation Analysts typically accessing higher-level strategic roles due to their focus on market data and employee incentives.
Challenges Faced in Each Role
Payroll Specialists frequently encounter challenges related to maintaining compliance with constantly changing tax regulations and ensuring accurate, timely payroll processing to avoid penalties and employee dissatisfaction. Compensation Analysts face difficulties in designing competitive salary structures that align with market trends, budget constraints, and internal equity while conducting detailed compensation benchmarking and data analysis. Both roles require meticulous attention to detail and the ability to adapt to evolving legal and economic landscapes to support organizational talent management effectively.
Deciding Between Payroll Specialist and Compensation Analyst
Choosing between a Payroll Specialist and a Compensation Analyst depends on the organization's focus: Payroll Specialists manage accurate employee payment processing, tax compliance, and payroll record maintenance, while Compensation Analysts develop salary structures, conduct market salary benchmarking, and analyze compensation trends to ensure competitive pay. Businesses prioritizing operational accuracy and regulatory adherence benefit from hiring Payroll Specialists, whereas those aiming to strategically align compensation with market standards and internal equity lean toward Compensation Analysts. Understanding the distinct roles, skill sets, and objectives of each position is crucial for making an informed decision that supports organizational goals and employee satisfaction.
Payroll Specialist vs Compensation Analyst Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com