A Public Housing Manager oversees day-to-day operations, ensuring that community policies are implemented and residents' needs are met effectively. In contrast, a Public Housing Inspector conducts thorough inspections to verify compliance with safety, quality, and regulatory standards of the housing units. Both roles are essential for maintaining livable, safe, and well-managed public housing communities.
Table of Comparison
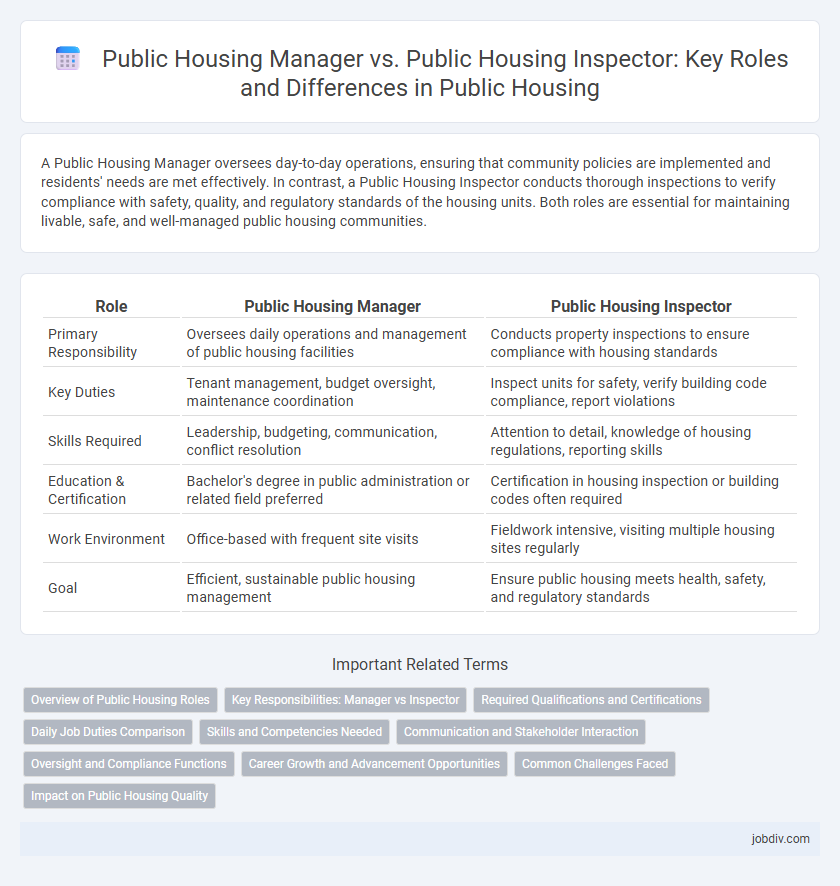
| Role | Public Housing Manager | Public Housing Inspector |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Responsibility | Oversees daily operations and management of public housing facilities | Conducts property inspections to ensure compliance with housing standards |
| Key Duties | Tenant management, budget oversight, maintenance coordination | Inspect units for safety, verify building code compliance, report violations |
| Skills Required | Leadership, budgeting, communication, conflict resolution | Attention to detail, knowledge of housing regulations, reporting skills |
| Education & Certification | Bachelor's degree in public administration or related field preferred | Certification in housing inspection or building codes often required |
| Work Environment | Office-based with frequent site visits | Fieldwork intensive, visiting multiple housing sites regularly |
| Goal | Efficient, sustainable public housing management | Ensure public housing meets health, safety, and regulatory standards |
Overview of Public Housing Roles
Public Housing Managers oversee the day-to-day operations, tenant relations, and maintenance of public housing properties to ensure safe, affordable living environments. Public Housing Inspectors conduct inspections to verify compliance with housing codes, safety standards, and contractual obligations, identifying necessary repairs or violations. Both roles are essential for maintaining quality and regulatory adherence in public housing systems.
