A Mullah is a Muslim cleric trained in Islamic theology and law, often serving as a local religious leader or teacher in a mosque. A Mufti holds a higher scholarly rank with the authority to issue formal legal opinions (fatwas) on complex Islamic jurisprudence issues. Both play vital roles in guiding the religious and legal practices of Muslim communities, but the Mufti's decisions carry greater weight in matters of Islamic law.
Table of Comparison
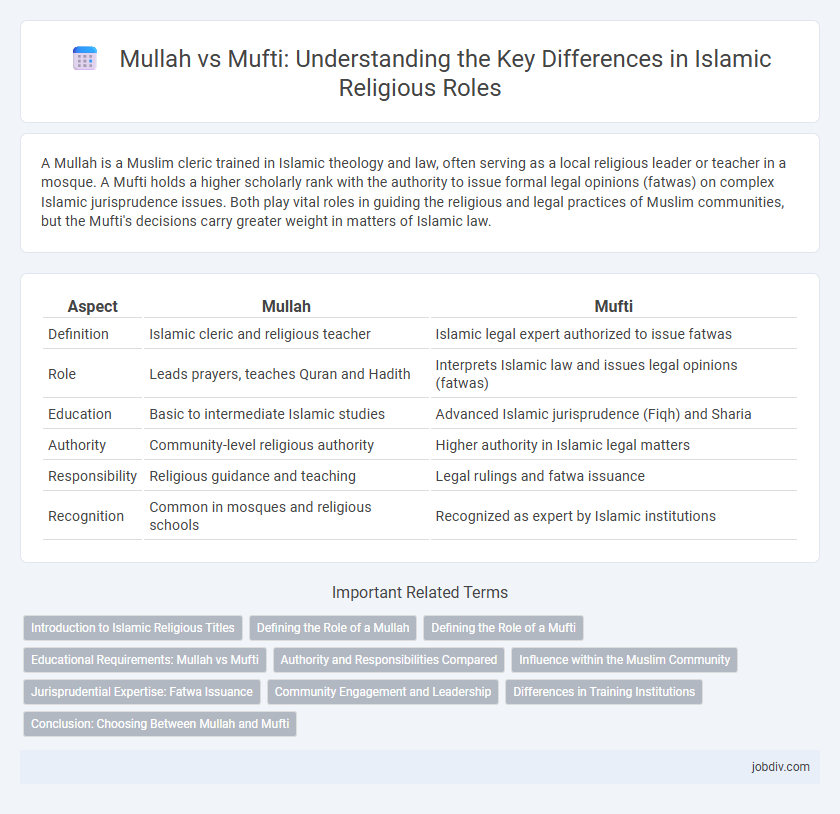
| Aspect | Mullah | Mufti |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Islamic cleric and religious teacher | Islamic legal expert authorized to issue fatwas |
| Role | Leads prayers, teaches Quran and Hadith | Interprets Islamic law and issues legal opinions (fatwas) |
| Education | Basic to intermediate Islamic studies | Advanced Islamic jurisprudence (Fiqh) and Sharia |
| Authority | Community-level religious authority | Higher authority in Islamic legal matters |
| Responsibility | Religious guidance and teaching | Legal rulings and fatwa issuance |
| Recognition | Common in mosques and religious schools | Recognized as expert by Islamic institutions |
Introduction to Islamic Religious Titles
Mullah and Mufti are prominent Islamic religious titles with distinct roles and responsibilities in the Muslim community. A Mullah typically serves as a local religious leader or teacher, often involved in leading prayers, delivering sermons, and providing basic Islamic education. In contrast, a Mufti is a qualified Islamic jurist authorized to issue fatwas, which are formal legal opinions on complex religious matters, reflecting advanced scholarly expertise in Sharia law.
Defining the Role of a Mullah
A Mullah is a religious scholar in Islamic communities who primarily leads prayers, delivers sermons, and provides basic religious education. Unlike a Mufti, who is authorized to issue formal legal opinions or fatwas based on Islamic law, a Mullah's role is more focused on spiritual guidance and community leadership. Mullahs often serve as imams in mosques, facilitating religious rituals and cultivating the moral and ethical understanding of their congregations.
