Print publishers specialize in physical formats such as books, magazines, and newspapers, offering tactile experiences that appeal to traditional readers and collectors. Digital publishers focus on online content distribution, enabling instant access, interactive features, and broader reach through e-books, websites, and apps. Both formats have unique advantages, with print providing durability and credibility, while digital excels in convenience and multimedia integration.
Table of Comparison
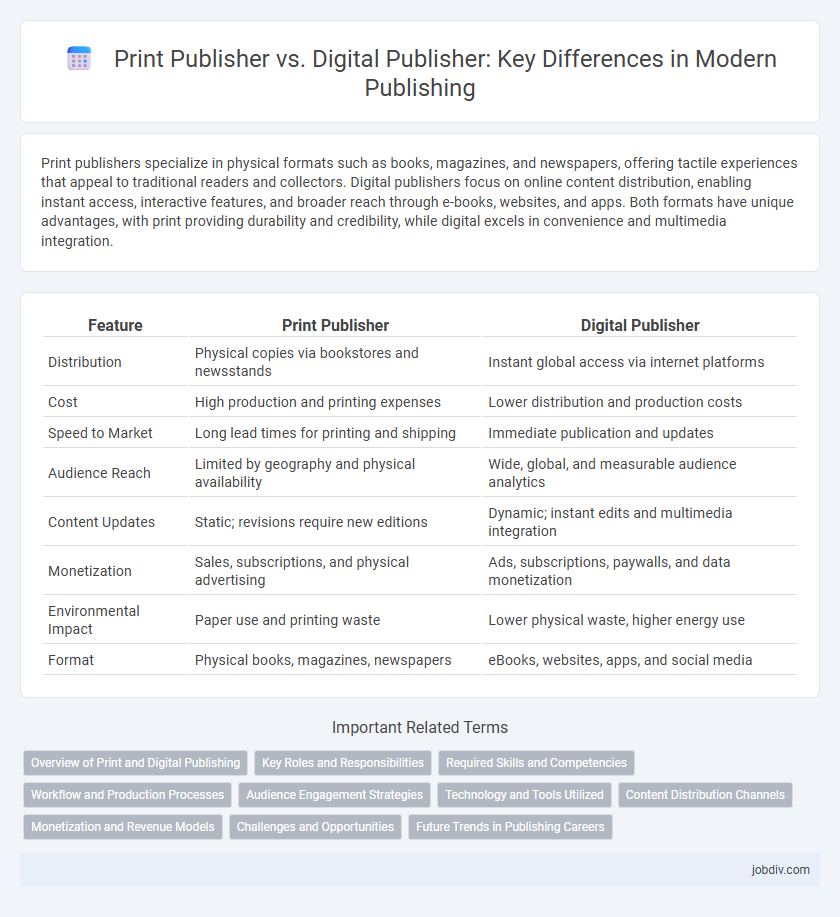
| Feature | Print Publisher | Digital Publisher |
|---|---|---|
| Distribution | Physical copies via bookstores and newsstands | Instant global access via internet platforms |
| Cost | High production and printing expenses | Lower distribution and production costs |
| Speed to Market | Long lead times for printing and shipping | Immediate publication and updates |
| Audience Reach | Limited by geography and physical availability | Wide, global, and measurable audience analytics |
| Content Updates | Static; revisions require new editions | Dynamic; instant edits and multimedia integration |
| Monetization | Sales, subscriptions, and physical advertising | Ads, subscriptions, paywalls, and data monetization |
| Environmental Impact | Paper use and printing waste | Lower physical waste, higher energy use |
| Format | Physical books, magazines, newspapers | eBooks, websites, apps, and social media |
Overview of Print and Digital Publishing
Print publishing involves the production and distribution of physical materials such as books, magazines, and newspapers, relying on traditional printing presses and supply chains. Digital publishing encompasses electronic content delivery via websites, eBooks, and mobile apps, leveraging online platforms and digital rights management. The shift towards digital publishing offers enhanced accessibility, real-time updates, and interactive multimedia integration, while print publishing maintains tangible quality and collector value.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Print publishers manage the production, distribution, and marketing of physical books and magazines, overseeing processes like printing, binding, and inventory control to ensure high-quality tangible products reach retailers and consumers. Digital publishers focus on creating, formatting, and distributing content through online platforms, optimizing for SEO, user engagement, and multimedia integration to maximize digital reach and accessibility. Both roles require strategic content management, rights acquisition, and coordination with authors and advertisers, but print emphasizes physical logistics while digital prioritizes technological platforms and data analytics.
