A Recreation Assistant supports recreational activities by organizing equipment, assisting participants, and ensuring safety during events, enhancing the overall experience. A Recreation Programmer designs and plans comprehensive recreational programs tailored to community needs, focusing on long-term engagement and resource allocation. Both roles are essential for effective recreation management, with the Assistant handling operational tasks and the Programmer managing strategic development.
Table of Comparison
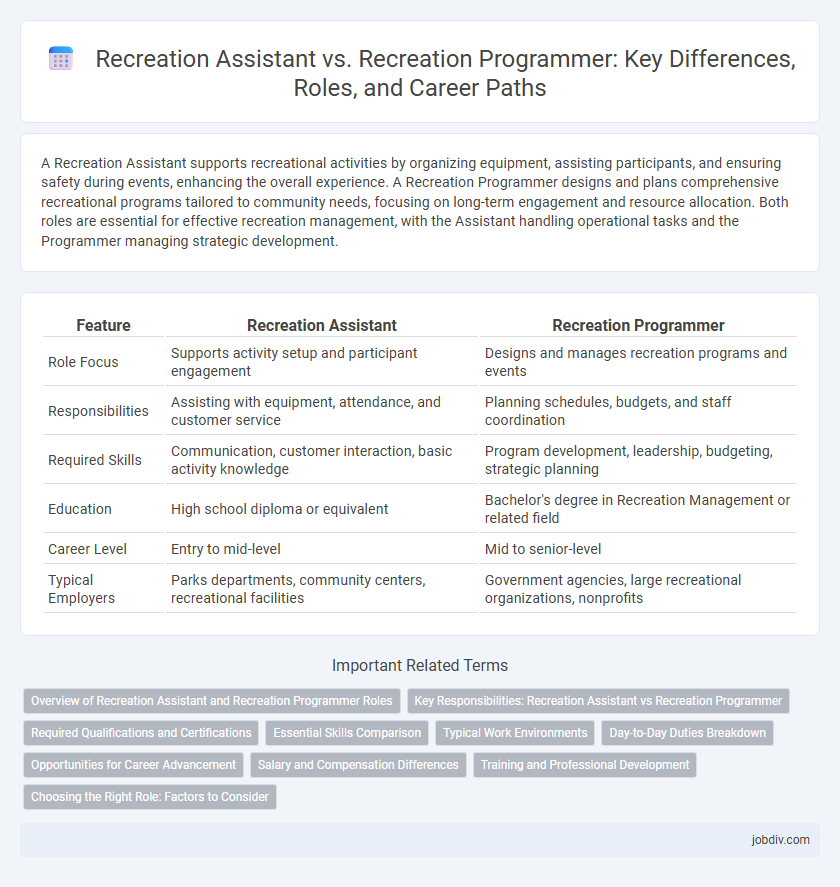
| Feature | Recreation Assistant | Recreation Programmer |
|---|---|---|
| Role Focus | Supports activity setup and participant engagement | Designs and manages recreation programs and events |
| Responsibilities | Assisting with equipment, attendance, and customer service | Planning schedules, budgets, and staff coordination |
| Required Skills | Communication, customer interaction, basic activity knowledge | Program development, leadership, budgeting, strategic planning |
| Education | High school diploma or equivalent | Bachelor's degree in Recreation Management or related field |
| Career Level | Entry to mid-level | Mid to senior-level |
| Typical Employers | Parks departments, community centers, recreational facilities | Government agencies, large recreational organizations, nonprofits |
Overview of Recreation Assistant and Recreation Programmer Roles
Recreation Assistants support the delivery of recreational activities by setting up equipment, supervising participants, and ensuring safety guidelines are followed in community centers, parks, or recreational facilities. Recreation Programmers design, plan, and coordinate diverse recreational programs and events tailored to community needs, often managing budgets, staff, and collaboration with local organizations. Both roles contribute to enhancing community engagement and promoting active lifestyles, with Recreation Programmers focusing more on strategic planning and Recreation Assistants on operational execution.
