Monks dedicate their lives to spiritual practice, often living in monasteries with a focus on meditation, prayer, and community service. Nuns commit to similar religious vows but typically engage in different roles within convents, emphasizing nurturing, teaching, and supporting charitable activities. Both monks and nuns embody deep devotion, discipline, and a shared pursuit of spiritual enlightenment.
Table of Comparison
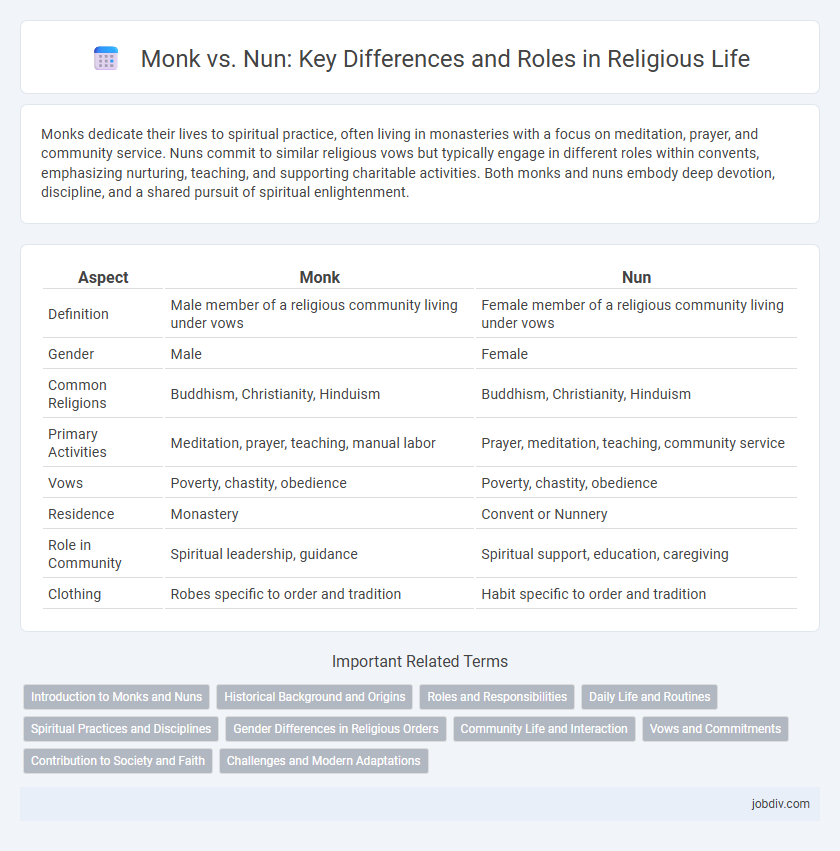
| Aspect | Monk | Nun |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Male member of a religious community living under vows | Female member of a religious community living under vows |
| Gender | Male | Female |
| Common Religions | Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism | Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism |
| Primary Activities | Meditation, prayer, teaching, manual labor | Prayer, meditation, teaching, community service |
| Vows | Poverty, chastity, obedience | Poverty, chastity, obedience |
| Residence | Monastery | Convent or Nunnery |
| Role in Community | Spiritual leadership, guidance | Spiritual support, education, caregiving |
| Clothing | Robes specific to order and tradition | Habit specific to order and tradition |
Introduction to Monks and Nuns
Monks and nuns are members of religious communities devoted to spiritual practice, often living under vows of poverty, chastity, and obedience. Monks typically reside in monasteries where they engage in prayer, meditation, and work, while nuns live in convents or abbeys dedicating their lives to similar spiritual disciplines. Both play vital roles in preserving religious traditions and serving their faith communities through devotion and service.
Historical Background and Origins
Monks and nuns trace their origins to early Christian monasticism, emerging in the 3rd and 4th centuries as individuals sought solitude and spiritual discipline away from secular society. Monks primarily lived in monasteries following strict communal or solitary rules, while nuns established convents to pursue similar religious devotion under female leadership. Both traditions evolved independently across cultures, with monks found in Eastern Orthodox, Catholic, and Buddhist orders, and nuns especially prominent in Catholicism and Buddhism, reflecting diverse historical contexts and spiritual practices.
Roles and Responsibilities
Monks primarily engage in spiritual practices such as meditation, prayer, and study, often living in monastic communities with a focus on solitude and contemplation. Nuns also dedicate themselves to prayer and religious duties but frequently participate more actively in community service, education, and healthcare. Both roles emphasize vows of poverty, chastity, and obedience, yet their responsibilities diverge based on doctrinal traditions and communal needs within religious orders.
Daily Life and Routines
Monks and nuns follow disciplined daily routines centered on prayer, meditation, and communal work within their monastic communities. Monks often engage in manual labor such as agriculture or maintenance, while nuns may focus more on teaching, healthcare, or crafting sacred items. Both dedicate significant hours to chanting, studying scriptures, and performing rituals that reinforce spiritual growth and communal harmony.
Spiritual Practices and Disciplines
Monks engage in rigorous meditation, chanting, and solitary retreats to deepen spiritual insight, often embracing strict ascetic practices to cultivate detachment from worldly desires. Nuns emphasize communal prayer, acts of service, and contemplative study, nurturing spiritual growth through collective worship and disciplined routines within monastic communities. Both monks and nuns follow vows of celibacy and obedience, dedicating their lives to inner purification and divine connection through diverse but complementary spiritual disciplines.
Gender Differences in Religious Orders
Monks and nuns represent distinct gender roles within religious orders, often reflecting varying responsibilities and communal living arrangements shaped by tradition and doctrine. Monks typically engage in more public-facing roles such as teaching and community service, while nuns frequently focus on contemplative practices and caregiving within cloistered environments. These gender-specific practices highlight the broader theological interpretations and historical developments influencing religious life in Christianity, Buddhism, and other faiths.
Community Life and Interaction
Monks and nuns each embrace community life through disciplined routines and shared spiritual practices within monasteries and convents, fostering deep interpersonal bonds. Monastic communities often emphasize collective prayer, work, and study, creating an environment of mutual support and accountability. Interaction within these religious communities strengthens commitment to vows and cultivates a harmonious atmosphere centered on faith and service.
Vows and Commitments
Monks and nuns both commit to vows of poverty, chastity, and obedience, reflecting their dedication to spiritual life within monastic communities. Monks often take vows specific to their order, emphasizing solitude and prayer, while nuns typically focus on communal living and service. These vows shape their daily routines, spiritual practices, and lifelong devotion to religious discipline.
Contribution to Society and Faith
Monks dedicate their lives to prayer, teaching, and preserving religious texts, often serving as spiritual guides and scholars within their communities. Nuns contribute through charitable works, education, and healthcare, promoting social welfare and nurturing faith-based outreach programs. Both monks and nuns play vital roles in sustaining religious traditions and fostering communal support that strengthens societal values.
Challenges and Modern Adaptations
Monks and nuns face distinct challenges in preserving spiritual discipline amid modern distractions, with monks often dealing with solitude and physical labor, while nuns navigate community service and family expectations. Modern adaptations include the integration of digital technology for virtual retreats and online religious education, facilitating broader engagement without compromising monastic vows. Both groups increasingly embrace sustainable living and social advocacy, reflecting evolving interpretations of traditional roles within contemporary society.
Monk vs Nun Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com