Pharmacists are healthcare professionals responsible for dispensing medications, counseling patients, and ensuring the safe and effective use of prescription drugs. Pharmacy technicians support pharmacists by preparing medications, managing inventory, and handling administrative tasks under the supervision of a licensed pharmacist. Both roles are essential in delivering quality pharmaceutical care but differ significantly in scope of practice, education requirements, and regulatory responsibilities.
Table of Comparison
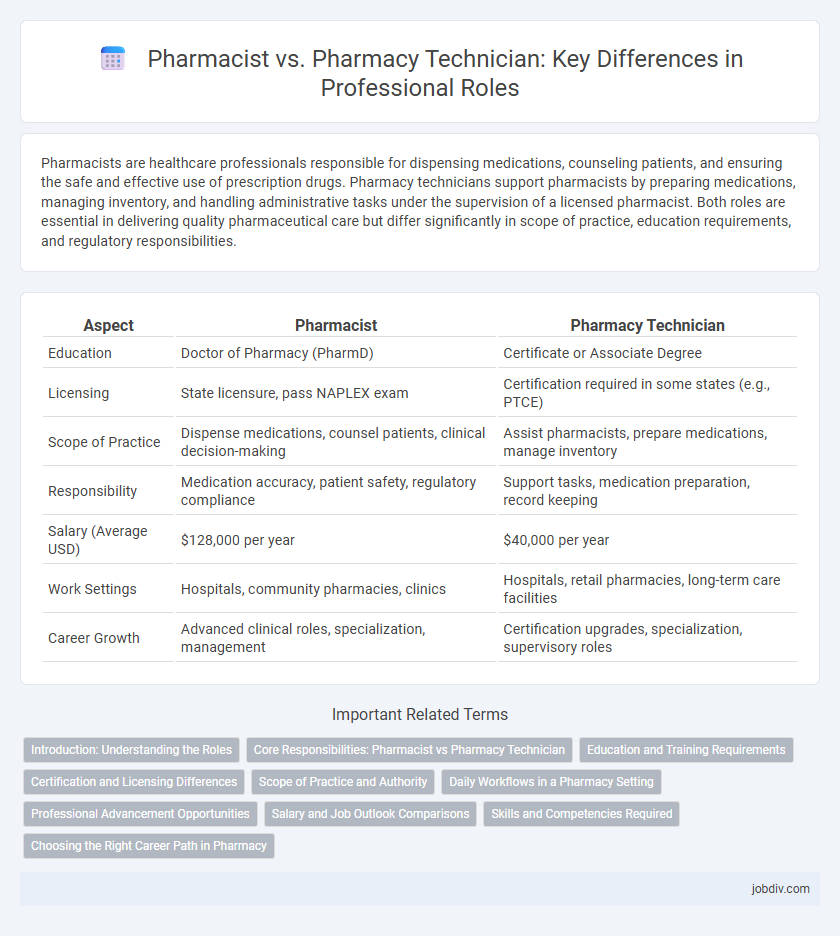
| Aspect | Pharmacist | Pharmacy Technician |
|---|---|---|
| Education | Doctor of Pharmacy (PharmD) | Certificate or Associate Degree |
| Licensing | State licensure, pass NAPLEX exam | Certification required in some states (e.g., PTCE) |
| Scope of Practice | Dispense medications, counsel patients, clinical decision-making | Assist pharmacists, prepare medications, manage inventory |
| Responsibility | Medication accuracy, patient safety, regulatory compliance | Support tasks, medication preparation, record keeping |
| Salary (Average USD) | $128,000 per year | $40,000 per year |
| Work Settings | Hospitals, community pharmacies, clinics | Hospitals, retail pharmacies, long-term care facilities |
| Career Growth | Advanced clinical roles, specialization, management | Certification upgrades, specialization, supervisory roles |
Introduction: Understanding the Roles
Pharmacists are healthcare professionals responsible for dispensing medications, providing patient counseling, and ensuring the safe and effective use of pharmaceutical drugs. Pharmacy technicians assist pharmacists by preparing prescriptions, managing inventory, and handling administrative tasks to support pharmacy operations efficiently. Understanding the distinct responsibilities of pharmacists and pharmacy technicians is essential to optimize collaboration and improve patient care outcomes in healthcare settings.
