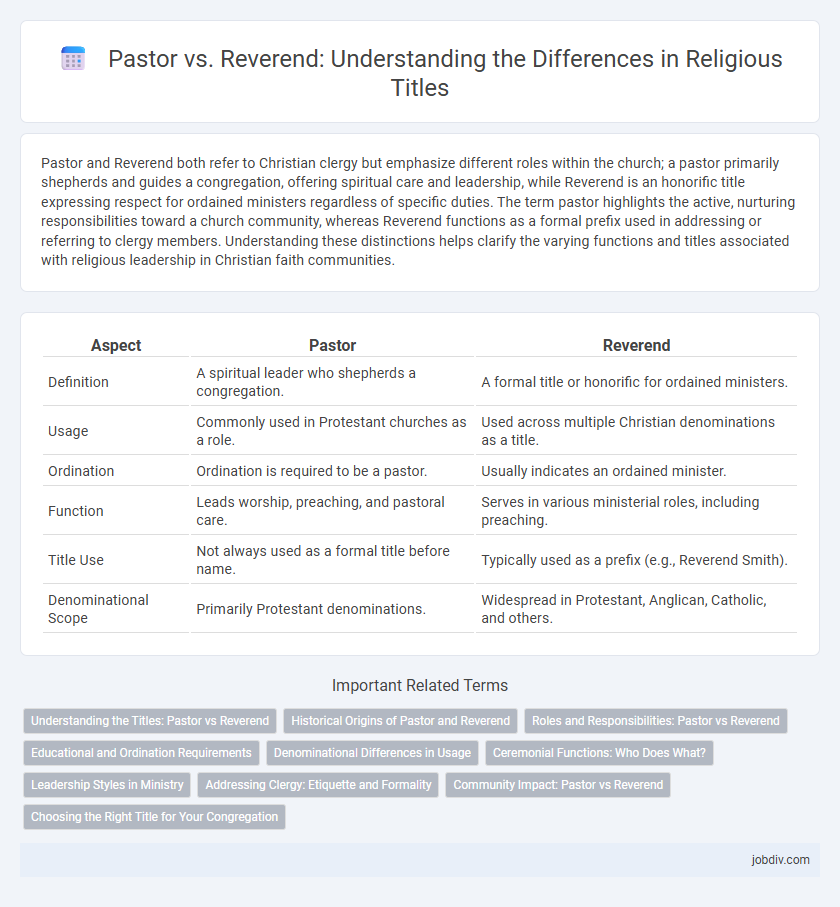
Pastor and Reverend both refer to Christian clergy but emphasize different roles within the church; a pastor primarily shepherds and guides a congregation, offering spiritual care and leadership, while Reverend is an honorific title expressing respect for ordained ministers regardless of specific duties. The term pastor highlights the active, nurturing responsibilities toward a church community, whereas Reverend functions as a formal prefix used in addressing or referring to clergy members. Understanding these distinctions helps clarify the varying functions and titles associated with religious leadership in Christian faith communities.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Pastor | Reverend |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A spiritual leader who shepherds a congregation. | A formal title or honorific for ordained ministers. |
| Usage | Commonly used in Protestant churches as a role. | Used across multiple Christian denominations as a title. |
| Ordination | Ordination is required to be a pastor. | Usually indicates an ordained minister. |
| Function | Leads worship, preaching, and pastoral care. | Serves in various ministerial roles, including preaching. |
| Title Use | Not always used as a formal title before name. | Typically used as a prefix (e.g., Reverend Smith). |
| Denominational Scope | Primarily Protestant denominations. | Widespread in Protestant, Anglican, Catholic, and others. |
Understanding the Titles: Pastor vs Reverend
The title "Pastor" specifically refers to a clergy member who provides spiritual guidance and leadership to a congregation, emphasizing their role in shepherding and caring for church members. "Reverend," on the other hand, is an honorific used broadly for ordained ministers across various Christian denominations, highlighting respect rather than specific duties. Understanding these distinctions helps clarify roles within church leadership and the varying expectations tied to each title.
