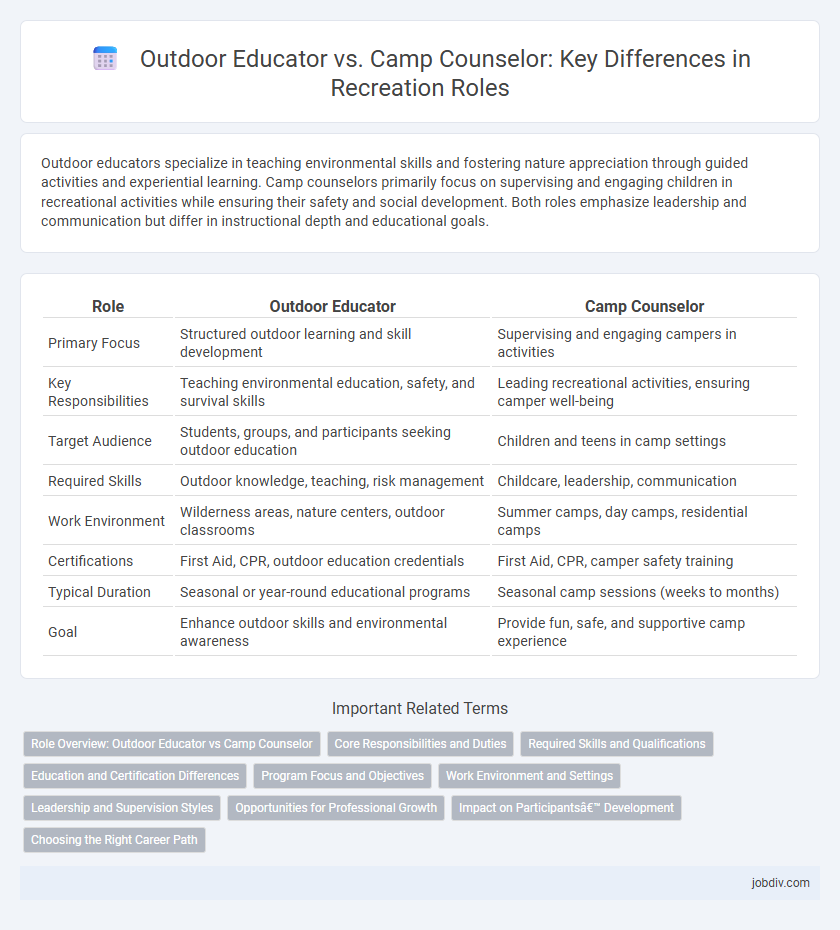
Outdoor educators specialize in teaching environmental skills and fostering nature appreciation through guided activities and experiential learning. Camp counselors primarily focus on supervising and engaging children in recreational activities while ensuring their safety and social development. Both roles emphasize leadership and communication but differ in instructional depth and educational goals.
Table of Comparison
| Role | Outdoor Educator | Camp Counselor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Structured outdoor learning and skill development | Supervising and engaging campers in activities |
| Key Responsibilities | Teaching environmental education, safety, and survival skills | Leading recreational activities, ensuring camper well-being |
| Target Audience | Students, groups, and participants seeking outdoor education | Children and teens in camp settings |
| Required Skills | Outdoor knowledge, teaching, risk management | Childcare, leadership, communication |
| Work Environment | Wilderness areas, nature centers, outdoor classrooms | Summer camps, day camps, residential camps |
| Certifications | First Aid, CPR, outdoor education credentials | First Aid, CPR, camper safety training |
| Typical Duration | Seasonal or year-round educational programs | Seasonal camp sessions (weeks to months) |
| Goal | Enhance outdoor skills and environmental awareness | Provide fun, safe, and supportive camp experience |
Role Overview: Outdoor Educator vs Camp Counselor
Outdoor educators design and lead structured learning experiences in natural settings, focusing on environmental education, survival skills, and team-building activities. Camp counselors supervise campers' daily activities, ensuring safety, fostering social interaction, and facilitating recreational games or arts and crafts. Both roles require strong leadership and communication skills but differ in their primary goals and educational emphasis.