Key Responsibilities: Manager vs Inspector
Public Housing Managers oversee the administration, maintenance, and budgeting of housing programs, ensuring compliance with housing regulations and coordinating tenant services to promote community well-being. Public Housing Inspectors conduct regular site inspections to assess property conditions, identify code violations, and verify adherence to safety and health standards within public housing units. While managers focus on operational leadership and policy implementation, inspectors emphasize regulatory compliance and physical property evaluations.
Required Qualifications and Certifications
Public Housing Managers typically require a bachelor's degree in public administration, social work, or a related field, along with certifications such as Certified Property Manager (CPM) or Public Housing Manager (PHM). Public Housing Inspectors generally need a high school diploma or equivalent, with specialized certifications including the Housing Quality Standards (HQS) certification and Lead-Based Paint Inspector certification. Both roles demand knowledge of federal housing regulations, but Managers emphasize administrative credentials while Inspectors prioritize technical inspection certifications.
Daily Job Duties Comparison
Public Housing Managers oversee tenant leasing, budgeting, and community relations to ensure efficient property management and compliance with housing regulations. Public Housing Inspectors conduct routine inspections to evaluate property conditions, verify maintenance standards, and enforce health and safety codes. While Managers focus on administrative and operational tasks, Inspectors prioritize physical assessments and regulatory compliance on-site.
Skills and Competencies Needed
Public Housing Managers require strong leadership skills, financial acumen, and proficiency in managing housing operations and staff to ensure compliance with housing regulations. Public Housing Inspectors need expertise in property evaluation, attention to detail, and knowledge of safety codes to assess and document housing conditions accurately. Both roles demand excellent communication abilities and a thorough understanding of federal and local housing policies to maintain public housing quality and safety.
Communication and Stakeholder Interaction
Public Housing Managers coordinate with tenants, government agencies, and maintenance teams to ensure effective service delivery and address community concerns promptly. Public Housing Inspectors primarily communicate with maintenance staff and regulatory bodies to assess property compliance and safety standards, providing detailed reports for decision-makers. Both roles require strong interpersonal skills, but Managers engage more frequently in stakeholder negotiations and tenant relations, while Inspectors focus on technical evaluations and regulatory adherence.
Oversight and Compliance Functions
Public Housing Managers supervise overall property operations, ensuring compliance with federal housing regulations and managing tenant relations to uphold housing quality standards. Public Housing Inspectors conduct detailed on-site evaluations to verify that units meet safety codes, habitability requirements, and regulatory guidelines. Both roles collaborate to enforce oversight, with managers focusing on strategic compliance and inspectors performing systematic evaluations to maintain public housing integrity.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Public Housing Managers typically have broader responsibilities including overseeing operations, managing budgets, and leading teams, which often positions them for senior roles in housing administration and policy development. Public Housing Inspectors focus primarily on compliance and condition assessments, with career advancement limited to specialized inspection roles or supervisory positions within inspection teams. Managers benefit from greater upward mobility due to their comprehensive project oversight and strategic planning skills, making their career growth prospects more diverse and expansive.
Common Challenges Faced
Public Housing Managers and Public Housing Inspectors face common challenges such as ensuring compliance with regulatory standards, addressing maintenance and safety issues, and managing resident concerns efficiently. Both roles require navigating limited budgets while maintaining quality living conditions and adhering to federal and local housing policies. Effective communication between managers and inspectors is crucial to resolve issues promptly and improve overall housing operations.
Impact on Public Housing Quality
Public Housing Managers directly influence public housing quality by overseeing property maintenance, tenant relations, and ensuring compliance with housing regulations, which leads to improved living conditions and resident satisfaction. Public Housing Inspectors play a critical role by conducting thorough evaluations of housing units to identify safety hazards, code violations, and maintenance needs, thereby facilitating timely repairs and adherence to quality standards. The collaboration between managers and inspectors ensures comprehensive oversight, enhancing overall housing quality and promoting safe, affordable living environments.
Public Housing Manager vs Public Housing Inspector Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com