Historical Origins of Pastor and Reverend
The title "Pastor" originates from the Latin word for "shepherd," reflecting early Christian leaders' role in guiding their congregations. "Reverend," derived from the Latin "reverendus," meaning "to be revered," emerged in the medieval church as an honorific for clergy recognized for their piety and authority. Both titles evolved within distinct historical contexts, shaping their contemporary use in various Christian denominations.
Roles and Responsibilities: Pastor vs Reverend
A pastor primarily serves as the spiritual leader responsible for preaching, counseling, and overseeing the day-to-day functions of a local congregation. A reverend is an honorific title often used to address ordained clergy, signifying respect rather than specifying a particular role or set of duties. While all pastors can be reverends, not all reverends function as pastors, as some may serve in academic, administrative, or specialized ministerial capacities.
Educational and Ordination Requirements
Pastors often hold a seminary degree or a theological diploma and undergo formal ordination through a denominational hierarchy, emphasizing both education and spiritual calling. Reverends typically receive ordination status after completing similar theological education but the title is more commonly used as an honorific for ordained ministers across various Christian denominations. Educational requirements for both roles generally include biblical studies, theology, and pastoral training, though specific ordination processes vary by denomination.
Denominational Differences in Usage
Pastor is commonly used in Protestant denominations to describe the leader of a congregation, emphasizing a shepherding role, while Reverend is an honorific title applied across various Christian denominations, including Anglican, Catholic, and Methodist churches. In Baptist and Evangelical traditions, Pastor often denotes both spiritual authority and pastoral care, whereas Reverend serves as a formal address for ordained clergy without specifying their function. The use of these terms varies by denomination, reflecting differences in theological emphasis and church governance structures.
Ceremonial Functions: Who Does What?
Pastors primarily lead congregational worship, deliver sermons, and provide spiritual guidance within their church community, while reverends often hold broader responsibilities including officiating religious ceremonies such as weddings, baptisms, and funerals. The title "Reverend" is an honorific used across various denominations to address ordained ministers who perform sacramental duties. Ceremonial functions may overlap, but reverends are typically recognized for their formal authority to conduct official rites within and beyond regular services.
Leadership Styles in Ministry
Pastors often emphasize relational leadership, focusing on personal care, counseling, and community building within their congregation. Reverends typically embody a more formal leadership style, prioritizing liturgical duties, preaching, and maintaining doctrinal fidelity. Both roles require spiritual guidance, but pastors generally adopt a more hands-on approach, while reverends balance administrative responsibilities with ceremonial functions.
Addressing Clergy: Etiquette and Formality
Pastors are typically addressed as "Pastor" followed by their last name, reflecting their role as spiritual caregivers and leaders within a congregation. Reverends, a formal title honoring ordained ministers, are often addressed as "Reverend" or "The Reverend" with their full name, emphasizing respect and clerical status in formal settings. Correctly addressing clergy according to their specific title upholds tradition, conveys respect, and acknowledges their distinct roles within religious communities.
Community Impact: Pastor vs Reverend
Pastors often engage directly with their congregations through counseling, community outreach, and organizing local events, fostering a deep relational impact within the community. Reverends, typically addressing broader ecclesiastical roles, may focus on preaching, theological education, and denominational leadership, influencing the community through spiritual guidance and institutional development. Both roles contribute significantly, but pastors usually maintain a more hands-on presence in daily community life.
Choosing the Right Title for Your Congregation
Choosing the right title for your congregation hinges on understanding the distinct roles and traditions associated with "Pastor" and "Reverend." Pastor generally refers to a spiritual leader actively shepherding a local church community, emphasizing pastoral care and guidance. Reverend serves as a formal honorific often used for ordained clergy across various denominations, highlighting respect and official status without specifying pastoral duties.
Pastor vs Reverend Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com