Shamans and medicine men both serve as spiritual healers but differ in cultural roles and practices. Shamans often engage in trance states to communicate with spirits, guiding healing through rituals and soul journeys. Medicine men typically rely on herbal knowledge and community-based ceremonies to restore physical and spiritual balance.
Table of Comparison
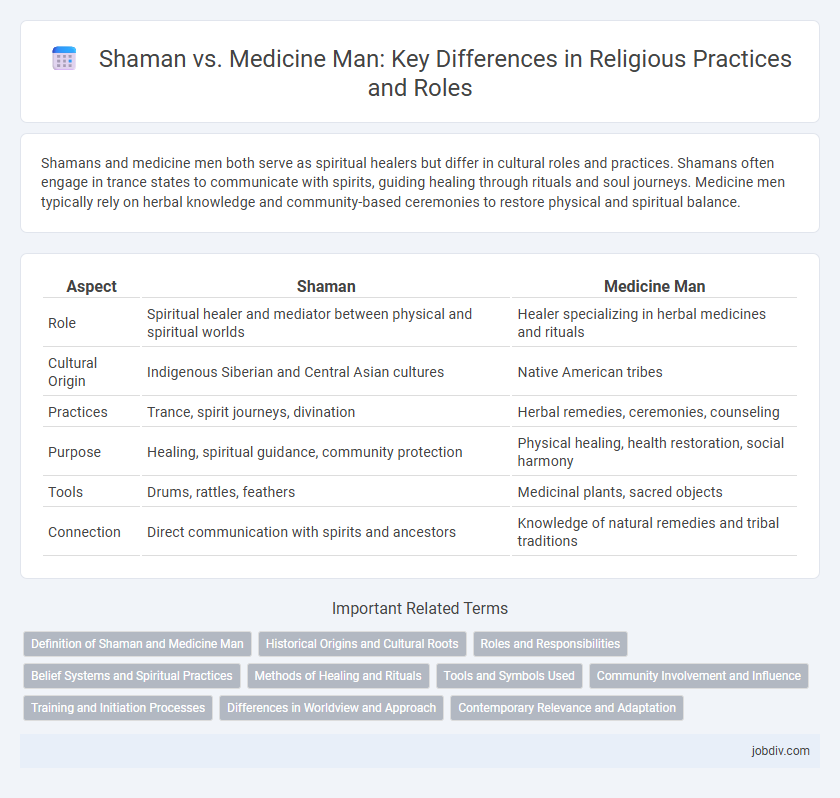
| Aspect | Shaman | Medicine Man |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Spiritual healer and mediator between physical and spiritual worlds | Healer specializing in herbal medicines and rituals |
| Cultural Origin | Indigenous Siberian and Central Asian cultures | Native American tribes |
| Practices | Trance, spirit journeys, divination | Herbal remedies, ceremonies, counseling |
| Purpose | Healing, spiritual guidance, community protection | Physical healing, health restoration, social harmony |
| Tools | Drums, rattles, feathers | Medicinal plants, sacred objects |
| Connection | Direct communication with spirits and ancestors | Knowledge of natural remedies and tribal traditions |
Definition of Shaman and Medicine Man
A shaman is a spiritual healer who interacts with the spirit world through trance and ritual to restore balance and guide souls, often found in Indigenous and animistic traditions. A medicine man serves as a traditional healer, utilizing knowledge of herbs, rituals, and community wisdom to promote physical and spiritual well-being. Both roles emphasize healing but differ in methods and cultural contexts, with shamans often engaging in shamanic journeys and medicine men focusing on herbal remedies and ceremonies.
Historical Origins and Cultural Roots
Shamans trace their origins to Siberian and Central Asian indigenous tribes where they acted as spiritual intermediaries using trance and ritual healing. Medicine men historically emerge from Native American cultures, serving as custodians of tribal knowledge in herbal medicine, rituals, and healing practices unique to their communities. Both roles share a deep cultural foundation centered on healing and spiritual guidance, but differ in practices shaped by distinct geographical, cultural, and ethnological roots.
Roles and Responsibilities
Shamans primarily serve as spiritual intermediaries, conducting rituals to communicate with the spirit world for healing and guidance, while medicine men focus on using herbal remedies and traditional medicines to treat physical ailments. Shamans often engage in trance states or vision quests to diagnose and resolve spiritual imbalances, whereas medicine men emphasize practical healing techniques grounded in botanical knowledge. Both roles are integral to indigenous health systems, blending spiritual and physical approaches to maintain community well-being.
Belief Systems and Spiritual Practices
Shamans typically engage with animistic belief systems, acting as intermediaries between the physical and spiritual worlds through trance and ritualistic ceremonies to heal and guide their communities. Medicine men often focus on herbal remedies and ancestral knowledge within a more localized spiritual tradition, emphasizing physical healing alongside spiritual balance. Both roles serve as vital spiritual leaders, but shamans prioritize ecstatic spiritual experiences while medicine men maintain established community healing practices.
Methods of Healing and Rituals
Shamans employ trance states and spirit journeys to mediate between the physical and spiritual worlds, utilizing drumming, chanting, and plant-based entheogens to facilitate healing and divine guidance. Medicine men rely on herbal remedies, physical treatments, and ritualistic prayers within their community, emphasizing the practical application of medicinal knowledge and ancestral blessings. Both practices integrate spiritual rituals, but shamans focus more on direct interaction with spirits, while medicine men use established traditional medicinal techniques combined with ceremonial rites.
Tools and Symbols Used
Shamans typically employ ritualistic drums, feathers, and spirit stones to facilitate communication with the spirit world, symbolizing their connection to nature and transcendence. Medicine men utilize medicinal herbs, animal parts, and symbolic masks to heal physical ailments and invoke protective spiritual forces within their community. Both practitioners rely on distinct tools and symbols that reflect their unique roles and cultural significance in traditional healing and spiritual guidance.
Community Involvement and Influence
Shamans often serve as spiritual leaders deeply embedded within their communities, using rituals and ceremonies to connect members with the spirit world and promote collective well-being. Medicine men typically focus on healing practices involving herbal remedies and physical treatments, playing a crucial role in addressing individual and communal health concerns. Both figures hold influential positions in maintaining the cultural and spiritual health of indigenous societies, but shamans emphasize spiritual guidance while medicine men prioritize practical healing.
Training and Initiation Processes
Shamans undergo rigorous spiritual training involving extended isolation, trance induction, and direct interaction with the spirit world to acquire healing and divination skills. Medicine men typically receive knowledge through apprenticeship within their community, learning herbal remedies, rituals, and cultural healing practices passed down orally. Both initiation processes emphasize deep connection with ancestral traditions but differ in their approach to spiritual empowerment and community roles.
Differences in Worldview and Approach
Shamans engage in spiritual journeys to communicate with spirits and heal through trance-induced states, reflecting a holistic worldview connecting the individual with nature and the cosmos. Medicine men primarily focus on herbal remedies and rituals grounded in the physical and social well-being of the community, emphasizing empirical knowledge passed through generations. The shaman's approach is mystical and transformational, while the medicine man's method centers on practical healing and maintaining societal harmony.
Contemporary Relevance and Adaptation
Shamans and medicine men continue to hold significant roles in contemporary indigenous communities by adapting traditional healing practices to modern health challenges. Their integration of spiritual rituals with herbal medicine addresses both physical and mental wellness, often complementing Western medical approaches. This adaptation fosters cultural preservation while meeting the evolving healthcare needs of their communities.
Shaman vs Medicine Man Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com