Quality Assurance (QA) involves systematic processes and procedures designed to prevent defects and ensure that quality standards are met throughout the development lifecycle. Quality Control (QC) focuses on identifying and correcting defects in the final products through rigorous testing and inspection activities. Both QA and QC are essential components of a comprehensive quality management system that drives continuous improvement and delivers reliable results.
Table of Comparison
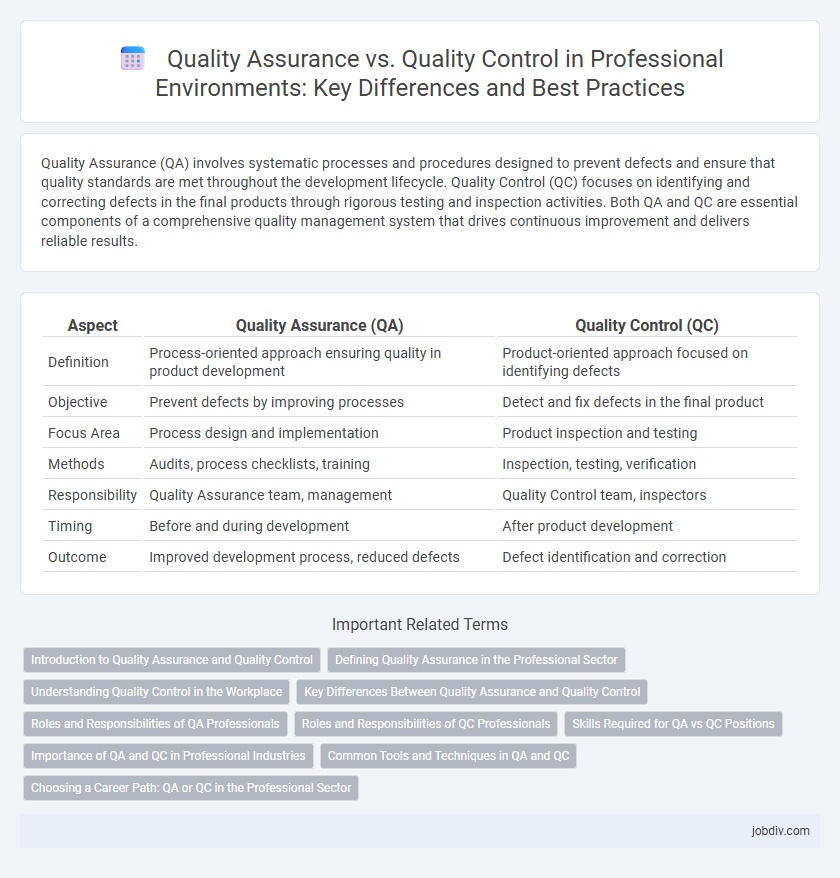
| Aspect | Quality Assurance (QA) | Quality Control (QC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process-oriented approach ensuring quality in product development | Product-oriented approach focused on identifying defects |
| Objective | Prevent defects by improving processes | Detect and fix defects in the final product |
| Focus Area | Process design and implementation | Product inspection and testing |
| Methods | Audits, process checklists, training | Inspection, testing, verification |
| Responsibility | Quality Assurance team, management | Quality Control team, inspectors |
| Timing | Before and during development | After product development |
| Outcome | Improved development process, reduced defects | Defect identification and correction |
Introduction to Quality Assurance and Quality Control
Quality Assurance (QA) encompasses systematic processes designed to prevent defects and ensure quality standards are met throughout the product development lifecycle. Quality Control (QC) involves the operational techniques and activities used to verify that the final products conform to specified requirements and identify any defects. Both QA and QC play critical roles in maintaining and improving product quality by addressing different aspects of the quality management process.
Defining Quality Assurance in the Professional Sector
Quality Assurance in the professional sector refers to a systematic process designed to ensure that products and services meet predefined standards through planned and documented activities. It focuses on preventing defects by improving development and production methodologies, thereby guaranteeing consistency and reliability. This proactive approach involves audits, process checks, and continuous improvement to uphold organizational excellence.
Understanding Quality Control in the Workplace
Quality Control in the workplace involves systematic processes to monitor and verify that products or services meet predefined standards, ensuring consistency and reliability. It emphasizes defect detection through inspections, testing, and corrective actions to prevent non-conformities. Effective Quality Control integrates real-time feedback loops that enhance operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Key Differences Between Quality Assurance and Quality Control
Quality Assurance (QA) focuses on preventing defects through process-oriented activities, ensuring that quality standards are defined and consistently met during product development. Quality Control (QC) involves product-oriented activities that identify defects in the final outputs through inspection, testing, and validation procedures. Key differences include QA's proactive approach centered on process improvement versus QC's reactive role in detecting and correcting defects in delivered products.
Roles and Responsibilities of QA Professionals
Quality Assurance professionals focus on designing and implementing systematic processes to prevent defects in products or services, ensuring compliance with industry standards and organizational policies. Their responsibilities include developing quality management plans, conducting audits, and facilitating continuous improvement practices to enhance operational efficiency. QA specialists also collaborate with cross-functional teams to train staff on quality standards and monitor process adherence throughout the development lifecycle.
Roles and Responsibilities of QC Professionals
Quality Control professionals are responsible for inspecting products, conducting tests, and identifying defects to ensure compliance with quality standards. Their role involves implementing corrective actions, maintaining detailed documentation, and collaborating closely with production teams to prevent errors. These responsibilities are critical in minimizing defects and ensuring product reliability in manufacturing and service industries.
Skills Required for QA vs QC Positions
Quality Assurance (QA) roles require strong analytical skills, process-oriented thinking, and expertise in designing test plans, risk management, and software development lifecycles. Quality Control (QC) positions focus more on hands-on testing skills, attention to detail, defect identification, and proficiency in executing test cases and reporting. Mastery of tools like Jira for QA and Selenium for QC often distinguishes the technical competencies needed in each domain.
Importance of QA and QC in Professional Industries
Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) are crucial in professional industries to ensure product reliability, customer satisfaction, and compliance with regulatory standards. QA focuses on process improvements and prevention of defects throughout the development lifecycle, while QC involves the identification and correction of defects in finished products. Together, they minimize errors, reduce costs associated with rework, and enhance overall organizational credibility.
Common Tools and Techniques in QA and QC
Quality Assurance utilizes process audit checklists, cause-and-effect diagrams, and statistical process control tools to prevent defects and ensure product quality. Quality Control employs inspection, sampling techniques, and control charts to detect defects and verify product conformance to specifications. Both QA and QC leverage root cause analysis and Six Sigma methodologies to enhance overall quality and reduce variability.
Choosing a Career Path: QA or QC in the Professional Sector
Choosing a career path in Quality Assurance (QA) or Quality Control (QC) depends on your interest in process improvement versus product inspection. QA professionals focus on developing and implementing systematic processes to prevent defects, emphasizing proactive quality management. QC specialists concentrate on identifying defects in finished products through rigorous testing and inspection, playing a critical role in maintaining product standards.
Quality Assurance vs Quality Control Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com