Residential leasing involves renting properties such as apartments, houses, or condos primarily for personal living, with shorter lease terms and tenant-friendly regulations. Commercial leasing pertains to properties used for business purposes, including offices, retail spaces, and warehouses, often requiring longer lease durations and customized agreements to accommodate business needs. Understanding the differences in legal requirements, lease structures, and maintenance responsibilities is crucial for both landlords and tenants in navigating residential versus commercial leasing effectively.
Table of Comparison
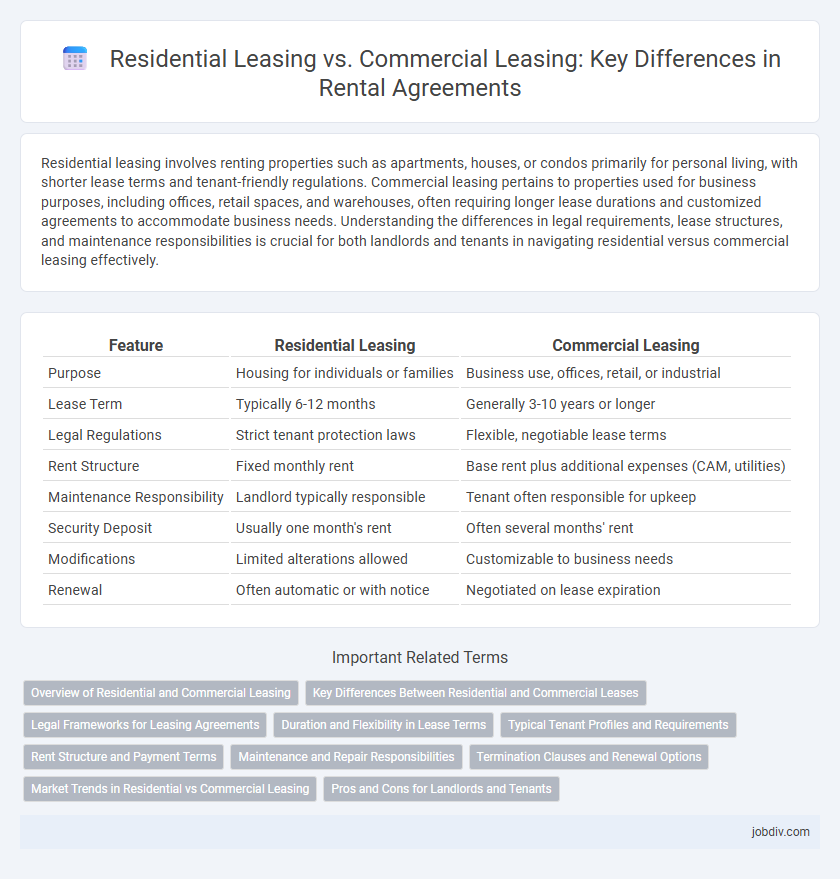
| Feature | Residential Leasing | Commercial Leasing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Housing for individuals or families | Business use, offices, retail, or industrial |
| Lease Term | Typically 6-12 months | Generally 3-10 years or longer |
| Legal Regulations | Strict tenant protection laws | Flexible, negotiable lease terms |
| Rent Structure | Fixed monthly rent | Base rent plus additional expenses (CAM, utilities) |
| Maintenance Responsibility | Landlord typically responsible | Tenant often responsible for upkeep |
| Security Deposit | Usually one month's rent | Often several months' rent |
| Modifications | Limited alterations allowed | Customizable to business needs |
| Renewal | Often automatic or with notice | Negotiated on lease expiration |
Overview of Residential and Commercial Leasing
Residential leasing involves renting living spaces such as apartments, houses, and condos primarily for personal use, governed by tenant protection laws and typically offering shorter lease terms. Commercial leasing pertains to renting spaces for business purposes, including offices, retail stores, and warehouses, often featuring longer, more negotiable lease agreements with terms tailored to business needs. Both types of leasing require thorough understanding of lease conditions, rights, and responsibilities to ensure compliance and protect interests of landlords and tenants.