Core Responsibilities and Duties
Outdoor educators design and implement experiential learning programs that teach participants outdoor skills, environmental awareness, and team-building activities in natural settings. Camp counselors supervise and engage campers, ensuring their safety while leading recreational activities, fostering social development, and managing daily camp routines. Both roles require strong leadership and communication skills, but outdoor educators emphasize educational outcomes, whereas camp counselors focus on camper care and activity facilitation.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Outdoor educators require strong knowledge of environmental science, leadership skills, and certifications in first aid and wilderness survival to effectively design and lead educational programs. Camp counselors need excellent interpersonal communication, conflict resolution abilities, and basic safety training to supervise and engage children in recreational activities. Both roles demand adaptability, teamwork, and a genuine passion for outdoor learning and youth development.
Education and Certification Differences
Outdoor educators typically hold specialized certifications like Wilderness First Responder (WFR) or Leave No Trace Instructor credentials, emphasizing comprehensive environmental education and risk management. Camp counselors may require basic first aid and CPR certification, focusing more on general camper supervision and activity facilitation. Educational backgrounds for outdoor educators often include degrees in environmental science or outdoor recreation, whereas camp counselors may have varied academic qualifications with practical experience.
Program Focus and Objectives
Outdoor educators design curriculum centered on environmental awareness, skill development, and nature-based learning experiences to foster stewardship and personal growth. Camp counselors concentrate on creating a fun, safe, and socially engaging environment for campers through recreational activities and team-building exercises. Both roles aim to enhance participant experience but differ in their emphasis on educational outcomes versus recreational enjoyment.
Work Environment and Settings
Outdoor educators typically work in natural settings such as forests, parks, and wilderness areas, facilitating experiential learning and environmental education. Camp counselors operate primarily within campgrounds or recreational facilities, supervising activities and ensuring camper safety. Both roles demand adaptability to outdoor conditions, but outdoor educators often engage in more structured educational programs, while camp counselors focus on recreational and social experiences.
Leadership and Supervision Styles
Outdoor educators employ experiential leadership techniques that emphasize active participation and skill-building in natural settings, fostering independence and environmental stewardship among participants. Camp counselors adopt a more supportive supervision style, focusing on emotional guidance, safety enforcement, and creating a fun, inclusive atmosphere for children and teens. Both roles require strong communication and adaptability, but outdoor educators typically lead structured educational activities while counselors prioritize relational support and group management.
Opportunities for Professional Growth
Outdoor educators often have expanded opportunities for professional growth through certifications like Wilderness First Responder and leadership development courses, enhancing their expertise in outdoor skills and safety. Camp counselors gain valuable experience in child development and program management, which can lead to positions in youth programming, education, or recreational management. Both roles offer pathways to specialized careers in adventure therapy, environmental education, and nonprofit outdoor organizations, depending on individual skills and interests.
Impact on Participants’ Development
Outdoor educators facilitate experiential learning through nature-based activities, promoting critical thinking, resilience, and environmental stewardship among participants. Camp counselors support social development by fostering teamwork, communication skills, and emotional growth in a supervised, recreational setting. Both roles significantly contribute to personal growth, but outdoor educators emphasize skill-building related to nature and leadership, while camp counselors focus on interpersonal relationships and group dynamics.
Choosing the Right Career Path
Outdoor educators specialize in environmental instruction and wilderness skills, providing structured learning experiences in natural settings. Camp counselors focus on supervising and engaging campers through team-building activities and recreational programs. Evaluating personal skills, interests in leadership versus education, and long-term career goals helps determine the most suitable role in outdoor recreation.
Outdoor Educator vs Camp Counselor Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com