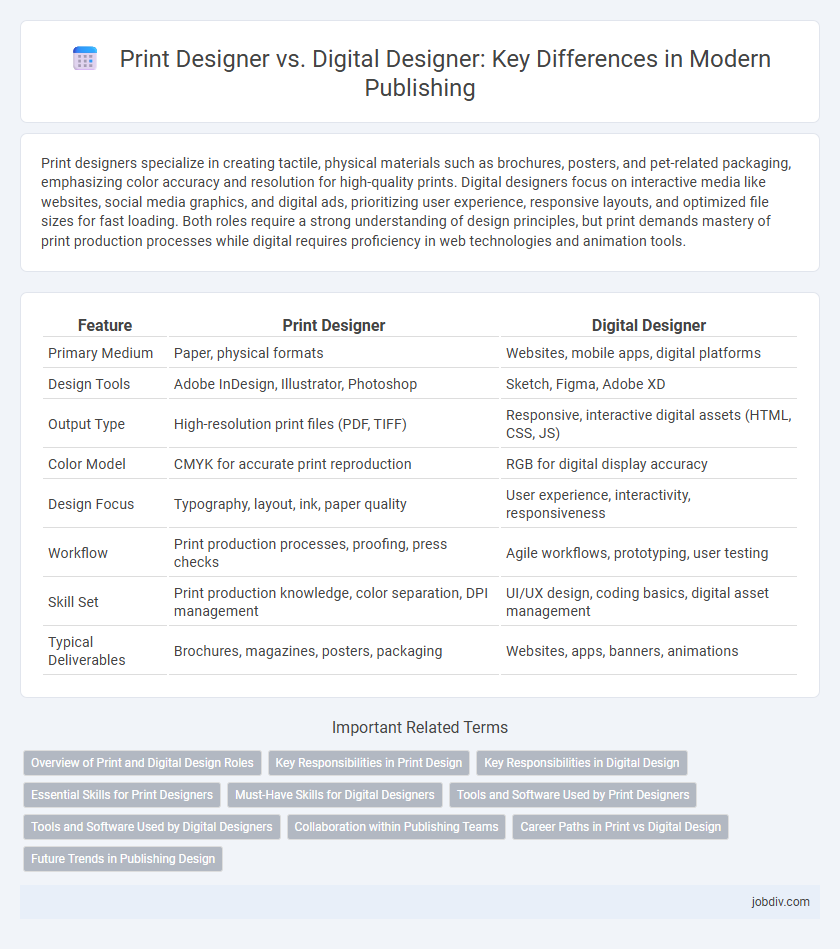
Print designers specialize in creating tactile, physical materials such as brochures, posters, and pet-related packaging, emphasizing color accuracy and resolution for high-quality prints. Digital designers focus on interactive media like websites, social media graphics, and digital ads, prioritizing user experience, responsive layouts, and optimized file sizes for fast loading. Both roles require a strong understanding of design principles, but print demands mastery of print production processes while digital requires proficiency in web technologies and animation tools.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Print Designer | Digital Designer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Medium | Paper, physical formats | Websites, mobile apps, digital platforms |
| Design Tools | Adobe InDesign, Illustrator, Photoshop | Sketch, Figma, Adobe XD |
| Output Type | High-resolution print files (PDF, TIFF) | Responsive, interactive digital assets (HTML, CSS, JS) |
| Color Model | CMYK for accurate print reproduction | RGB for digital display accuracy |
| Design Focus | Typography, layout, ink, paper quality | User experience, interactivity, responsiveness |
| Workflow | Print production processes, proofing, press checks | Agile workflows, prototyping, user testing |
| Skill Set | Print production knowledge, color separation, DPI management | UI/UX design, coding basics, digital asset management |
| Typical Deliverables | Brochures, magazines, posters, packaging | Websites, apps, banners, animations |
Overview of Print and Digital Design Roles
Print designers specialize in creating visually compelling layouts for physical media such as magazines, brochures, and packaging, emphasizing color accuracy, typography, and resolution for high-quality print output. Digital designers focus on interactive media, including websites, apps, and social media content, prioritizing user experience, responsive design, and animation. Both roles require proficiency in design software but apply different technical skills and design principles tailored to their respective platforms.