Required Skills and Competencies
Print publishers require strong expertise in traditional production processes, including paper selection, offset printing, and distribution logistics, combined with skills in editorial management and physical inventory control. Digital publishers must excel in content management systems, SEO strategies, data analytics, and digital marketing to optimize audience engagement across multiple online platforms. Both roles demand proficiency in project management, editorial judgment, and adaptability to rapidly evolving media technologies.
Workflow and Production Processes
Print publishers rely on traditional workflows involving physical proofs, offset printing, and distribution logistics, which require extended production timelines and material management. Digital publishers utilize automated content management systems, real-time updates, and multi-platform distribution, enabling faster production cycles and streamlined workflows. The integration of digital tools in publishing accelerates content delivery while print production maintains rigorous quality control through established tactile processes.
Audience Engagement Strategies
Print publishers enhance audience engagement through tactile experiences such as high-quality paper, limited edition prints, and interactive supplements like bookmarks or augmented reality features. Digital publishers leverage real-time analytics, personalized content recommendations, and interactive multimedia elements, including videos and polls, to maintain dynamic reader interaction. Both platforms prioritize audience feedback channels, but digital methods offer more immediate and scalable engagement opportunities.
Technology and Tools Utilized
Print publishers rely heavily on traditional offset printing technology, advanced prepress software, and high-quality paper stock to produce tangible books, magazines, and newspapers. Digital publishers utilize content management systems (CMS), cloud-based design tools, and data analytics platforms to create, distribute, and optimize content across online channels. Both sectors leverage automation and digital asset management (DAM) systems, but digital publishing prioritizes responsive design and multimedia integration for enhanced user engagement.
Content Distribution Channels
Print publishers primarily distribute content through physical channels such as bookstores, newsstands, and direct mail, relying on tangible media like magazines, newspapers, and books. Digital publishers utilize online platforms including websites, social media, email newsletters, and mobile apps to reach global audiences instantly with eBooks, articles, and multimedia content. The shift towards digital distribution increasingly enables real-time analytics and personalized content delivery, contrasting with the fixed, location-dependent reach of print distribution.
Monetization and Revenue Models
Print publishers primarily generate revenue through physical product sales, subscription fees, and advertisements placed in magazines or newspapers, relying on higher production and distribution costs. Digital publishers monetize content via diverse streams including programmatic advertising, subscription models, paywalls, sponsored content, and affiliate marketing, benefiting from lower marginal costs and real-time analytics. The shift to digital platforms allows publishers to leverage data-driven strategies for personalized ads and dynamic pricing, significantly enhancing monetization efficiency and revenue scalability.
Challenges and Opportunities
Print publishers face challenges such as high production costs, limited distribution reach, and declining readership due to digital consumption preferences. Digital publishers encounter opportunities in real-time analytics, global audience engagement, and diversified revenue streams through advertising and subscriptions. Both models must navigate evolving consumer behaviors and technological advancements to remain competitive in the publishing industry.
Future Trends in Publishing Careers
Print publishers increasingly integrate digital technologies to sustain relevance, emphasizing hybrid skills in both traditional and digital content creation. Digital publishers leverage AI and data analytics to personalize content and optimize distribution channels, driving growth in immersive media formats such as AR and VR. Careers in publishing demand adaptability, with professionals focusing on digital literacy, multimedia storytelling, and cross-platform marketing to meet evolving consumer behaviors.
Print Publisher vs Digital Publisher Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com