Key Differences Between Residential and Commercial Leases
Residential leasing typically involves shorter lease terms ranging from six months to a year, while commercial leases often span several years to secure long-term business stability. Residential leases focus on tenant protections, standard rental agreements, and regulated rent increases, whereas commercial leases offer more flexibility but require detailed negotiations on terms such as maintenance, insurance, and property use. Rent amounts in commercial leasing are generally higher and based on market demand, square footage, and location, contrasting with residential rent controlled by local housing laws.
Legal Frameworks for Leasing Agreements
Residential leasing agreements are governed primarily by tenant protection laws, which impose strict regulations on rent control, eviction procedures, and maintenance responsibilities to safeguard tenant rights. Commercial leasing contracts are subject to more flexible legal frameworks, often negotiated case-by-case, allowing for customized terms regarding lease duration, rent adjustments, and property use. Understanding the distinct statutory provisions and case law precedents for each leasing type is crucial for drafting enforceable agreements that minimize legal disputes.
Duration and Flexibility in Lease Terms
Residential leasing typically offers shorter lease durations, often ranging from six months to one year, providing tenants with greater flexibility to relocate or adjust living arrangements. Commercial leasing usually involves longer terms, commonly three to five years or more, designed to provide stability for businesses that require consistent operational space. Flexibility in commercial leases is often limited, with fewer options for early termination or modifications compared to residential leases.
Typical Tenant Profiles and Requirements
Residential leasing typically involves individual tenants or families seeking apartments, houses, or condos primarily for personal living purposes, with requirements centered on creditworthiness, income verification, and rental history. Commercial leasing attracts business entities such as retailers, offices, or industrial firms requiring spaces that accommodate specific operational needs, including square footage, zoning compliance, and lease flexibility for business growth. Tenant profiles in residential leases prioritize stable income and long-term occupancy, whereas commercial leases emphasize business viability, location suitability, and tailored lease terms.
Rent Structure and Payment Terms
Residential leasing typically involves fixed monthly rent payments with standardized lease terms, often including utilities in the rent or as separate charges. Commercial leasing features more complex rent structures such as base rent plus additional costs like maintenance, taxes, and insurance, often called triple net leases. Payment terms in commercial leases are usually longer, with provisions for rent escalations and variable payment schedules based on business performance or lease duration.
Maintenance and Repair Responsibilities
Residential leasing typically places maintenance and repair responsibilities on landlords for major structural issues and essential systems such as plumbing, heating, and electrical. Commercial leasing often shifts these responsibilities to tenants, especially for interior repairs and upkeep, depending on the lease agreement terms like triple net leases. Understanding the distinctions in maintenance obligations is crucial for mitigating costs and ensuring compliance with lease contracts in both residential and commercial properties.
Termination Clauses and Renewal Options
Residential leasing termination clauses typically require shorter notice periods, often 30 to 60 days, reflecting tenant protections under state laws, while commercial leasing agreements usually mandate longer notice times and may include penalties for early termination. Renewal options in residential leases often follow a month-to-month extension or a fixed-term renewal with limited negotiation, whereas commercial leases commonly provide landlords and tenants with multiple renewal terms, sometimes including rent escalation clauses tied to market rates. Understanding these distinctions ensures both landlords and tenants manage lease obligations and future occupancy expectations effectively.
Market Trends in Residential vs Commercial Leasing
Residential leasing shows a strong upward trend driven by increasing urbanization, remote work flexibility, and demand for affordable living spaces, with rental prices rising consistently across major metropolitan areas. Commercial leasing experiences fluctuating market dynamics influenced by shifts in retail, office space utilization, and industrial demand, with a growing preference for flexible lease terms and hybrid work environments impacting vacancy rates. Data from recent real estate reports highlight that while residential leases maintain steady growth and shorter vacancy periods, commercial leases often face longer vacancy durations and slower recovery depending on industry-specific economic conditions.
Pros and Cons for Landlords and Tenants
Residential leasing offers landlords steady income with lower vacancy risks and tenants the benefit of shorter lease terms and legal protections, but it often yields lower rental income and tighter regulation compared to commercial leases. Commercial leasing provides landlords higher rent potential and longer lease stability while giving tenants customization opportunities and business growth potential, yet it carries higher vacancy risks and less regulatory oversight. Both leasing types require careful consideration of market conditions, lease terms, and maintenance responsibilities for optimal landlord and tenant outcomes.
Residential Leasing vs Commercial Leasing Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com