Key Responsibilities in Print Design
Print designers specialize in creating visually compelling layouts for physical media such as magazines, brochures, posters, and packaging, ensuring color accuracy and print-ready files. They work extensively with software like Adobe InDesign, Illustrator, and Photoshop to prepare designs that meet the technical specifications of printers, including bleed, trim, and resolution requirements. Key responsibilities include selecting appropriate typography, mastering print production processes, and collaborating with printers to maintain quality control throughout the print run.
Key Responsibilities in Digital Design
Digital designers specialize in creating visually compelling content optimized for web, mobile, and social media platforms, ensuring user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) principles drive engagement and accessibility. Their key responsibilities include designing interactive graphics, animations, and layouts using software like Adobe XD, Figma, and Sketch, while collaborating closely with developers to implement responsive designs. They also manage digital assets, optimize images for fast loading times, and continuously test designs across devices to enhance usability and performance.
Essential Skills for Print Designers
Print designers must master color theory, typography, and layout principles to create visually compelling and print-ready materials. Proficiency in software like Adobe InDesign, Illustrator, and Photoshop is crucial for producing high-quality print designs with precise resolution and color accuracy. Strong knowledge of print production processes, including paper types, finishing techniques, and bleed settings, ensures designs meet industry standards and printing specifications.
Must-Have Skills for Digital Designers
Digital designers must excel in user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) design, mastering tools like Adobe XD, Sketch, and Figma to create interactive, engaging content optimized for various devices. Proficiency in HTML, CSS, and basic JavaScript enables seamless collaboration with developers and enhances dynamic web design capabilities. Strong skills in animation software such as After Effects and an understanding of responsive design principles are essential to craft visually compelling, adaptable digital content.
Tools and Software Used by Print Designers
Print designers utilize specialized software such as Adobe InDesign, Illustrator, and QuarkXPress to create high-resolution layouts optimized for physical media. These tools support precise control over color calibration, CMYK color modes, bleed settings, and typography to ensure accurate print reproduction. Mastery of prepress workflows, including trapping and imposition, distinguishes print design software from digital design applications centered on screen display.
Tools and Software Used by Digital Designers
Digital designers primarily use software such as Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, and After Effects for creating interactive and web-optimized graphics, while print designers rely on tools like Adobe InDesign and QuarkXPress tailored for layout and print production. Digital design also involves software like Sketch, Figma, and Adobe XD, which facilitate prototyping, user interface design, and collaboration in real-time. These tools support responsive design, animation, and multimedia integration, distinguishing digital design workflows from traditional print-focused processes.
Collaboration within Publishing Teams
Print designers and digital designers collaborate by blending expertise in typography, layout, and color theory tailored for physical and digital media within publishing teams. Effective communication ensures seamless integration of print-ready assets with interactive digital content, enhancing brand consistency across platforms. Utilizing collaborative tools like Adobe Creative Cloud and real-time feedback systems streamlines workflow, reduces errors, and accelerates project timelines.
Career Paths in Print vs Digital Design
Print designers typically build careers centered around traditional media such as brochures, posters, and packaging, requiring expertise in typography, color theory, and print production techniques. Digital designers focus on creating user interfaces, websites, and interactive media, emphasizing skills in UX/UI design, coding, and digital tools like Adobe XD and Figma. Career paths in print design often lead to roles in advertising agencies, publishing houses, and branding firms, while digital design careers expand into tech companies, startups, and multimedia production studios.
Future Trends in Publishing Design
Print designers in publishing will increasingly integrate augmented reality (AR) to create interactive experiences that blend physical books with digital content, enhancing reader engagement. Digital designers will leverage AI-driven tools to personalize layouts and optimize content delivery across multiple platforms, ensuring accessibility and adaptability in evolving media formats. Both roles must adapt to sustainable practices and cross-disciplinary skills as publishing embraces eco-friendly materials and immersive technologies.
Print Designer vs Digital Designer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com