Defining the Role of a Mufti
A Mufti is a highly trained Islamic scholar authorized to interpret Sharia law and issue formal legal opinions known as fatwas, guiding Muslims in matters of religious practice and daily life. Unlike a Mullah, who primarily leads prayers and performs community religious duties, a Mufti's role centers on providing authoritative jurisprudential rulings based on extensive knowledge of the Quran, Hadith, and Islamic legal tradition. The position of a Mufti requires advanced study at recognized Islamic institutions, emphasizing expertise in fiqh (Islamic jurisprudence) to resolve complex theological and ethical questions.
Educational Requirements: Mullah vs Mufti
Mullahs typically acquire their education through madrasas, focusing on foundational Islamic knowledge, Quranic studies, and basic jurisprudence, often completing their training in religious schools within local communities. Muftis undergo more advanced and specialized education, including in-depth study of Islamic law (Fiqh) and its applications, often requiring years of scholarly research and certification to issue formal fatwas. The Mufti's education emphasizes mastery of complex legal interpretations, whereas the Mullah's training centers on general religious instruction and community guidance.
Authority and Responsibilities Compared
Mullahs typically serve as local Islamic scholars and prayer leaders, providing religious guidance and leading community prayers, whereas Muftis possess higher authority to issue formal fatwas based on Islamic jurisprudence. Muftis undergo extensive training in Sharia law and are responsible for interpreting complex religious queries, influencing both individual and collective religious practices. The authority of Muftis often extends beyond the local level, impacting legal and societal norms within Islamic communities.
Influence within the Muslim Community
Mullahs and Muftis hold distinct yet complementary roles within the Muslim community, with Mullahs primarily serving as local religious leaders who guide daily worship and community affairs, while Muftis are recognized for their authoritative religious jurisprudence and issuance of fatwas that influence broader Islamic law and practice. The influence of a Mullah is often localized, directly impacting congregational knowledge and spiritual adherence, whereas Muftis shape doctrinal interpretation and legal opinions that resonate across diverse Muslim populations. Both positions command respect, but Muftis typically wield greater influence in shaping religious norms and legal rulings within Islamic jurisprudence.
Jurisprudential Expertise: Fatwa Issuance
A Mufti is a recognized Islamic scholar specialized in issuing fatwas, authoritative legal opinions based on deep jurisprudential expertise in fiqh. While a Mullah often serves as a religious teacher or community leader, a Mufti's role centers on interpreting Sharia law to provide detailed guidance on complex legal and ethical issues. Fatwa issuance requires extensive knowledge of the Quran, Hadith, and classical jurisprudence, setting Muftis apart as essential figures in Islamic legal decision-making.
Community Engagement and Leadership
Mullahs serve as local religious leaders guiding daily prayers and teaching Islamic principles within their communities, fostering close interpersonal connections. Muftis hold advanced scholarly authority to issue formal legal opinions (fatwas) that influence community practices and resolve complex religious matters. Both roles are pivotal in community engagement and leadership, with Mullahs focusing on grassroots spiritual guidance and Muftis providing authoritative religious rulings.
Differences in Training Institutions
Mullahs typically receive their religious training at local madrasas, focusing on memorization of the Quran, basic Islamic jurisprudence, and community leadership, often emphasizing traditional and grassroots education. Muftis usually undergo advanced scholarly training at specialized Islamic universities or higher madrasas, where they engage deeply with Islamic law (fiqh) and are authorized to issue formal legal opinions (fatwas). The distinction in their educational background reflects their differing roles, with Mullahs serving as local religious teachers and Muftis acting as expert jurists in Islamic law.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Mullah and Mufti
Choosing between a Mullah and a Mufti depends on the specific religious guidance needed; a Mullah typically leads prayers and provides basic religious education, while a Mufti holds advanced Islamic legal knowledge and issues formal fatwas. The decision hinges on whether one seeks general spiritual leadership or authoritative jurisprudential rulings. Understanding these roles ensures appropriate religious consultation aligned with one's Islamic requirements.
Mullah vs Mufti Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com