Key Responsibilities: Recreation Assistant vs Recreation Programmer
Recreation Assistants primarily support the implementation of recreational activities by preparing equipment, assisting participants, and ensuring safety during programs. Recreation Programmers develop, plan, and evaluate recreational programs tailored to community needs, managing budgets and coordinating staff. Both roles collaborate to enhance participant experience, with the programmer focusing on strategic development and the assistant on operational execution.
Required Qualifications and Certifications
A Recreation Assistant typically requires a high school diploma or equivalent, with certifications such as CPR and First Aid often preferred to ensure participant safety during activities. In contrast, a Recreation Programmer generally demands a bachelor's degree in recreation management, kinesiology, or a related field, alongside specialized certifications like Certified Park and Recreation Professional (CPRP) to design and implement comprehensive recreational programs. Both roles emphasize knowledge of risk management and effective communication, but Programmers are expected to have advanced skills in program development and administrative tasks.
Essential Skills Comparison
Recreation Assistants excel in interpersonal communication, basic event coordination, and safety monitoring, ensuring participant engagement and well-being during activities. Recreation Programmers demonstrate advanced skills in program development, budgeting, and strategic planning, enabling them to design comprehensive recreational services aligned with community needs. Both roles require proficiency in customer service and knowledge of recreation management software, yet Programmers typically possess stronger analytical and leadership capabilities.
Typical Work Environments
Recreation Assistants typically work in community centers, parks, and recreational facilities, supporting program delivery and participant engagement. Recreation Programmers often operate in municipal agencies, schools, or nonprofit organizations, focusing on designing and managing diverse recreational activities. Both roles frequently collaborate in environments that prioritize community wellness and active lifestyles.
Day-to-Day Duties Breakdown
Recreation Assistants primarily oversee facility maintenance, supervise participants, and assist with activity setup to ensure smooth operation during events. Recreation Programmers focus on designing, developing, and coordinating recreational activities, managing budgets, and evaluating program effectiveness to meet community needs. Both roles collaborate to enhance program delivery, but Assistants handle direct participant interaction while Programmers emphasize planning and administration.
Opportunities for Career Advancement
Recreation Assistants gain hands-on experience organizing community events, which serves as a foundation for advancing to roles such as Recreation Programmer. Recreation Programmers have opportunities to design and manage larger-scale programs, often leading to supervisory or management positions within parks and recreation departments. Career advancement is facilitated by acquiring skills in budgeting, staff coordination, and program evaluation, enhancing prospects in public, private, and nonprofit sectors.
Salary and Compensation Differences
Recreation Assistants typically earn an hourly wage ranging from $12 to $18, reflecting entry-level responsibilities such as supporting program activities and supervising participants. Recreation Programmers command higher salaries, often between $40,000 and $60,000 annually, due to their roles in designing, planning, and managing recreational programs and budgets. Compensation differences stem from the increased expertise, leadership duties, and strategic planning required for Recreation Programmers compared to the more operational tasks handled by Recreation Assistants.
Training and Professional Development
Recreation Assistants typically receive on-the-job training focusing on basic program implementation and customer service skills, while Recreation Programmers undergo formal education in recreation management or related fields, emphasizing program design, budgeting, and leadership development. Continuous professional development for Recreation Programmers often includes certifications such as CPR, first aid, and specialized recreation programming courses to stay current with industry standards. Both roles benefit from workshops and seminars, but Recreation Programmers engage more deeply in strategic planning and community outreach training to effectively manage and innovate recreational activities.
Choosing the Right Role: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right role between a Recreation Assistant and a Recreation Programmer depends on your desired level of responsibility and skill application, as Recreation Assistants typically support daily operations and assist with activity facilitation, while Recreation Programmers focus on designing, planning, and evaluating recreational programs. Consider your interest in administrative tasks and program development, since Recreation Programmers require strong project management abilities and creativity in program innovation. Salary expectations and required qualifications also vary, with Recreation Programmers generally needing higher education and offering greater career advancement opportunities compared to Recreation Assistants.
Recreation Assistant vs Recreation Programmer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com