Core Responsibilities: Pharmacist vs Pharmacy Technician
Pharmacists are responsible for reviewing prescriptions, ensuring accurate medication dispensing, and providing patient counseling on drug interactions and side effects. Pharmacy technicians assist by preparing and labeling medications, managing inventory, and supporting pharmacists with administrative and clerical tasks. Both roles require adherence to safety protocols and collaboration to maintain efficient pharmacy operations.
Education and Training Requirements
Pharmacists must complete a Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm.D.) degree, typically a four-year professional program following undergraduate prerequisites, and pass licensure exams such as the NAPLEX. Pharmacy technicians usually require a high school diploma and may undergo formal training programs or obtain certification through organizations like the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB). The extensive education and clinical training pharmacists receive enable them to provide comprehensive medication management, while pharmacy technicians assist with technical and administrative tasks under pharmacist supervision.
Certification and Licensing Differences
Pharmacists require a Doctor of Pharmacy (PharmD) degree and must pass the North American Pharmacist Licensure Examination (NAPLEX) along with state-specific licensing exams to practice legally. Pharmacy technicians generally need a high school diploma, completion of a pharmacy technician training program, and certification through the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB) or the National Healthcareer Association (NHA), with licensing requirements varying by state. The scope of practice is defined by these certifications and licenses, with pharmacists authorized to provide clinical decision-making and patient counseling, while technicians assist with dispensing under supervision.
Scope of Practice and Authority
Pharmacists hold a comprehensive scope of practice that includes verifying prescriptions, counseling patients, managing medication therapy, and overseeing pharmacy operations with full legal authority to make clinical decisions. Pharmacy technicians support pharmacists by preparing and dispensing medications, managing inventory, and handling administrative tasks under direct supervision, without the authority to provide clinical consultations or make prescribing decisions. Regulatory requirements strictly delineate these roles to ensure patient safety and maintain professional accountability within the pharmacy setting.
Daily Workflows in a Pharmacy Setting
Pharmacists oversee medication dispensing, clinical consultations, and ensure regulatory compliance while managing patient safety and drug interactions. Pharmacy technicians support these tasks by preparing prescriptions, managing inventory, and handling administrative duties to streamline workflow efficiency. Together, their collaborative roles enhance the accuracy and speed of pharmaceutical services in a pharmacy setting.
Professional Advancement Opportunities
Pharmacists have broader professional advancement opportunities, including specialization in clinical pharmacy, research, and management roles within healthcare settings. Pharmacy technicians typically advance through certification and experience, qualifying for supervisory positions or specialized tasks such as compounding or medication therapy management support. Continuous education and obtaining advanced credentials significantly enhance career progression for both professionals, with pharmacists accessing higher-level leadership and clinical decision-making roles.
Salary and Job Outlook Comparisons
Pharmacists earn a median annual salary of approximately $128,000, significantly higher than pharmacy technicians who average around $36,000 per year. The job outlook for pharmacists is projected to grow by 3% over the next decade, reflecting more moderate demand, while pharmacy technician roles are expected to increase by 7%, driven by expanding healthcare needs and pharmacy services. Differences in salary and job growth highlight the distinct professional responsibilities and required qualifications between pharmacists and pharmacy technicians.
Skills and Competencies Required
Pharmacists require advanced knowledge in pharmacology, patient counseling, and clinical decision-making to ensure safe medication use and manage complex drug therapies. Pharmacy technicians must possess strong organizational skills, attention to detail, and proficiency in medication dispensing under supervision, emphasizing accuracy and regulatory compliance. Both roles demand excellent communication abilities and a thorough understanding of pharmacy law and ethics to support effective healthcare delivery.
Choosing the Right Career Path in Pharmacy
Pharmacists possess advanced clinical knowledge and are responsible for medication therapy management, patient counseling, and overseeing pharmacy operations, requiring a Doctor of Pharmacy (PharmD) degree and licensure. Pharmacy technicians support pharmacists by preparing medications, managing inventory, and handling administrative tasks, typically requiring certification and on-the-job training. Choosing the right career path depends on desired responsibility level, educational commitment, and interest in patient care versus technical support within the pharmacy setting.
Pharmacist vs Pharmacy Technician Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com